Abstract
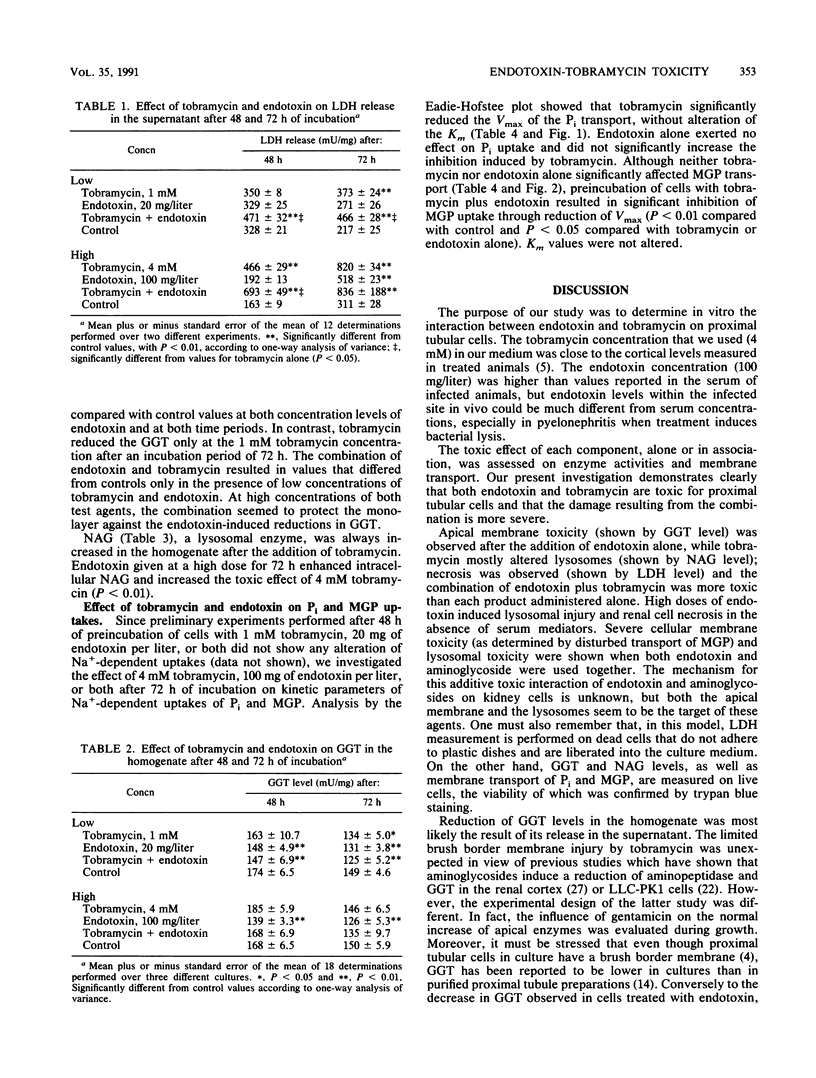
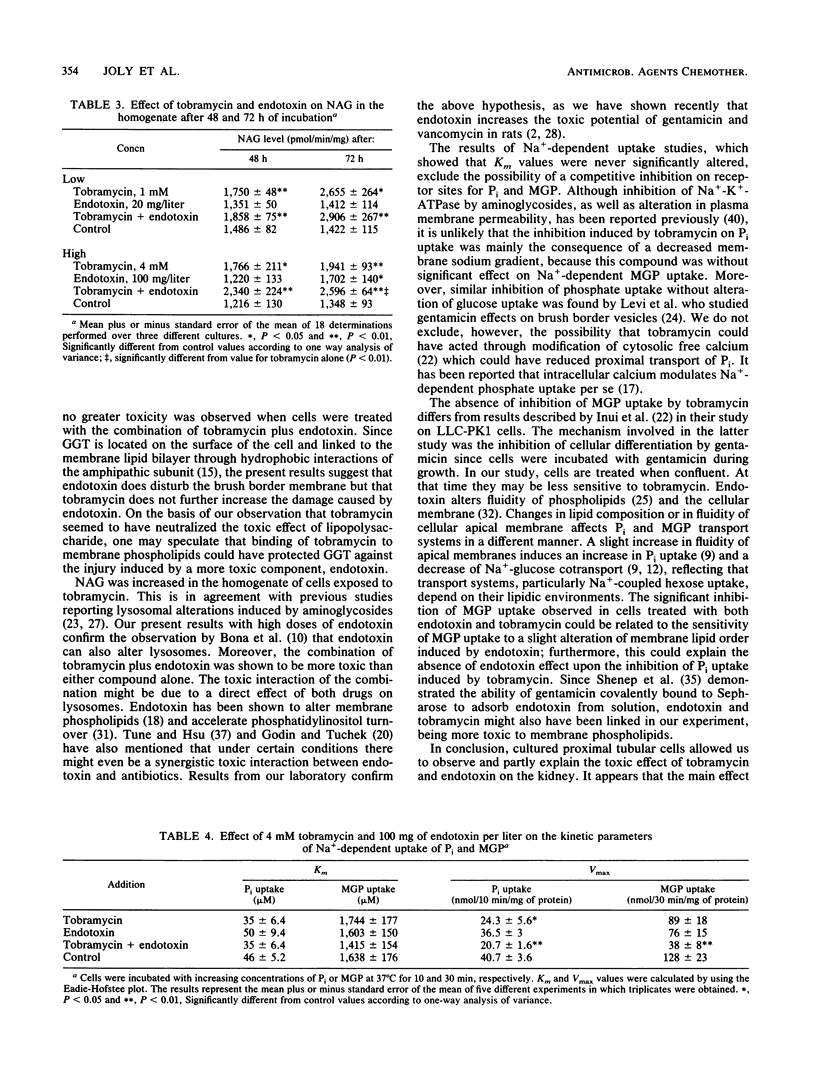
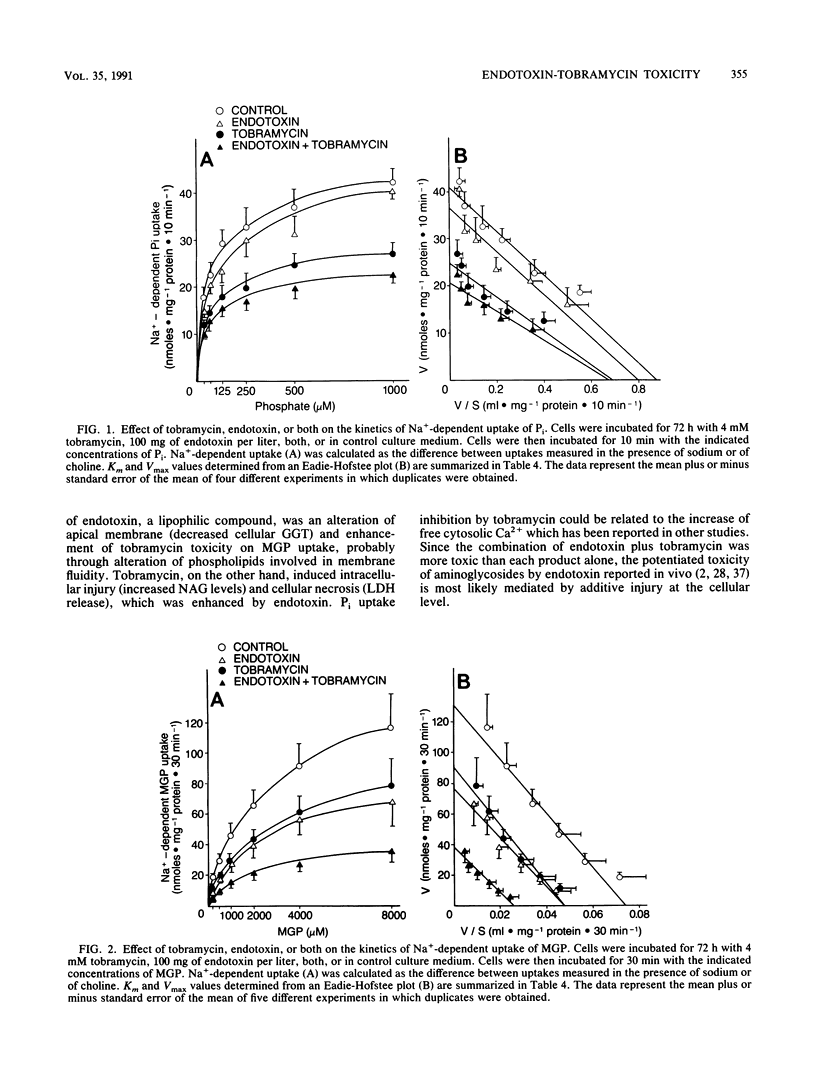
Aminoglycoside-induced renal damage is enhanced in animals with Escherichia coli pyelonephritis. Bacterial endotoxin is liberated during antibiotic therapy. The toxic effect of endotoxin and tobramycin, alone or in combination, was investigated in primary cultures of rabbit proximal tubular cells grown to confluence in serum-free medium. Sodium-dependent uptakes of Pi and alpha-methylglucopyranoside (MGP) and enzymatic activities (lactate dehydrogenase [LDH] released as a marker of cell necrosis and gamma-glutamyltransferase [GGT] and N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase [NAG] present in the homogenate as markers of brush border membrane and lysosome integrity) were measured. Cells were exposed to (i) endotoxin (20 mg/liter), tobramycin (1 mM), or endotoxin plus tobramycin for 48 h, or (ii) endotoxin (100 mg/liter), tobramycin (4 mM), or endotoxin plus tobramycin for 72 h. Endotoxin alone did not alter Pi uptake, but tobramycin inhibited Pi uptake through a decrease in Vmax. The effect was not enhanced by the combination of endotoxin and tobramycin. Endotoxin and tobramycin alone exerted no significant effect upon MGP uptake, but strong inhibition of the Vmax was observed after exposure to a combination of endotoxin plus tobramycin, without alteration of the Km. Endotoxin decreased residual GGT activity in the cell homogenate. Tobramycin increased LDH release in the medium and NAG activity in the homogenate. Endotoxin plus tobramycin resulted in an additive effect upon LDH and NAG activities. In conclusion, by disturbing apical membrane integrity, endotoxin increased tobramycin toxicity in vitro in the absence of serum hormonal mediator.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel G. B., Neu H. C. The nephrotoxicity of antimicrobial agents (first of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1977 Mar 24;296(12):663–670. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197703242961205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auclair P., Tardif D., Beauchamp D., Gourde P., Bergeron M. G. Prolonged endotoxemia enhances the renal injuries induced by gentamicin in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 May;34(5):889–895. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.5.889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp D., Poirier A., Bergeron M. G. Increased nephrotoxicity of gentamicin in pyelonephritic rats. Kidney Int. 1985 Aug;28(2):106–113. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bello-Reuss E., Weber M. R. Electrophysiological studies on primary cultures of proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 2):F490–F498. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.3.F490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Bergeron Y. Influence of endotoxin on the intrarenal distribution of gentamicin, netilmicin, tobramycin, amikacin, and cephalothin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Bergeron Y., Marois Y. Autoradiography of tobramycin uptake by the proximal and distal tubules of normal and endotoxin-treated rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1005–1009. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Trottier S., Lessard C., Beauchamp D., Gagnon P. M. Disturbed intrarenal distribution of gentamicin in experimental pyelonephritis due to Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Sep;146(3):436–439. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.3.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biber J., Brown C. D., Murer H. Sodium-dependent transport of phosphate in LLC-PK1 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Nov 23;735(3):325–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90145-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bona C., Chedid L., Lamensans A. In vitro attachment of radioactive endotoxins to lysosomes. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):532–536. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.532-536.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrière B., Le Grimellec C. Effects of benzyl alcohol on enzyme activities and D-glucose transport in kidney brush-border membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 28;857(2):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90340-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caverzasio J., Brown C. D., Biber J., Bonjour J. P., Murer H. Adaptation of phosphate transport in phosphate-deprived LLC-PK1 cells. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 2):F122–F127. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.1.F122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. D., Alavi N., Livingston D., Hiller S., Taub M. Characterization of primary rabbit kidney cultures that express proximal tubule functions in a hormonally defined medium. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):118–126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curthoys N. P., Hughey R. P. Characterization and physiological function of rat renal gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase. Enzyme. 1979;24(6):383–403. doi: 10.1159/000458694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EHRMANN R. L., GEY G. O. The growth of cells on a transparent gel of reconstituted rat-tail collagen. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1956 Jun;16(6):1375–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried V. A., Rothfield L. I. Interactions between lipopolysaccharide and phosphatidylethanolamine in molecular monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 4;514(1):69–82. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander G., Shahedi M., Le Grimellec C., Amiel C. Increase in membrane fluidity and opening of tight junctions have similar effects on sodium-coupled uptakes in renal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11183–11188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godin D. V., Tuchek J. M. Plasma acid phosphatase levels in endotoxaemia: modification by drugs and chemically detoxified endotoxins. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):421–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11015.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui K., Saito H., Iwata T., Hori R. Aminoglycoside-induced alterations in apical membranes of kidney epithelial cell line (LLC-PK1). Am J Physiol. 1988 Feb;254(2 Pt 1):C251–C257. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.2.C251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauss T. C., Weinberg J. M., Humes H. D. Alterations in renal cortical phospholipid content induced by gentamicin: time course, specificity, and subcellular localization. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):F535–F546. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.5.F535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M. S., Onji T., Snelgrove N. E. Changes in phase transition temperature of phospholipids induced by endotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 15;710(2):248–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin J. P., Viotte G., Vandewalle A., Van Hoof F., Tulkens P., Fillastre J. P. Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity: a cell biology approach. Kidney Int. 1980 Nov;18(5):583–590. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngeleka M., Beauchamp D., Tardif D., Auclair P., Gourde P., Bergeron M. G. Endotoxin increases the nephrotoxic potential of gentamicin and vancomycin plus gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):721–727. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUGH D., LEABACK D. H., WALKER P. G. Studies on glucosaminidase; N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase in rat kidney. Biochem J. 1957 Mar;65(3):464–469. doi: 10.1042/bj0650464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persijn J. P., van der Slik W. A new method for the determination of gamma-glutamyltransferase in serum. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1976 Sep;14(9):421–427. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1976.14.1-12.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosoff P. M., Cantley L. C. Lipopolysaccharide and phorbol esters induce differentiation but have opposite effects on phosphatidylinositol turnover and Ca2+ mobilization in 70Z/3 pre-B lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9209–9215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Leive L. Effect of variations in lipopolysaccharide on the fluidity of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2077–2081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwertz D. W., Kreisberg J. I., Venkatachalam M. A. Gentamicin-induced alterations in pig kidney epithelial (LLC-PK1) cells in culture. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jan;236(1):254–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenep J. L., Barton R. P., Mogan K. A. Role of antibiotic class in the rate of liberation of endotoxin during therapy for experimental gram-negative bacterial sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1012–1018. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. A., Acosta D., Bruckner J. V. Development of a primary culture system of rat kidney cortical cells to evaluate the nephrotoxicity of xenobiotics. Food Chem Toxicol. 1986 Jun-Jul;24(6-7):551–556. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(86)90112-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tune B. M., Hsu C. Y. Augmentation of antibiotic nephrotoxicity by endotoxemia in the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Aug;234(2):425–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinay P., Gougoux A., Lemieux G. Isolation of a pure suspension of rat proximal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F403–F411. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle N. Acute renal failure in the 1980s: the importance of septic shock and of endotoxaemia. Nephron. 1982;30(3):193–200. doi: 10.1159/000182461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. D., Trimble M. E., Crespo L., Holohan P. D., Freedman J. C., Ross C. R. Inhibition of renal Na+, K+-adenosine triphosphatase by gentamicin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Nov;231(2):248–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuthrich R. P., Glimcher L. H., Yui M. A., Jevnikar A. M., Dumas S. E., Kelley V. E. MHC class II, antigen presentation and tumor necrosis factor in renal tubular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 1990 Feb;37(2):783–792. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


