Abstract
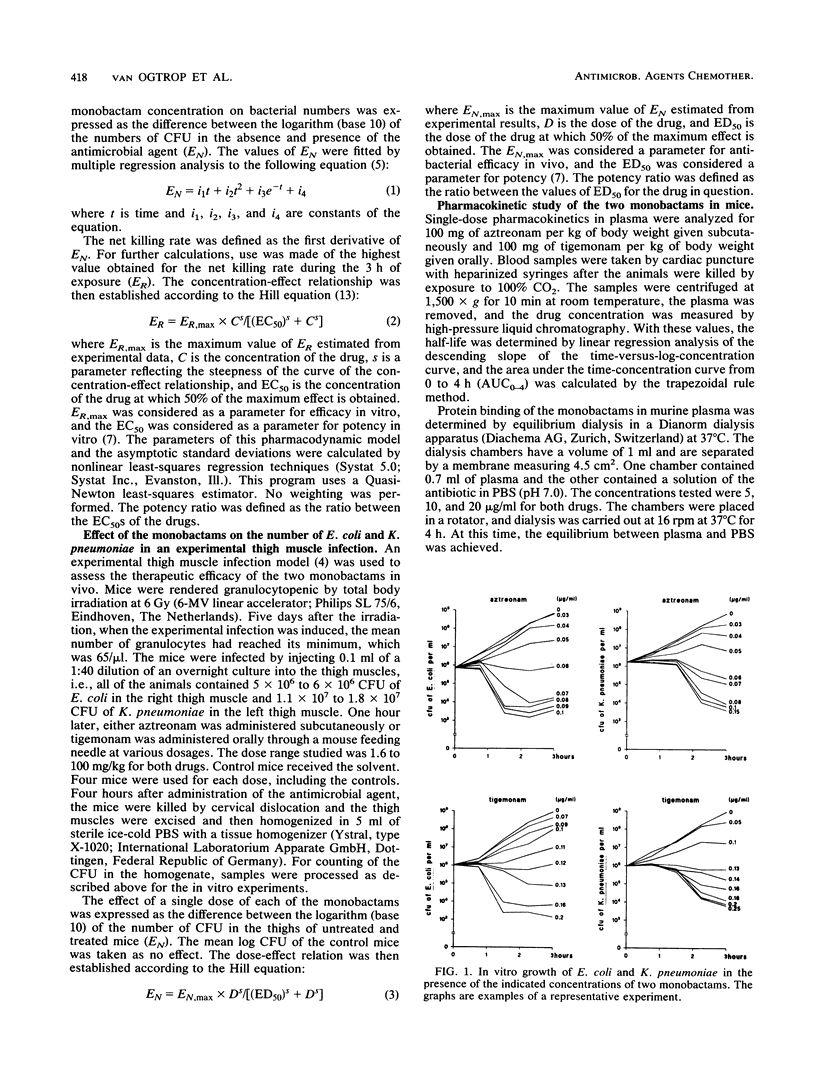
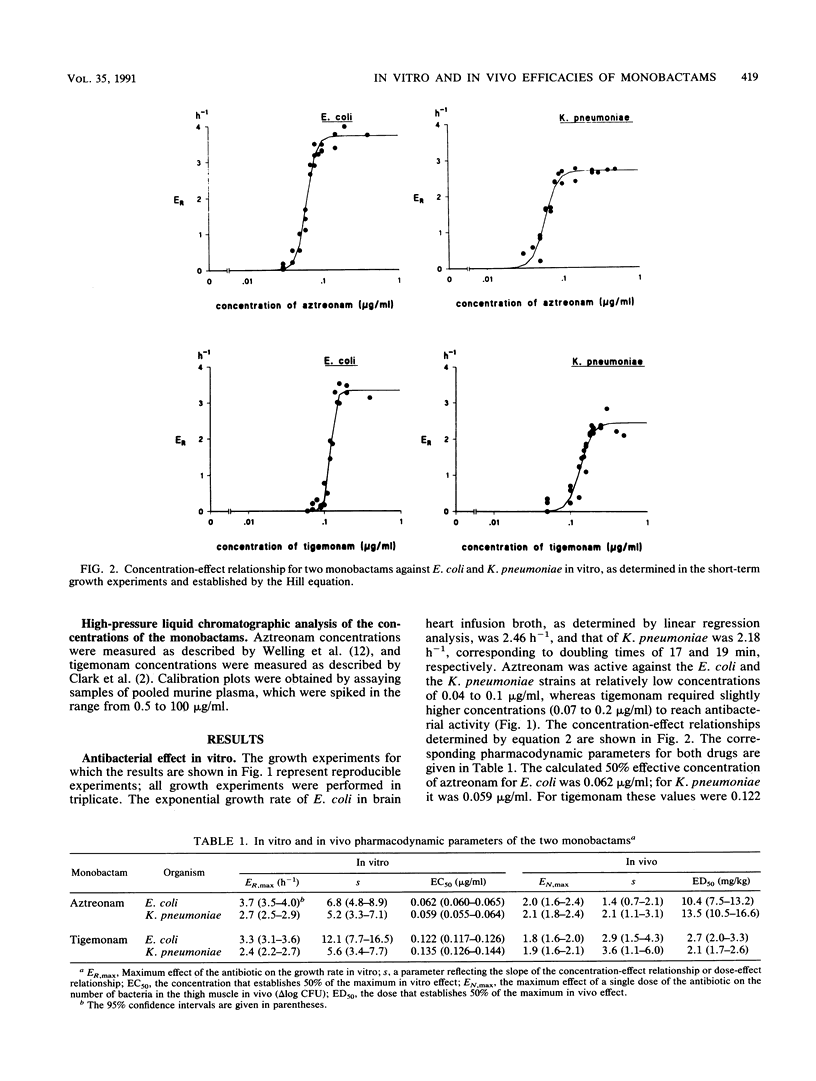
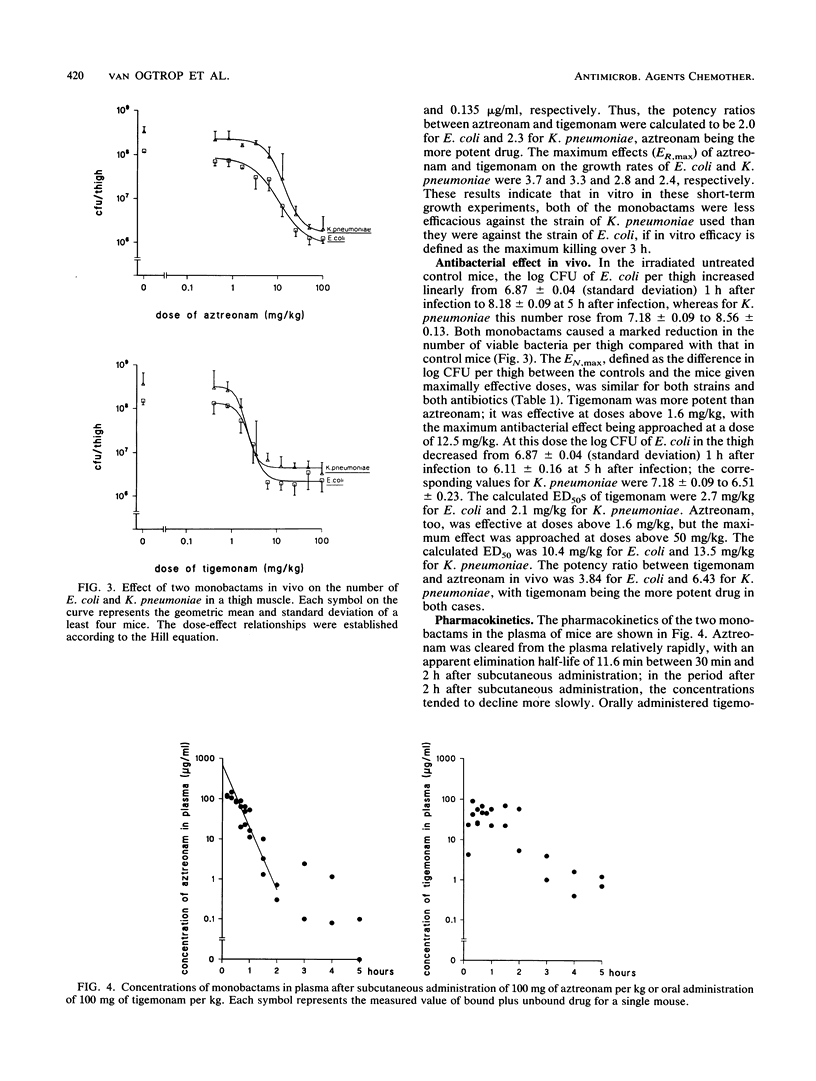
A study was performed to investigate the pharmacodynamics of aztreonam and tigemonam against Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in vitro and in vivo. The in vitro concentration-effect relationships were determined in short-term growth experiments. The in vivo dose-effect relationships were determined in an experimental thigh muscle infection in irradiated mice. In this model, E. coli was injected into one thigh muscle and K. pneumoniae was injected into the other. Throughout these experiments aztreonam was administered subcutaneously and tigemonam was administered orally. For analysis of the antibacterial pharmacodynamics, the following parameters were determined: the maximum effect as a parameter for efficacy, the 50% effective concentration (or dose) as a parameter for potency, and the slope of the concentration-effect relationship. To assess the relationship between the concentration of the antibiotic and the antibacterial effect in vivo, the pharmacokinetics of the two drugs in the plasma of mice were determined as well. The maximum in vitro and in vivo effects of aztreonam and tigemonam against both bacteria did not differ substantially. However, both drugs killed E. coli more effectively than K. pneumoniae, indicating that the maximum in vitro effect of these drugs against E. coli was higher than that against K. pneumoniae. The maximum in vivo effect of both drugs against E. coli was similar to that against K. pneumoniae. Furthermore, in vitro aztreonam was about twice as potent as tigemonam, but in vivo the reverse was the case. These findings were explained by pharmacokinetic differences between subcutaneously administered aztreonam and orally administered tigemonam, because concentrations of tigemonam in plasma remained at microbiologically active concentrations longer than those of aztreonam did.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brogden R. N., Heel R. C. Aztreonam. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1986 Feb;31(2):96–130. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198631020-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M., Olsen S. J., Weinberg D. S., Dalvi M., Whitney R. R., Bonner D. P., Sykes R. B. In vivo evaluation of tigemonam, a novel oral monobactam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):226–229. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. G., Rolston K. V., Fainstein V., Elting L., Walters R. S., Bodey G. P. Aztreonam therapy in neutropenic patients with cancer. Am J Med. 1986 Aug;81(2):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90258-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunst M. W., Mattie H. Cefazolin and cephradine: relationship between antibacterial activity in vitro and in mice experimentally infected with Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1978 Apr;137(4):391–402. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.4.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattie H., van Dokkum A. M., Brus-Weijer L., Krul A. M., van Strijen E. Antibacterial activity of four cephalosporins in an experimental infection in relation to in vitro effect and pharmacokinetics. J Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;162(3):717–722. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.3.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves D. S., Bywater M. J., Holt H. A. Antibacterial activity of the monobactam SQ 26,776 against antibiotic resistant enterobacteria, including Serratia spp. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):57–68. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Koster W. H., Bonner D. P. The new monobactams: chemistry and biology. J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;28(2):113–119. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1988.tb05734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S. K., Summerill R. A., Minassian B. F., Bush K., Visnic D. A., Bonner D. P., Sykes R. B. In vitro evaluation of tigemonam, a novel oral monobactam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):219–225. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelman B., Gudmundsson S., Leggett J., Turnidge J., Ebert S., Craig W. A. Correlation of antimicrobial pharmacokinetic parameters with therapeutic efficacy in an animal model. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):831–847. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling G. W., Groen G., Welling-Wester S., de Vries-Hospers H. G., van der Waaij D. Enzymatic inactivation of aztreonam by faecal enzyme preparations from healthy volunteers. Infection. 1987 May-Jun;15(3):188–191. doi: 10.1007/BF01646046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting B., Kelman A. W. The modelling of drug response. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Nov;59(5):311–315. doi: 10.1042/cs0590311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ogtrop M. L., Mattie H., Guiot H. F., van Strijen E., Hazekamp-van Dokkum A. M., van Furth R. Comparative study of the effects of four cephalosporins against Escherichia coli in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Oct;34(10):1932–1937. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.10.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


