Abstract
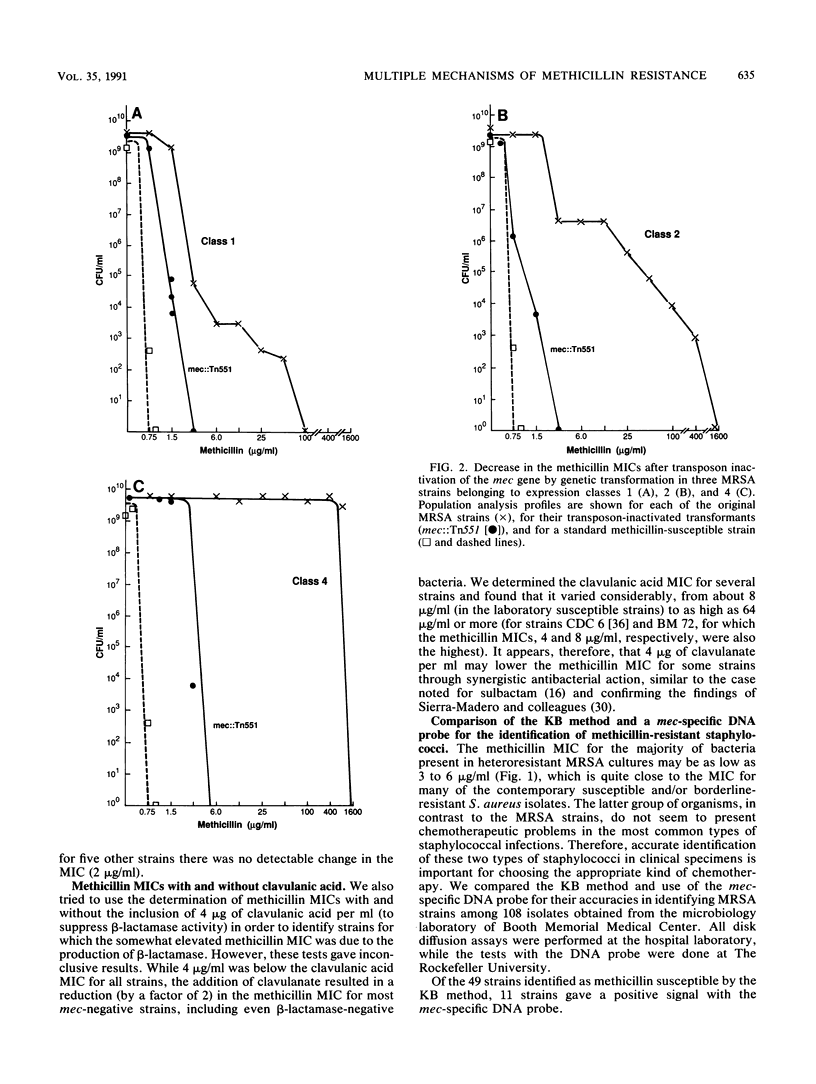
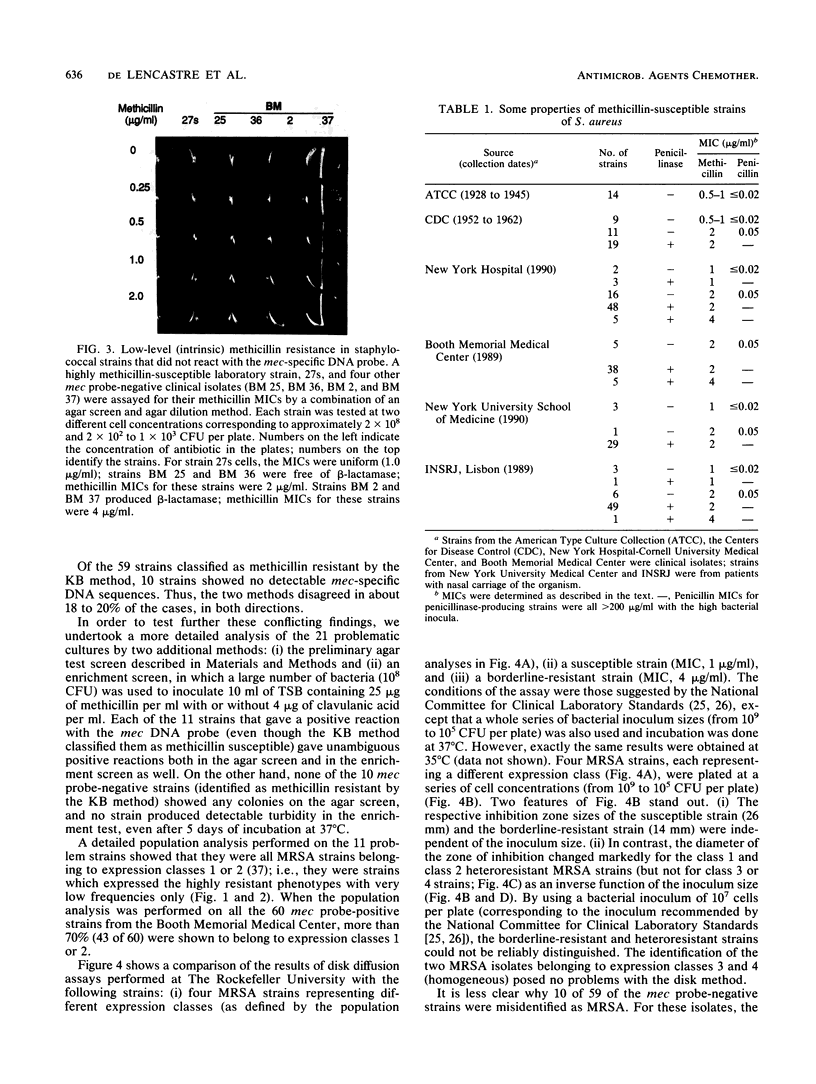
The mec gene of a number of clinical methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates exhibiting a variety of heterogeneous expression modes was selectively inactivated by allelic replacement mutagenesis. While the resistance level of each of the transformants was reduced, the methicillin MIC for these transformants was well above the MIC for susceptible laboratory strains of S. aureus and was similar to the methicillin MIC for many contemporary clinical isolates which did not react with the mec-specific DNA probe but which showed a low or borderline level of resistance to methicillin. A number of those strains had no detectable beta-lactamase, and for about half of the isolates that did carry plasmid-borne beta-lactamase, elimination of the plasmid caused only partial reduction of the methicillin MIC or no reduction at all. The findings suggest that many contemporary strains of staphylococci harbor a combination of at least three distinct beta-lactam resistance mechanisms: (i) the mechanism related to the acquisition of the foreign mec gene and (ii) a beta-lactamase-dependent and (iii) a beta-lactamase-independent mechanism, each one of which can provide a certain degree of resistance against penicillinase-resistant beta-lactam antibiotics.
Full text
PDF


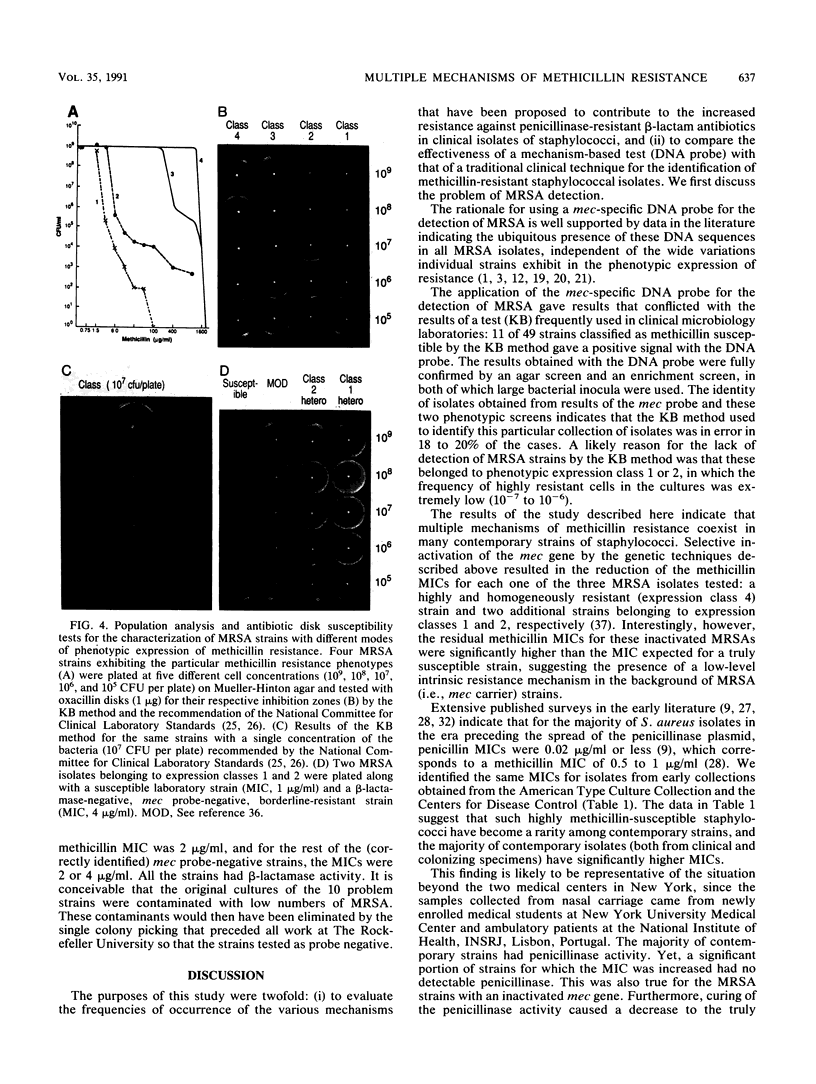


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G. L., Pennell E. Detection of methicillin resistance in staphylococci by using a DNA probe. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1720–1724. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER M. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1961 Jul;14:385–393. doi: 10.1136/jcp.14.4.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck W. D., Berger-Bächi B., Kayser F. H. Additional DNA in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and molecular cloning of mec-specific DNA. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):373–378. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.373-378.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger-Bächi B., Barberis-Maino L., Strässle A., Kayser F. H. FemA, a host-mediated factor essential for methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: molecular cloning and characterization. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Oct;219(1-2):263–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00261186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger-Bächi B., Strässle A., Kayser F. H. Characterization of an isogenic set of methicillin-resistant and susceptible mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;5(6):697–701. doi: 10.1007/BF02013308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Archer G., Matsuhashi M. Low-level methicillin resistance in strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):424–428. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Hartman B. J., Tomasz A. Increased amounts of a novel penicillin-binding protein in a strain of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus exposed to nafcillin. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):325–331. doi: 10.1172/JCI111965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINLAND M., FRANK P. F., WILCOX C. In vitro susceptibility of pathogenic staphylococci to seven antibiotics. Am J Clin Pathol. 1950 Apr;20(4):325–334. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/20.4.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackbarth C. J., Chambers H. F. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci: detection methods and treatment of infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jul;33(7):995–999. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.7.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handwerger S., Tomasz A. Alterations in penicillin-binding proteins of clinical and laboratory isolates of pathogenic Streptococcus pneumoniae with low levels of penicillin resistance. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):83–89. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. J., Tomasz A. Expression of methicillin resistance in heterogeneous strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):85–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglis B., Matthews P. R., Stewart P. R. The expression in Staphylococcus aureus of cloned DNA encoding methicillin resistance. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jun;134(6):1465–1469. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-6-1465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOX R., SMITH J. T. The nature of penicillin resistance in staphylococci. Lancet. 1961 Sep 2;2(7201):520–522. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)92958-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Arai S., Hayashi S., Sakaguchi T. In vitro effects of beta-lactams combined with beta-lactamase inhibitors against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):331–335. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblum J., Hartman B. J., Novick R. P., Tomasz A. Conversion of a homogeneously methicillin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus to heterogeneous resistance by Tn551-mediated insertional inactivation. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;5(6):714–718. doi: 10.1007/BF02013311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuhashi M., Song M. D., Ishino F., Wachi M., Doi M., Inoue M., Ubukata K., Yamashita N., Konno M. Molecular cloning of the gene of a penicillin-binding protein supposed to cause high resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):975–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.975-980.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews P. R., Reed K. C., Stewart P. R. The cloning of chromosomal DNA associated with methicillin and other resistances in Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jul;133(7):1919–1929. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-7-1919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews P., Tomasz A. Insertional inactivation of the mec gene in a transposon mutant of a methicillin-resistant clinical isolate of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1777–1779. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal L. K., Thornsberry C. The role of beta-lactamase in staphylococcal resistance to penicillinase-resistant penicillins and cephalosporins. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):832–839. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.832-839.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montanari M. P., Tonin E., Biavasco F., Varaldo P. E. Further characterization of borderline methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and analysis of penicillin-binding proteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 May;34(5):911–913. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.5.911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Tomasz A. Involvement of multiple genetic determinants in high-level methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):874–879. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.874-879.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROLINSON G. N., STEVENS S., BATCHELOR F. R., WOOD J. C., CHAIN E. B. Bacteriological studies on a new penicillin-BRL. 1241. Lancet. 1960 Sep 10;2(7150):564–567. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)91642-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi L., Tonin E., Cheng Y. R., Fontana R. Regulation of penicillin-binding protein activity: description of a methicillin-inducible penicillin-binding protein in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):828–831. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPINK W. W. Clinical and biologic significance of penicillin-resistant staphylococci, including observations with streptomycin, aureomycin, chloramphenicol, and terramycin. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Feb;37(2):278–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra-Madero J. G., Knapp C., Karaffa C., Washington J. A. Role of beta-lactamase and different testing conditions in oxacillin-borderline-susceptible staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Dec;32(12):1754–1757. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.12.1754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song M. D., Wachi M., Doi M., Ishino F., Matsuhashi M. Evolution of an inducible penicillin-target protein in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by gene fusion. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 31;221(1):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80373-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Pattee P. A. Transformation in Staphylococcus aureus: role of bacteriophage and incidence of competence among strains. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):778–788. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.778-788.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., McDougal L. K. Successful use of broth microdilution in susceptibility tests for methicillin-resistant (heteroresistant) staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1084–1091. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1084-1091.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Drugeon H. B., de Lencastre H. M., Jabes D., McDougall L., Bille J. New mechanism for methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: clinical isolates that lack the PBP 2a gene and contain normal penicillin-binding proteins with modified penicillin-binding capacity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1869–1874. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Nachman S., Leaf H. Stable classes of phenotypic expression in methicillin-resistant clinical isolates of staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonin E., Tomasz A. Beta-lactam-specific resistant mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Oct;30(4):577–583. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.4.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata K., Yamashita N., Konno M. Occurrence of a beta-lactam-inducible penicillin-binding protein in methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):851–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]