Abstract
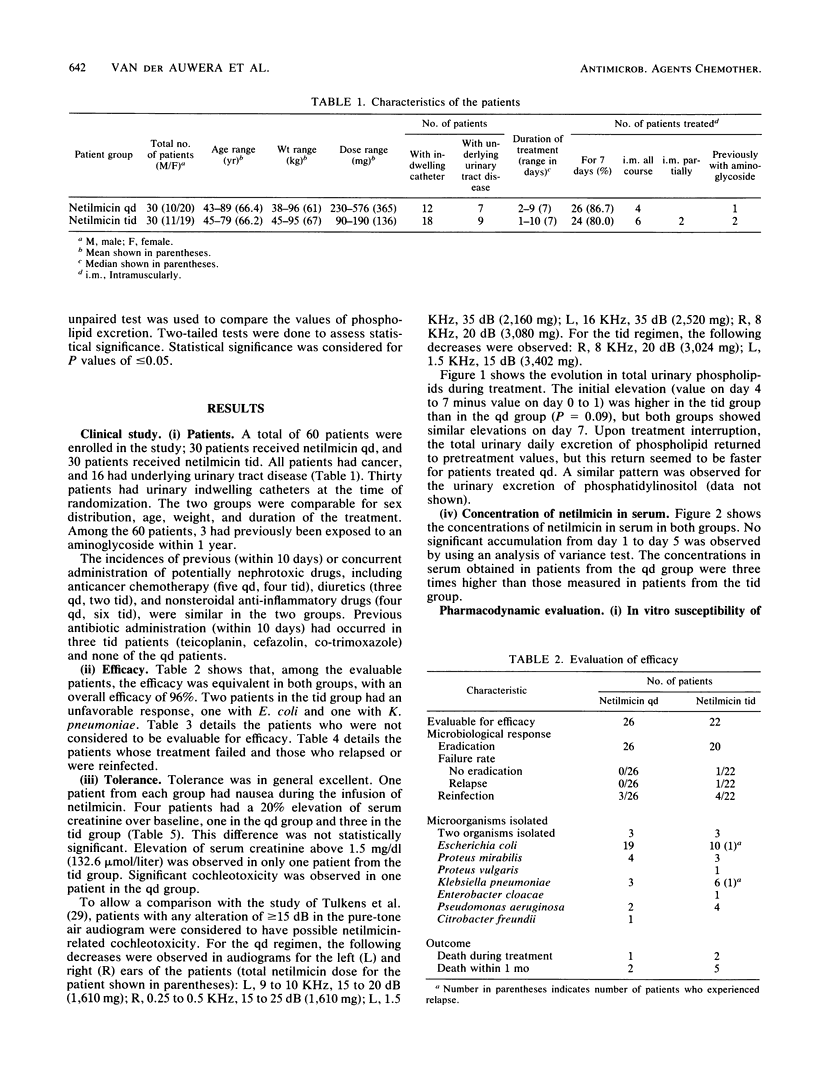
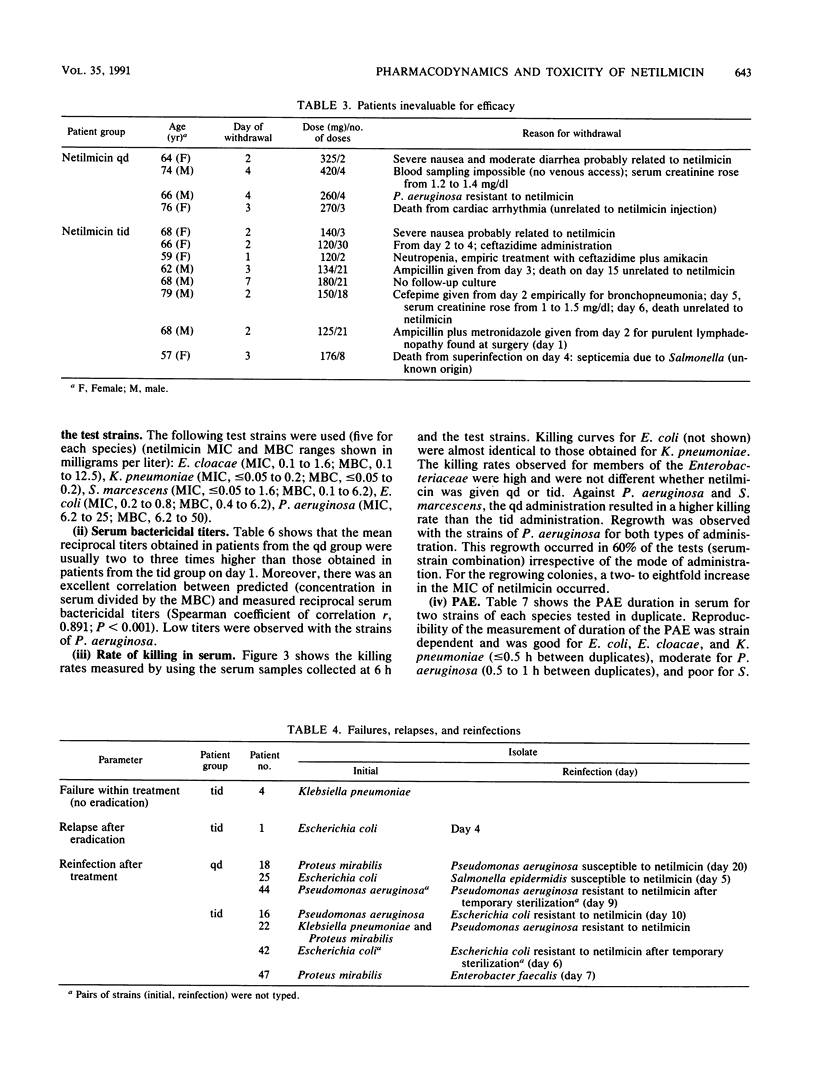
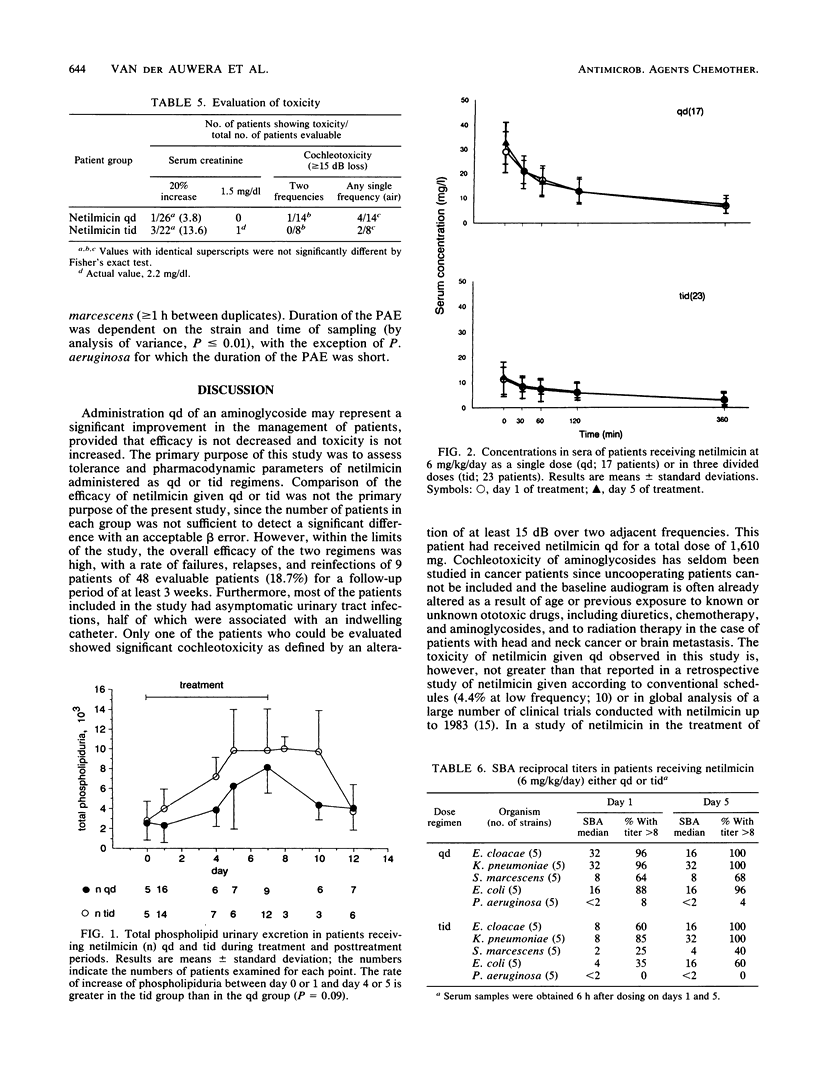
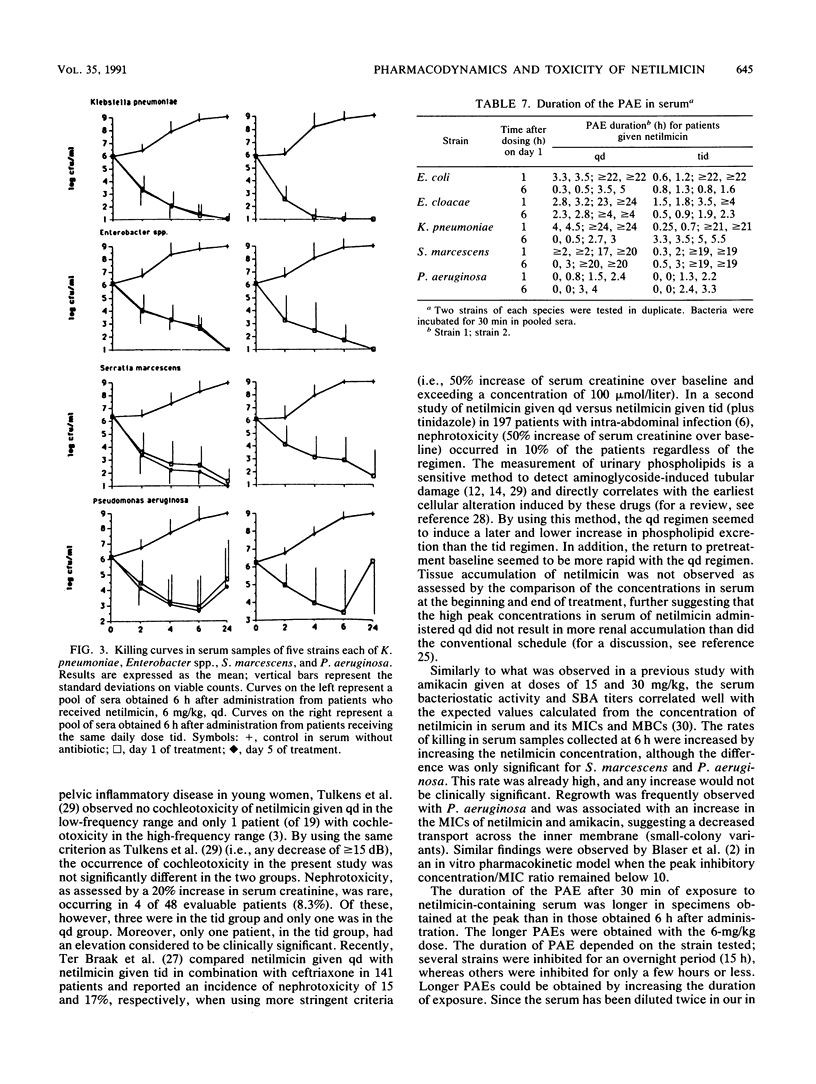
The pharmacologic parameters and toxicity of netilmicin (6 mg/kg/day) given once daily (qd) or thrice daily (tid) for the treatment of urinary tract infections were studied in a randomized prospective study of 60 cancer patients. The overall efficacy was 96%. Nephrotoxicity, assessed by the measure of urinary excretion of phospholipids, was lower for the patients receiving the qd regimen than for those receiving the tid regimen. Elevation of serum creatinine (20% over baseline) occurred in one patient receiving the qd regimen and in three receiving the tid regimen. Cochleotoxicity, assessed by pure-tone audiometry (250 to 18,000 Hz) occurred in one patient receiving the qd regimen and none receiving the tid regimen. Concentrations in sera were measured on days 1 and 5. No significant accumulation was observed in either group. Median serum bactericidal titers, expressed as reciprocal values (percentage of the sera with a titer greater than or equal to 8), were measured against 25 test organisms in samples collected 6 h after the administration of netilmicin and were, for the qd group, 16 (82%) against members of the family Enterobacteriaceae and less than 2 (8%) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and for the tid group, 4 (57%) against members of the Enterobacteriaceae and less than 2 (0%) against P. aeruginosa. The rate of killing in serum was rapid (2 to 3 log in 2 h against P. aeruginosa; 3 to 5 log in 2 h against members of the Enterobacteriaceae) and correlated with the sampling time and hence the concentration in serum of netilmicin. The duration of the postantibiotic effect in serum depended also on the strain and the sampling time of the serum.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett W. M., Plamp C. E., Gilbert D. N., Parker R. A., Porter G. A. The influence of dosage regimen on experimental gentamicin nephrotoxicity: dissociation of peak serum levels from renal failure. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):576–580. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser J., Stone B. B., Groner M. C., Zinner S. H. Comparative study with enoxacin and netilmicin in a pharmacodynamic model to determine importance of ratio of antibiotic peak concentration to MIC for bactericidal activity and emergence of resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1054–1060. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummett R. E., Fox K. E. Aminoglycoside-induced hearing loss in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jun;33(6):797–800. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.6.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buring J. E., Evans D. A., Mayrent S. L., Rosner B., Colton T., Hennekens C. H. Randomized trials of aminoglycoside antibiotics: quantitative overview. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Sep-Oct;10(5):951–957. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.5.951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake T. A., Hackbarth C. J., Sande M. A. Value of serum tests in combined drug therapy of endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Nov;24(5):653–657. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.5.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg J. M., Koffer H., Glick H. A., Connell M. L., Loss L. E., Talbot G. H., Shusterman N. H., Strom B. L. What is the cost of nephrotoxicity associated with aminoglycosides? Ann Intern Med. 1987 Dec;107(6):900–909. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-6-900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan S. T., Lau W. Y., Teoh-Chan C. H., Lau K. F., Mauracher E. H. Once daily administration of netilmicin compared with thrice daily, both in combination with metronidazole, in gangrenous and perforated appendicitis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jul;22(1):69–74. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatell J. M., Ferran F., Araujo V., Bonet M., Soriano E., Traserra J., SanMiguel J. G. Univariate and multivariate analyses of risk factors predisposing to auditory toxicity in patients receiving aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1383–1387. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuliano R. A., Verpooten G. A., Verbist L., Wedeen R. P., De Broe M. E. In vivo uptake kinetics of aminoglycosides in the kidney cortex of rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Feb;236(2):470–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim S., Van der Auwera P., Meunier F., Tulkens P. M. Effect of netilmicin and amikacin on urinary phospholipids excretion in humans. Arch Toxicol Suppl. 1989;13:413–416. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74117-3_81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josepovitz C., Levine R., Farruggella T., Kaloyanides G. J. Comparative effects of aminoglycosides on renal cortical and urinary phospholipids in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1986 May;182(1):1–5. doi: 10.3181/00379727-182-42300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahlmeter G., Dahlager J. I. Aminoglycoside toxicity - a review of clinical studies published between 1975 and 1982. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Jan;13 (Suppl A):9–22. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.suppl_a.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapusnik J. E., Hackbarth C. J., Chambers H. F., Carpenter T., Sande M. A. Single, large, daily dosing versus intermittent dosing of tobramycin for treating experimental pseudomonas pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):7–12. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D., Lietman P. S., Smith C. R. Clinical response to aminoglycoside therapy: importance of the ratio of peak concentration to minimal inhibitory concentration. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):93–99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D., Smith C. R., Lietman P. S. Association of aminoglycoside plasma levels with therapeutic outcome in gram-negative pneumonia. Am J Med. 1984 Oct;77(4):657–662. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90358-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D., Smith C. R., Lietman P. S. The association of aminoglycoside plasma levels with mortality in patients with gram-negative bacteremia. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):443–448. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Steigbigel R. T., Davis H. T., Chapman S. W. Method of reliable determination of minimal lethal antibiotic concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):699–708. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Bloxham D. D., Thompson W. L. Nephrotoxicity of gentamicin and tobramycin given once daily or continuously in dogs. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 May;4 (Suppl A):85–101. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.suppl_a.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B., Stratton C. W. Serum dilution test for bactericidal activity. II. Standardization and correlation with antimicrobial assays and susceptibility tests. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136(2):196–204. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculier J. P., Klastersky J. Significance of serum bactericidal activity in gram-negative bacillary bacteremia in patients with and without granulocytopenia. Am J Med. 1984 Mar;76(3):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90662-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulkens P. M. Nephrotoxicity of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Toxicol Lett. 1989 Mar;46(1-3):107–123. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(89)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera P., Klastersky J. Serum bactericidal activity and postantibiotic effect in serum of patients with urinary tract infection receiving high-dose amikacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1061–1068. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelman B., Gudmundsson S., Leggett J., Turnidge J., Ebert S., Craig W. A. Correlation of antimicrobial pharmacokinetic parameters with therapeutic efficacy in an animal model. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):831–847. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelman B., Gudmundsson S., Turnidge J., Leggett J., Craig W. A. In vivo postantibiotic effect in a thigh infection in neutropenic mice. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):287–298. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Swartz M. N. Drug therapy. Serum bactericidal activity as a monitor of antibiotic therapy. N Engl J Med. 1985 Apr 11;312(15):968–975. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198504113121507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. A., Norton D. R., Kohlhepp S. J., Kohnen P. W., Porter G. A., Houghton D. C., Brummett R. E., Bennett W. M., Gilbert D. N. The influence of tobramycin dosage regimens on nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, and antibacterial efficacy in a rat model of subcutaneous abscess. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):13–22. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries P. J., Verkooyen R. P., Leguit P., Verbrugh H. A. Prospective randomized study of once-daily versus thrice-daily netilmicin regimens in patients with intraabdominal infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;9(3):161–168. doi: 10.1007/BF01963832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Braak E. W., de Vries P. J., Bouter K. P., van der Vegt S. G., Dorrestein G. C., Nortier J. W., van Dijk A., Verkooyen R. P., Verbrugh H. A. Once-daily dosing regimen for aminoglycoside plus beta-lactam combination therapy of serious bacterial infections: comparative trial with netilmicin plus ceftriaxone. Am J Med. 1990 Jul;89(1):58–66. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90099-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



