Abstract
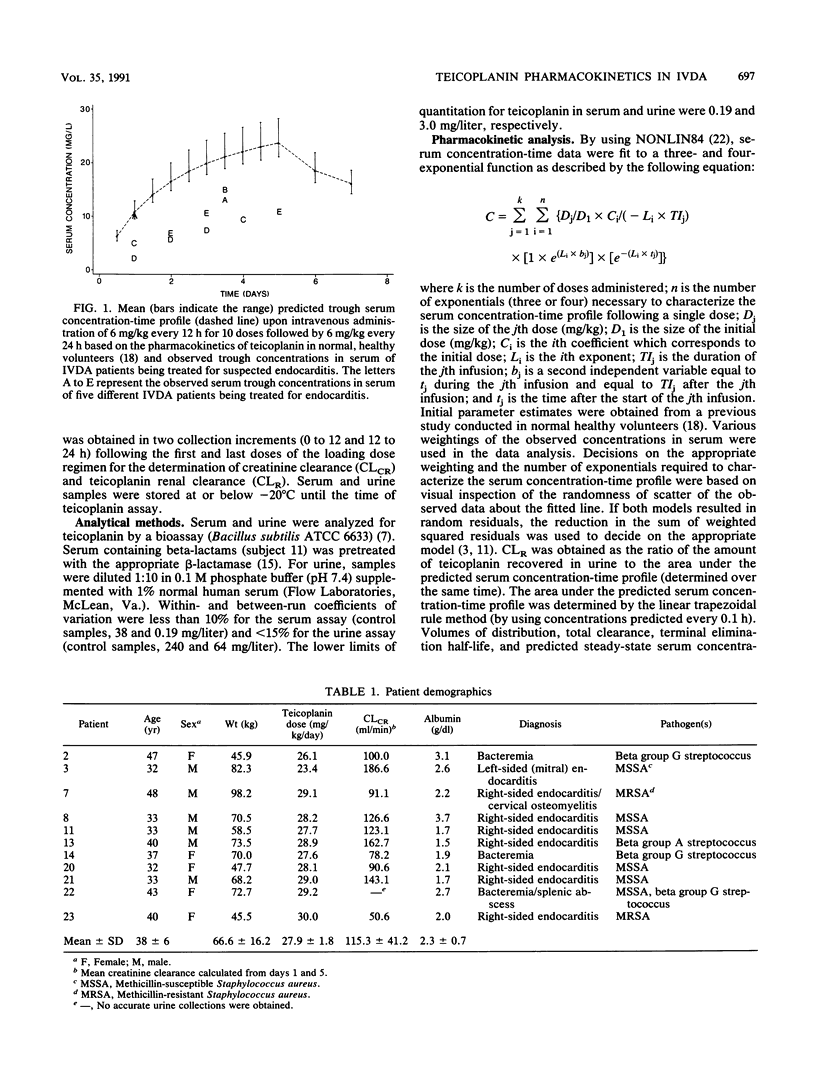
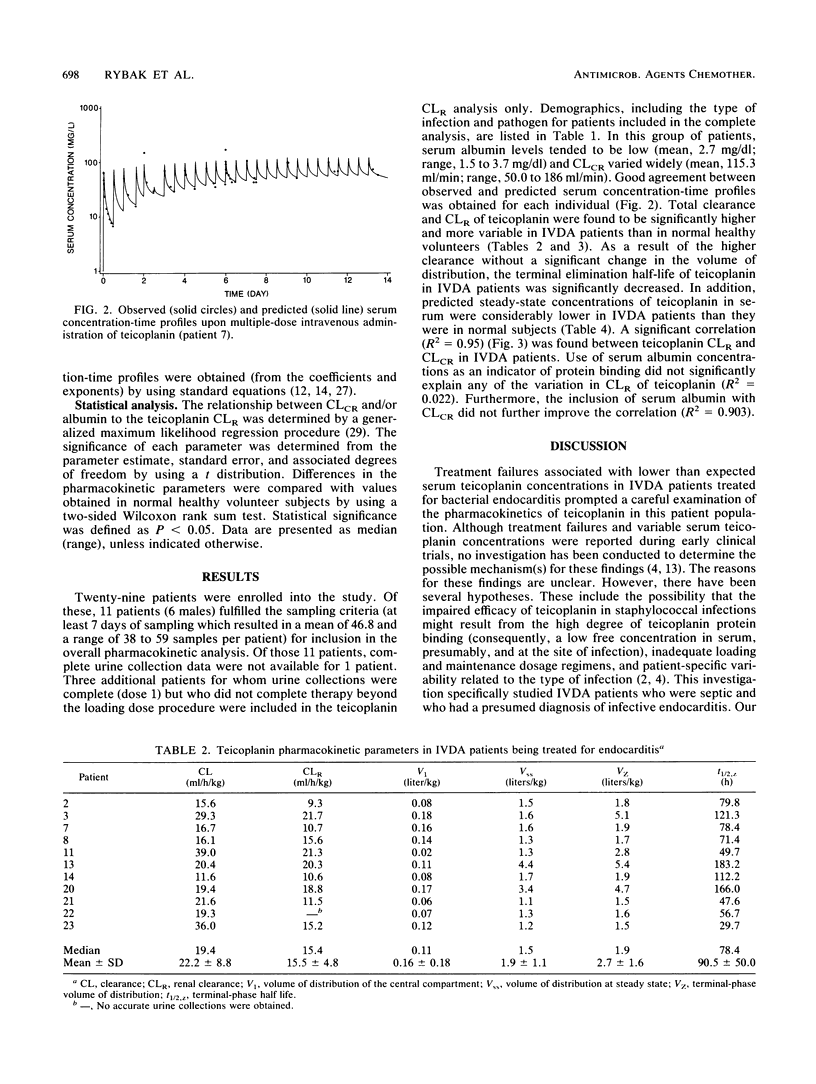
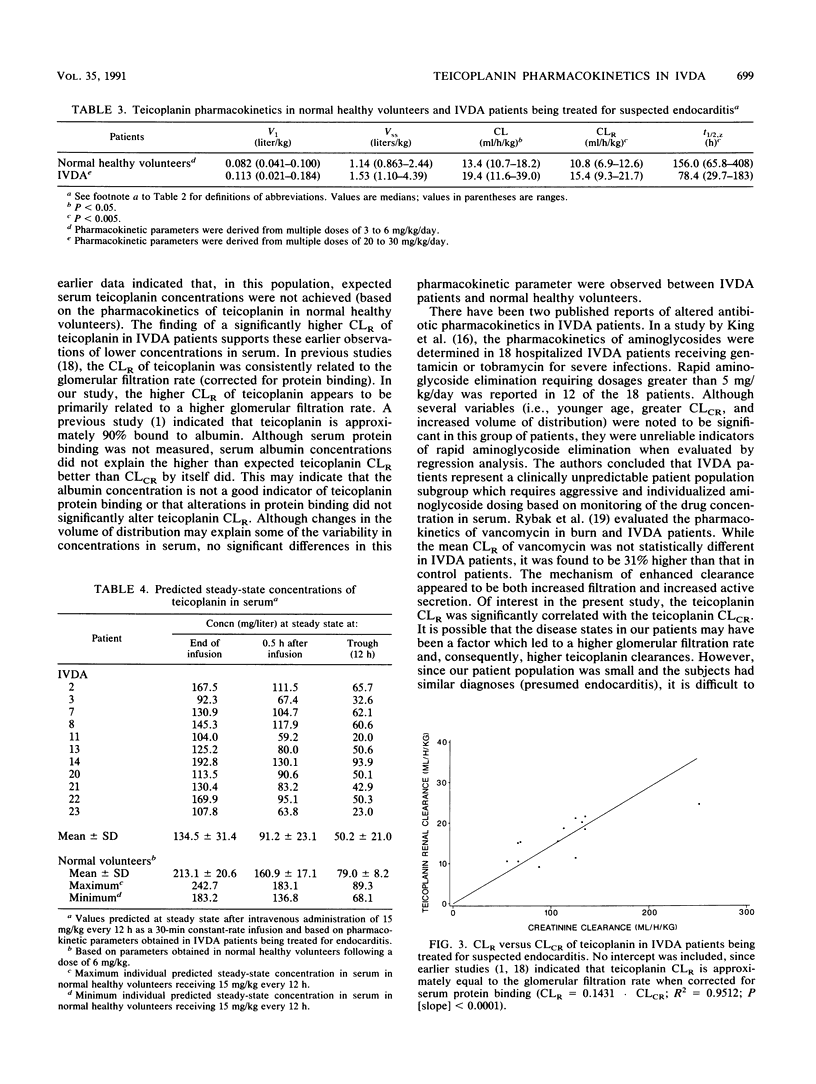
The pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin were determined after multiple 30-min intravenous infusions of 10 to 15 mg/kg every 12 to 24 h in 11 intravenous drug abuse (IVDA) patients being treated for bacterial endocarditis. Multiple serum samples were obtained over 7 to 14 days. Twenty-four-hour urine collections were obtained on days 1 and 5. Serum concentration-time data were analyzed by using multiple-dose pharmacokinetic analysis (NONLIN84). Results were compared with pharmacokinetic parameters derived from previous studies in normal healthy volunteers following multiple intravenous infusions of teicoplanin (3 to 6 mg/kg/day). Total and renal clearances of teicoplanin in IVDA patients were found to be significantly greater and more highly variable than those observed previously in normal healthy volunteers. As a result, predicted steady-state trough concentrations in serum may vary up to fivefold. The mechanism responsible for this variation appears to be related to the glomerular filtration rate. In IVDA patients, individualized teicoplanin dosage may be required in the treatment of bacterial endocarditis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assandri A., Bernareggi A. Binding of teicoplanin to human serum albumin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1987;33(2):191–195. doi: 10.1007/BF00544566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibler M. R., Frame P. T., Hagler D. N., Bode R. B., Staneck J. L., Thamlikitkul V., Harris J. E., Haregewoin A., Bullock W. E., Jr Clinical evaluation of efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and safety of teicoplanin for serious gram-positive infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):207–212. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxenbaum H. G., Riegelman S., Elashoff R. M. Statistical estimations in pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1974 Apr;2(2):123–148. doi: 10.1007/BF01061504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calain P., Krause K. H., Vaudaux P., Auckenthaler R., Lew D., Waldvogel F., Hirschel B. Early termination of a prospective, randomized trial comparing teicoplanin and flucloxacillin for treating severe staphylococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1987 Feb;155(2):187–191. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Sande M. A. Teicoplanin versus nafcillin and vancomycin in the treatment of experimental endocarditis caused by methicillin-susceptible or -resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):61–64. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debbia E., Pesce A., Schito G. C. In vitro interactions between teicoplanin and other antibiotics against enterococci and staphylococci. J Hosp Infect. 1986 Mar;7 (Suppl A):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(86)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson R. C., Hildebrand A. R., Hoffman P. F., Gibson C. B. A sensitive bioassay for teicoplanin in serum in the presence or absence of other antibiotics. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;12(3):235–241. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(89)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainstein V., LeBlanc B., Bodey G. P. Comparative in vitro study of teichomycin A2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Mar;23(3):497–499. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.3.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fietta A., Bersani C., Mangiarotti P., Gialdroni Grassi G. In vitro activity of teichomycin against isolates of gram-positive bacteria. Chemotherapy. 1983;29(4):275–282. doi: 10.1159/000238209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galetto D. W., Boscia J. A., Kobasa W. D., Kaye D. Teicoplanin compared with vancomycin for treatment of experimental endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):69–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glupczynski Y., Lagast H., Van der Auwera P., Thys J. P., Crokaert F., Yourassowsky E., Meunier-Carpentier F., Klastersky J., Kains J. P., Serruys-Schoutens E. Clinical evaluation of teicoplanin for therapy of severe infections caused by gram-positive bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):52–57. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. T., Dulworth J. K., Brackman M. A., Torney H. L., Gibson C. B., Hildebrand A. R., Weckbach L. S., Staneck J. L. Bioassay of teicoplanin in serum containing rifampin or a beta-lactam antibiotic. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Sep-Oct;12(5):449–454. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(89)90119-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. H., Creger R. J., Ellner J. J. Pharmacokinetics of tobramycin and gentamicin in abusers of intravenous drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):285–290. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martino P., Venditti M., Micozzi A., Brandimarte C., Gentile G., Santini C., Serra P. Teicoplanin in the treatment of gram-positive-bacterial endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1329–1334. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybak M. J., Albrecht L. M., Berman J. R., Warbasse L. H., Svensson C. K. Vancomycin pharmacokinetics in burn patients and intravenous drug abusers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 May;34(5):792–795. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.5.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanson D. C., Tadayon M. Activity of teicoplanin compared with vancomycin alone, and combined with gentamicin, against penicillin tolerant viridans streptococci and enterococci causing endocarditis. J Hosp Infect. 1986 Mar;7 (Suppl A):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(86)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullam P. M., Täuber M. G., Hackbarth C. J., Sande M. A. Therapeutic efficacy of teicoplanin in experimental enterococcal endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):135–136. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varaldo P. E., Debbia E., Schito G. C. In vitro activity of teichomycin and vancomycin alone and in combination with rifampin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Mar;23(3):402–406. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.3.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L., Tjandramaga B., Hendrickx B., Van Hecken A., Van Melle P., Verbesselt R., Verhaegen J., De Schepper P. J. In vitro activity and human pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):881–886. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. G. Linear pharmacokinetic equations allowing direct calculation of many needed pharmacokinetic parameters from the coefficients and exponents of polyexponential equations which have been fitted to the data. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1976 Oct;4(5):443–467. doi: 10.1007/BF01062831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. H., Grüneberg R. N., Webster A., Ridgway G. L. Teicoplanin in the treatment of infection caused by gram-positive organisms. J Hosp Infect. 1986 Mar;7 (Suppl A):101–103. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(86)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


