Abstract
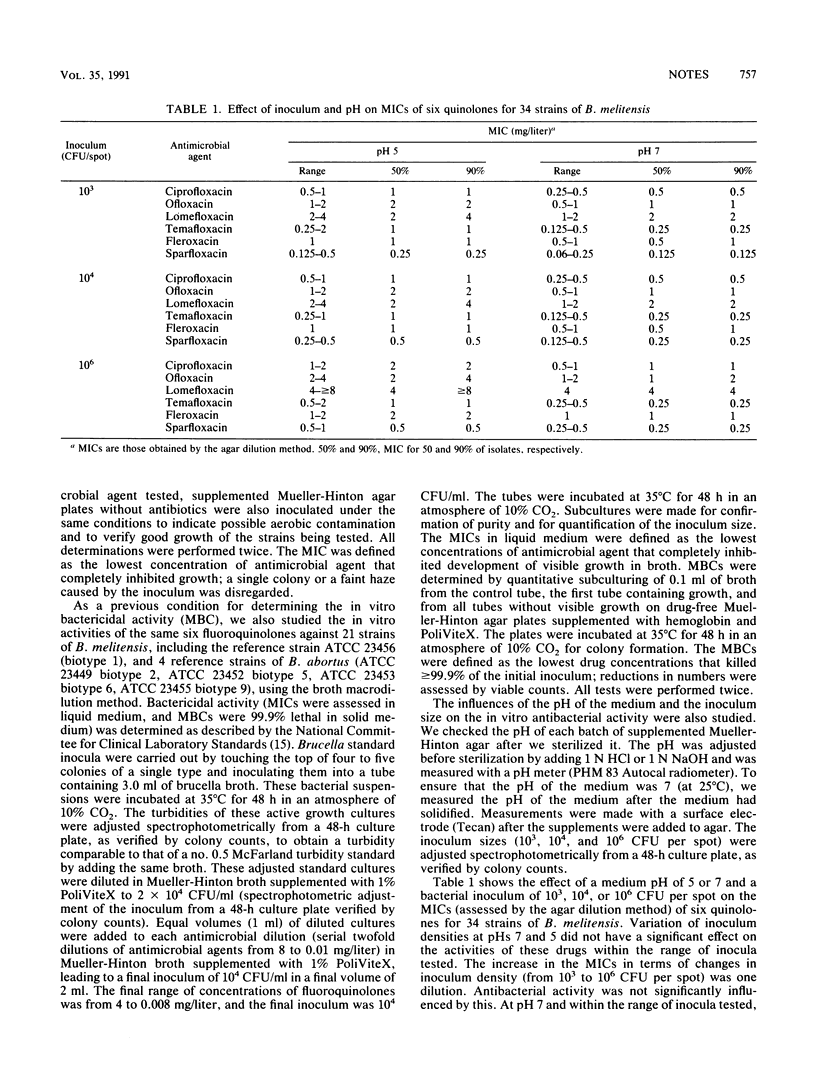
The in vitro activities of six fluoroquinolones against 43 Brucella spp. were compared by testing three different inocula at two medium pH values. The influence of the test conditions was moderate. The activities of all quinolones were lower at pH 5 and with a high inoculum size. Results indicate the lack of effective bactericidal activity of quinolones against most strains of Brucella spp., particularly B. abortus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acocella G., Bertrand A., Beytout J., Durrande J. B., Garcia Rodriguez J. A., Kosmidis J., Micoud M., Rey M., Rodriguez Zapata M., Roux J. Comparison of three different regimens in the treatment of acute brucellosis: a multicenter multinational study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Mar;23(3):433–439. doi: 10.1093/jac/23.3.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch J., Liñares J., López de Goicoechea M. J., Ariza J., Cisnal M. C., Martin R. In-vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, ceftriaxone and five other antimicrobial agents against 95 strains of Brucella melitensis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17(4):459–461. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.4.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Crane J. P., Blowers A. Effect of ciprofloxacin on intracellular organisms: in-vitro and in-vivo studies. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):43–48. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_d.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Crane J. P. Uptake of ciprofloxacin by human neutrophils. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jul;16(1):67–73. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Crane J. P. Uptake of ciprofloxacin by macrophages. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Apr;38(4):442–444. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.4.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gobernado M., Cantón E., Santos M. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin against Brucella melitensis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;3(4):371–371. doi: 10.1007/BF01977500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. Y., Dizon M., Kiel F. W. Comparative in vitro activities of ofloxacin, difloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and other selected antimicrobial agents against Brucella melitensis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1409–1410. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga H. High-performance liquid chromatography measurement of antimicrobial concentrations in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1904–1908. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Poole B. Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3327–3331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qadri S. M., Akhtar M., Ueno Y., al-Sibai M. B. Susceptibility of Brucella melitensis to fluoroquinolones. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1989;15(10):483–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. The fluoroquinolones: structures, mechanisms of action and resistance, and spectra of activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):581–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


