Abstract
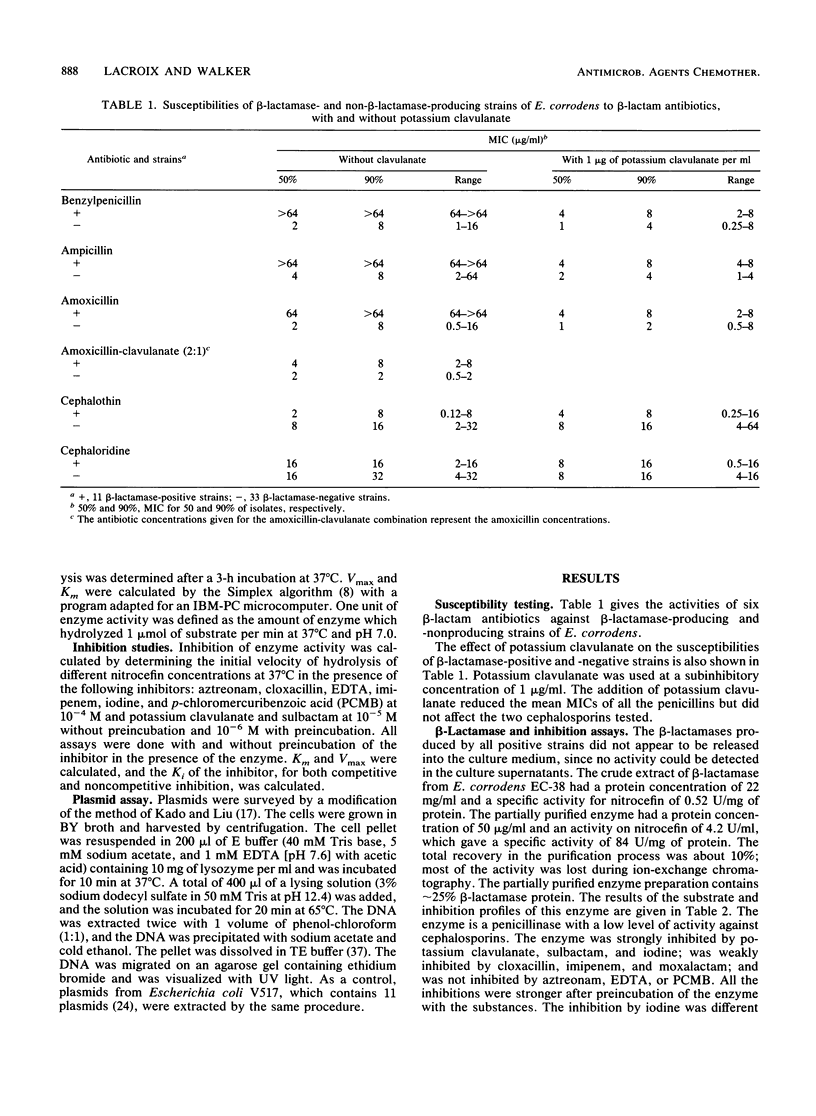
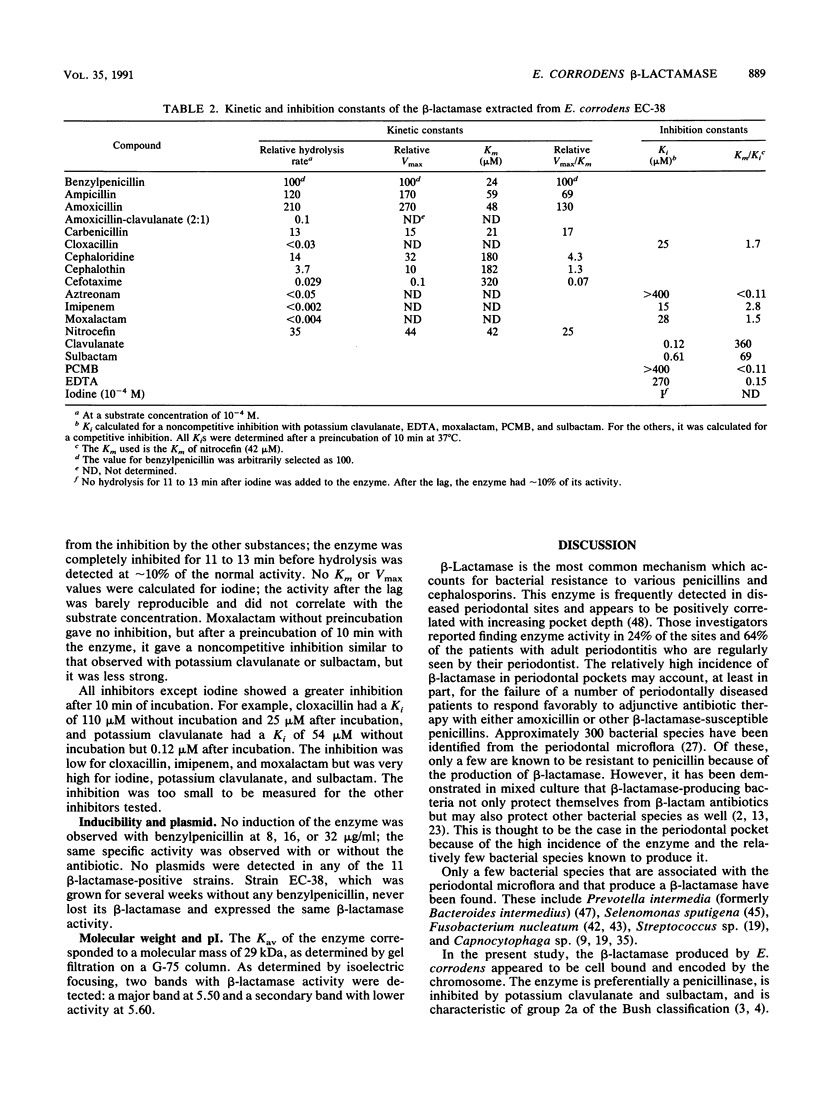
Eleven strains of Eikenella corrodens with beta-lactamase activity were isolated from a patient with refractory periodontitis who had previously been treated with penicillin antibiotics. These strains were relatively resistant to benzylpenicillin, amoxicillin, and ampicillin (MICs, greater than or equal to 64 micrograms/ml); susceptible to amoxicillin-clavulanate (2:1) (MICs, less than or equal to 4 micrograms/ml); and moderately susceptible to cephalothin and cephaloridine (MICs, 0.12 to 16 micrograms/ml). The addition of 1 microgram of potassium clavulanate, a beta-lactamase inhibitor, per ml resulted in a significant increase in the susceptibilities of these strains to penicillins but not to cephalosporins. Potassium clavulanate had no effect on non-beta-lactamase-producing strains. Enzyme production was constitutive since activity was not increased when cells were cultivated in the presence of benzylpenicillin. Enzyme activity was strongly inhibited by potassium clavulanate, sulbactam, and iodine; weakly inhibited by cloxacillin, imipenem, and moxalactam; but not inhibited by aztreonam, EDTA, or p-chloromercuribenzoate. By gel infiltration, the enzyme had an estimated molecular mass of 29 kDa. Isoelectric focusing of the partially purified enzyme gave a major beta-lactamase band at pH 5.50 and a minor band at pH 5.60. Plasmids were not detected in any of the 11 beta-lactamase-positive strains. This enzyme is considered to belong to class 2a of the Bush classification scheme.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourgault A. M., Rosenblatt J. E. Characterization of anaerobic gram-negative bacilli by using rapid slide tests for beta-lactamase production. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jun;9(6):654–656. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.6.654-656.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook I., Pazzaglia G., Coolbaugh J. C., Walker R. I. In-vivo protection of group A beta-haemolytic streptococci from penicillin by beta-lactamase-producing Bacteroides species. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Dec;12(6):599–606. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.6.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K. Classification of beta-lactamases: groups 1, 2a, 2b, and 2b'. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):264–270. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K. Classification of beta-lactamases: groups 2c, 2d, 2e, 3, and 4. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):271–276. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K., Freudenberger J. S., Sykes R. B. Interaction of azthreonam and related monobactams with beta-lactamases from gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):414–420. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K. Recent developments in beta-lactamase research and their implications for the future. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):681–690. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K., Singer S. B. Biochemical characteristics of extended broad spectrum beta-lactamases. Infection. 1989 Nov-Dec;17(6):429–433. doi: 10.1007/BF01645566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foweraker J. E., Hawkey P. M., Heritage J., Van Landuyt H. W. Novel beta-lactamase from Capnocytophaga sp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Aug;34(8):1501–1504. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.8.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraci J. E., Hermans P. E., Washington J. A., 2nd Eikenella corrodens endocarditis: report of cure in two cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1974 Dec;49(12):950–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E. J., Tarenzi L. A., Agyare E. O., Berger J. R. Prevalence of Eikenella corrodens in dental plaque. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):636–639. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.636-639.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackman A. S., Wilkins T. D. Influence of pencillinase production by strains of Bacteroides melaninogenicus and Bacteriodes oralis on pencillin therapy of an experimental mixed anaerobic infection in mice. Arch Oral Biol. 1976;21(6):385–389. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9969(76)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson F. L., Goodman Y. E., Bel F. R., Wong P. C., Whitehouse R. L. Taxonomic status of facultative and strictly anaerobic "corroding bacilli" that have been classified as Bacteroides corrodens. J Med Microbiol. 1971 May;4(2):171–184. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khairat O. Bacteroides corrodens isolated from bacteriaemias. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):29–40. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinder S. A., Holt S. C., Korman K. S. Penicillin resistance in the subgingival microbiota associated with adult periodontitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1127–1133. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1127-1133.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix J. M., Lamothe F., Malouin F. Role of Bacteroides bivius beta-lactamase in beta-lactam susceptibility. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Nov;26(5):694–698. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.5.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamothe F., Auger F., Lacroix J. M. Effect of clavulanic acid on the activities of ten beta-lactam agents against members of the Bacteroides fragilis group. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):662–665. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenski R. E., Hattingh S. E. Coexistence of two competitors on one resource and one inhibitor: a chemostat model based on bacteria and antibiotics. J Theor Biol. 1986 Sep 7;122(1):83–93. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(86)80226-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew A., Harris A. M., Marshall M. J., Ross G. W. The use of analytical isoelectric focusing for detection and identification of beta-lactamases. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):169–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami S., Yotsuji A., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Induction of beta-lactamase by various beta-lactam antibiotics in Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Sep;18(3):382–385. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.3.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musial C. E., Rosenblatt J. E. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of anaerobic bacteria isolated at the Mayo Clinic during 1982 through 1987: comparison with results from 1977 through 1981. Mayo Clin Proc. 1989 Apr;64(4):392–399. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)65727-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. G., Socransky S. S., Savitt E. D., Propas D. A., Crawford A. Studies of the microbiology of periodontosis. J Periodontol. 1976 Jul;47(7):373–379. doi: 10.1902/jop.1976.47.7.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez Trallero E., Garcia Arenzana J. M., Cilla Eguiluz G., Tovar Larrucea J. Beta-lactamase-producing Eikenella corrodens in an intraabdominal abscess. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):379–380. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Progulske A., Holt S. C. Studies on the growth of Eikenella corrodens strain 23834. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1987 Mar;2(1):2–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1987.tb00262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotger R., García-Valdés E., Trallero E. P. Characterization of a beta-lactamase-specifying plasmid isolated from Eikenella corrodens and its relationship to a commensal Neisseria plasmid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Sep;30(3):508–509. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.3.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rummens J. L., Gordts B., Van Landuyt H. W. In vitro susceptibility of Capnocytophaga species to 29 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):739–742. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Wong J., Wilkins T. D. Beta-Lactamase activity in strains of Bacteroides melaninogenicus and Bacteroides oralis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):142–146. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. C., Haffer C., Bratthall G. T., Visconti R. A., Socransky S. S. A study of the bacteria associated with advancing periodontitis in man. J Clin Periodontol. 1979 Oct;6(5):278–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1979.tb01931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Then R. L. Interaction of Ro 17-2301 (AMA-1080) with beta-lactamases. Chemotherapy. 1984;30(6):398–407. doi: 10.1159/000238300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunér K., Lindqvist L., Nord C. E. Characterization of a new beta-lactamase from Fusobacterium nucleatum by substrate profiles and chromatofocusing patterns. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jul;16(1):23–30. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunér K., Lindqvist L., Nord C. E. Purification and properties of a novel beta-lactamase from Fusobacterium nucleatum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jun;27(6):943–947. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.6.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdés M. V., Lobbins P. M., Slots J. Beta-lactamase producing bacteria in the human oral cavity. J Oral Pathol. 1982 Feb;11(1):58–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1982.tb00143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waley S. G. A spectrophotometric assay of beta-lactamase action on penicillins. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):789–790. doi: 10.1042/bj1390789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C. B., Pappas J. D., Tyler K. Z., Cohen S., Gordon J. M. Antibiotic susceptibilities of periodontal bacteria. In vitro susceptibilities to eight antimicrobial agents. J Periodontol. 1985 Nov;56(11 Suppl):67–74. doi: 10.1902/jop.1985.56.11s.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C. B., Tyler K. Z., Low S. B., King C. J. Penicillin-degrading enzymes in sites associated with adult periodontitis. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1987 Sep;2(3):129–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1987.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Bedford K. A. In vitro study of clavulanic acid in combination with penicillin, amoxycillin, and carbenicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):389–393. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



