Abstract
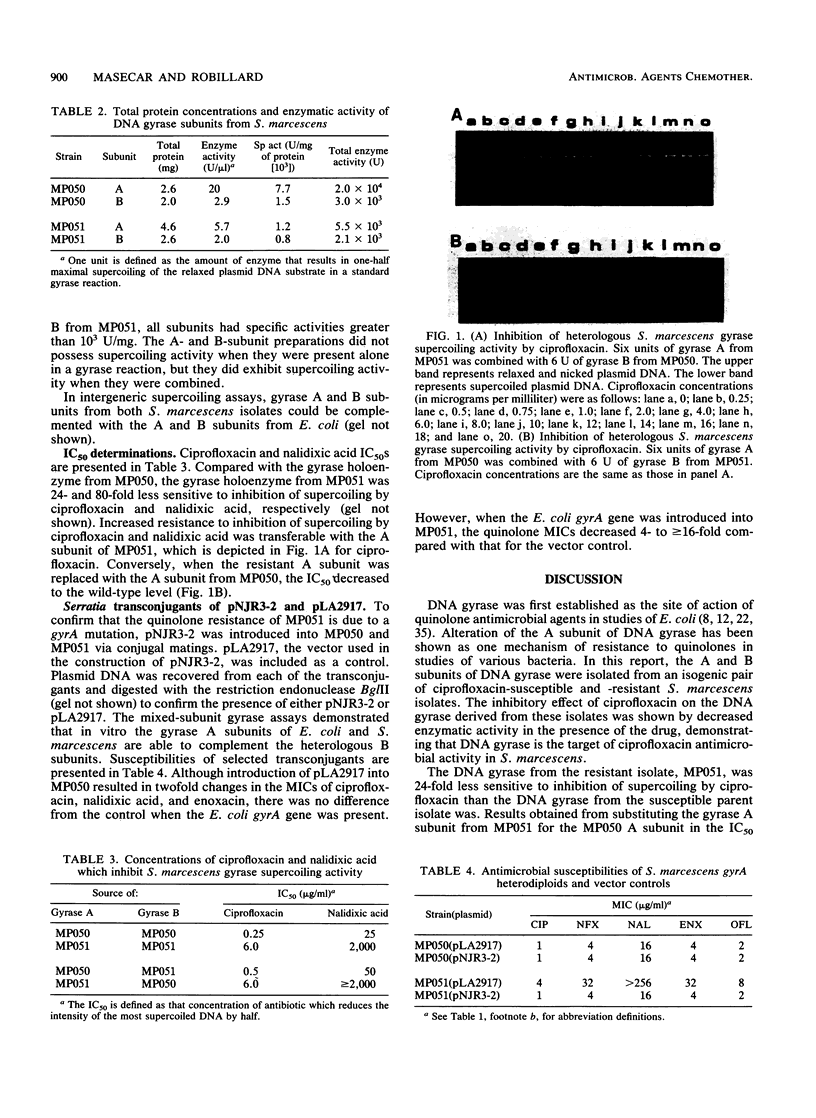
Spontaneous quinolone-resistant mutants of MP050, a quinolone-susceptible clinical strain of Serratia marcescens, were isolated on nutrient agar containing 0.5 microgram of ciprofloxacin per ml. One mutant, designated MP051, was selected for further study. Quinolone MICs for MP051 were 4- to 16-fold higher than those for MP050; nonquinolone MICs were unchanged. The DNA gyrase isolated from MP051 was 24-fold less sensitive to inhibition of supercoiling by ciprofloxacin than the DNA gyrase isolated from MP050 was. Inhibition studies on reconstituted combinations of heterologous gyrase subunits showed that the decreased inhibition was dependent on the A subunit of DNA gyrase from MP051. Further evidence that this decreased inhibition was due to a gyrA mutation was provided by analysis of Escherichia coli gyrA gene expression in S. marcescens heterodiploids containing pNJR3-2, a broad-host-range gyrA gene probe. Quinolone susceptibilities of MP051 heterodiploids containing the wild-type E. coli gyrA gene decreased to those of MP050, while quinolone susceptibilities of MP050 containing the same plasmid were unchanged. These results indicate that spontaneous quinolone resistance in MP051 was due to a mutation in gyrA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen L. N., Hanson R. S. Construction of broad-host-range cosmid cloning vectors: identification of genes necessary for growth of Methylobacterium organophilum on methanol. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):955–962. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.955-962.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyama H., Sato K., Fujii T., Fujimaki K., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification of Citrobacter freundii DNA gyrase and inhibition by quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):104–109. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang P., Gutmann L., Quentin C., Williamson R., Collatz E. Some properties of Serratia marcescens, Salmonella paratyphi A, and Enterobacter cloacae with non-enzyme-dependent multiple resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics, aminoglycosides, and quinolones. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):899–904. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin (Bay o 9867). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Oct;24(4):568–574. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.4.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimaki K., Fujii T., Aoyama H., Sato K., Inoue Y., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Quinolone resistance in clinical isolates of Serratia marcescens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):785–787. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Nash H. A. DNA gyrase: an enzyme that introduces superhelical turns into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein F. W., Gutmann L., Williamson R., Collatz E., Acar J. F. In vivo and in vitro emergence of simultaneous resistance to both beta-lactam and aminoglycoside antibiotics in a strain of Serratia marcescens. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 May-Jun;134A(3):329–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hane M. W., Wood T. H. Escherichia coli K-12 mutants resistant to nalidixic acid: genetic mapping and dominance studies. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):238–241. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.238-241.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins N. P., Peebles C. L., Sugino A., Cozzarelli N. R. Purification of subunits of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase and reconstitution of enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1773–1777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Aoyama H., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Isolation and characterization of norfloxacin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):248–253. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Mutations producing resistance to norfloxacin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):582–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Souza K. S., Tung C., McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Genetic and biochemical characterization of norfloxacin resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):639–644. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue Y., Sato K., Fujii T., Hirai K., Inoue M., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Some properties of subunits of DNA gyrase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and its nalidixic acid-resistant mutant. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2322–2325. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2322-2325.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanis J. A., Urwin G. H., Gray R. E., Beneton M. N., McCloskey E. V., Hamdy N. A., Murray S. A. Effects of intravenous etidronate disodium on skeletal and calcium metabolism. Am J Med. 1987 Feb 23;82(2A):55–70. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90488-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucain C., Regamey P., Bellido F., Pechére J. C. Resistance emerging after pefloxacin therapy of experimental Enterobacter cloacae peritonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jun;33(6):937–943. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.6.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masecar B. L., Celesk R. A., Robillard N. J. Analysis of acquired ciprofloxacin resistance in a clinical strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):281–286. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Mizuuchi M., O'Dea M. H., Gellert M. Cloning and simplified purification of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase A and B proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9199–9201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Gellert M. DNA gyrase: subunit structure and ATPase activity of the purified enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5960–5963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G., Malamy M. H. Comparisons of F factors and R factors: existence of independent regulation groups in F factors. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):81–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.81-88.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Nakamura M., Kojima T., Yoshida H. gyrA and gyrB mutations in quinolone-resistant strains of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Feb;33(2):254–255. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.2.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard N. J. Broad-host-range gyrase A gene probe. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Oct;34(10):1889–1894. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.10.1889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard N. J., Scarpa A. L. Genetic and physiological characterization of ciprofloxacin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):535–539. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Watanakunakorn C. Emergence of resistance to beta-lactams, aminoglycosides, and quinolones during combination therapy for infection due to Serratia marcescens. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):617–619. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inoue Y., Fujii T., Aoyama H., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of DNA gyrase from a fluoroquinolone-resistant strain of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):777–780. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scurlock T. R., Miller R. V. PaeExo IX: a unique deoxyribonuclease from Pseudomonas aeruginosa active in the presence of EDTA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):167–177. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudenbauer W. L., Orr E. DNA gyrase: affinity chromatography on novobiocin-Sepharose and catalytic properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3589–3603. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Higgins N. P., Cozzarelli N. R. DNA gyrase subunit stoichiometry and the covalent attachment of subunit A to DNA during DNA cleavage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3865–3874. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Peebles C. L., Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid: purification of Escherichia coli nalA gene product and its relationship to DNA gyrase and a novel nicking-closing enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H. Incomplete cross-resistance of nalidixic and pipemidic acid-resistant variants of Serratia marcescens against ciprofloxacin, enoxacin, and norfloxacin. Chemotherapy. 1985;31(1):34–39. doi: 10.1159/000238311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Spohr M., Bauer D. Plasmid-independent resistance of 'gray' colony variants of a strain of Serratia marcescens resistant to amikacin, cefotaxime and lamoxactam. Chemotherapy. 1983;29(4):265–274. doi: 10.1159/000238208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Kotera Y., Yosue K., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro emergence of quinolone-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli, Enterobacter cloacae, and Serratia marcescens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):173–175. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisser J., Wiedemann B. Elimination of plasmids by new 4-quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):700–702. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi J., Yoshida H., Yamayoshi M., Nakamura S. Nalidixic acid-resistant mutations of the gyrB gene of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Sep;204(3):367–373. doi: 10.1007/BF00331012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Nakamura M., Bogaki M., Nakamura S. Proportion of DNA gyrase mutants among quinolone-resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1273–1275. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Berlin O. G., Inderlied C. B. Activity of ciprofloxacin and other fluorinated quinolones against mycobacteria. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):23–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




