Abstract
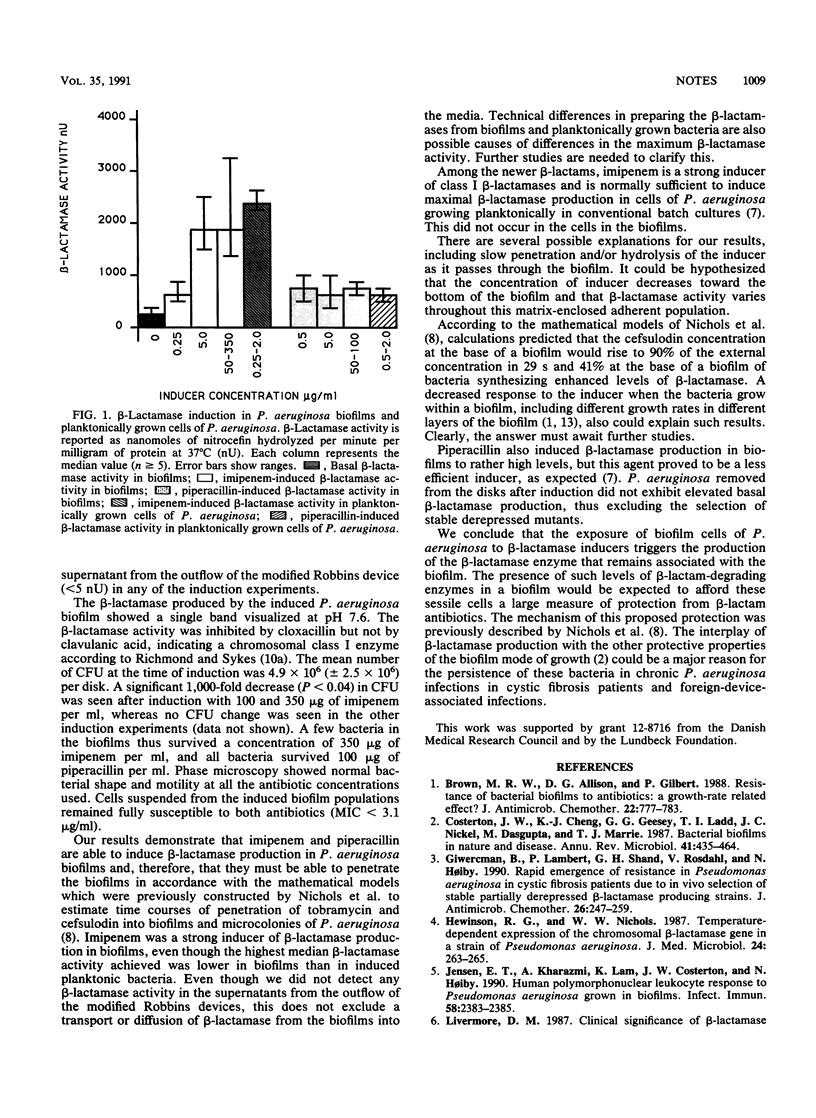
Imipenem induced high levels of beta-lactamase production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Piperacillin also induced beta-lactamase production in these biofilms but to a lesser degree. The combination of beta-lactamase production with other protective properties of the biofilm mode of growth could be a major reason for the persistence of this sessile bacterium in chronic infections.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown M. R., Allison D. G., Gilbert P. Resistance of bacterial biofilms to antibiotics: a growth-rate related effect? J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Dec;22(6):777–780. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.6.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Cheng K. J., Geesey G. G., Ladd T. I., Nickel J. C., Dasgupta M., Marrie T. J. Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:435–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giwercman B., Lambert P. A., Rosdahl V. T., Shand G. H., Høiby N. Rapid emergence of resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients due to in-vivo selection of stable partially derepressed beta-lactamase producing strains. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Aug;26(2):247–259. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewinson R. G., Nichols W. W. Temperature-dependent expression of the chromosomal beta-lactamase gene in a strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Nov;24(3):263–265. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-3-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. T., Kharazmi A., Lam K., Costerton J. W., Høiby N. Human polymorphonuclear leukocyte response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown in biofilms. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2383–2385. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2383-2385.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M., Yang Y. J. Beta-lactamase lability and inducer power of newer beta-lactam antibiotics in relation to their activity against beta-lactamase-inducibility mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. W., Evans M. J., Slack M. P., Walmsley H. L. The penetration of antibiotics into aggregates of mucoid and non-mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 May;135(5):1291–1303. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-5-1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel J. C., Ruseska I., Wright J. B., Costerton J. W. Tobramycin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells growing as a biofilm on urinary catheter material. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):619–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C. Chromosomal cephalosporinases responsible for multiple resistance to newer beta-lactam antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:573–593. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr, Moland E. S. Characterization of beta-lactamases in situ on polyacrylamide gels. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):951–952. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Then R. L. Ability of newer beta-lactam antibiotics to induce beta-lactamase production in Enterobacter cloacae. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;6(4):451–455. doi: 10.1007/BF02013109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


