Abstract
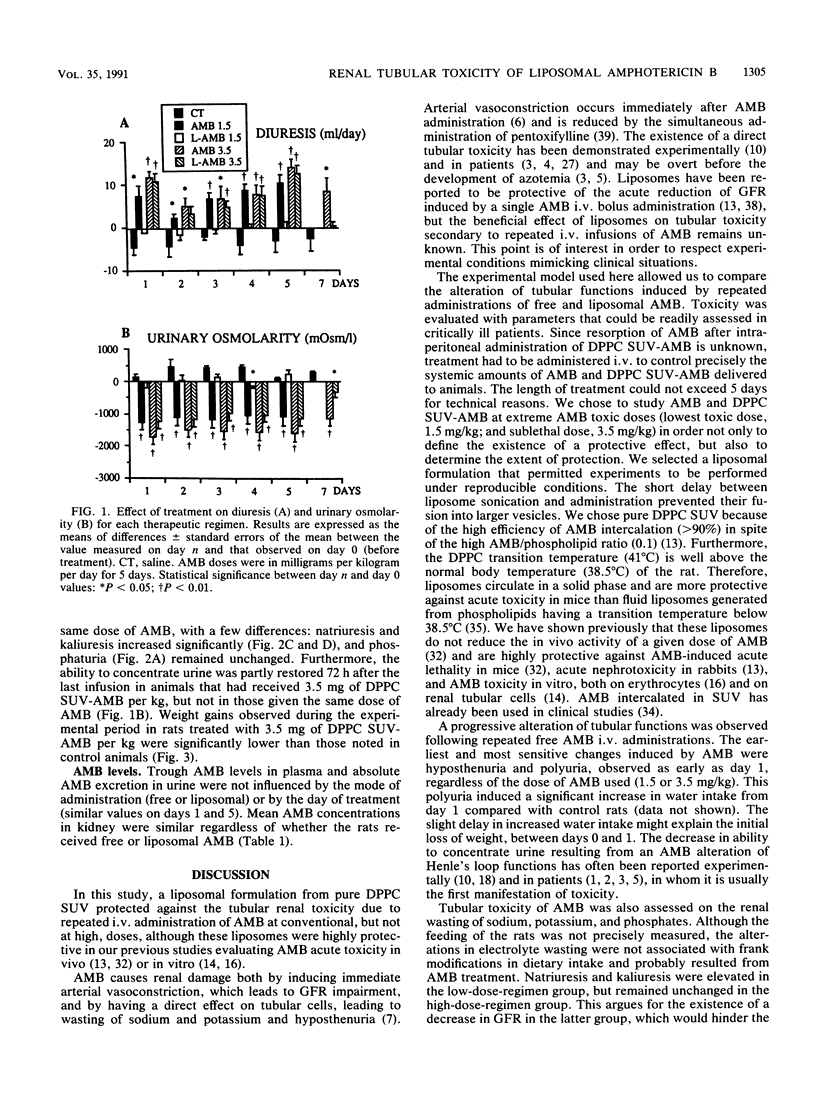
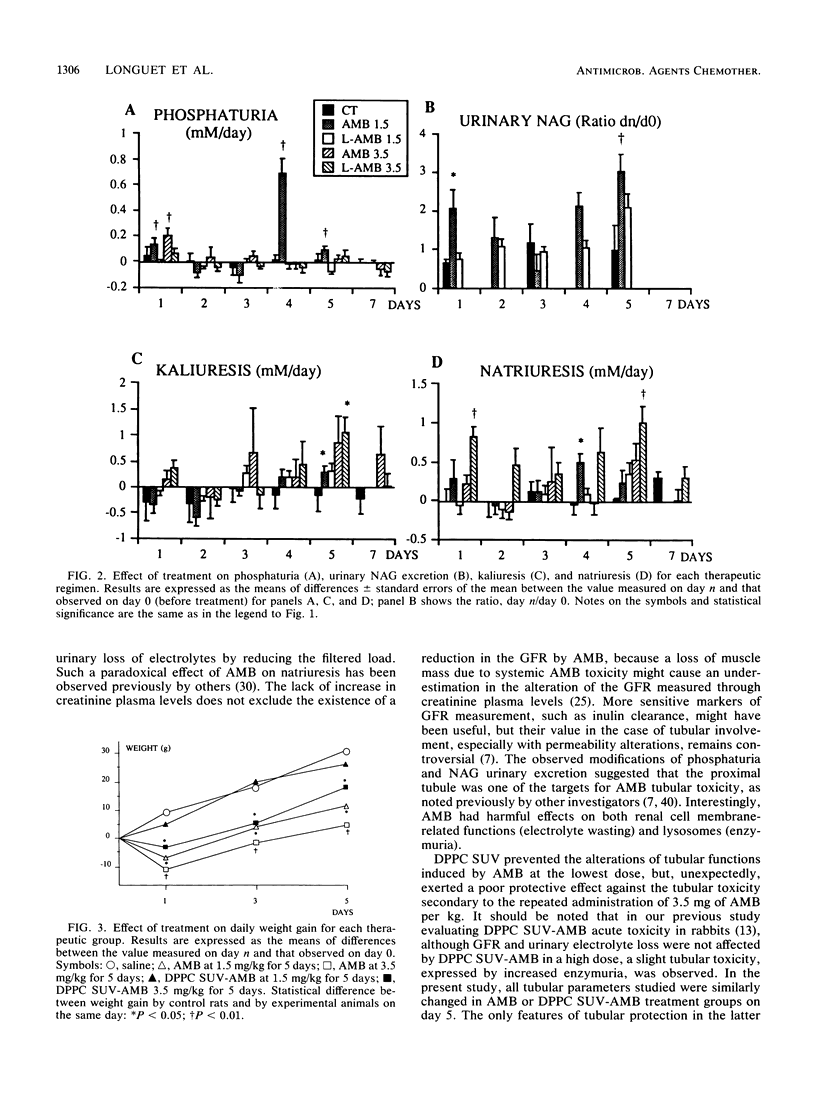
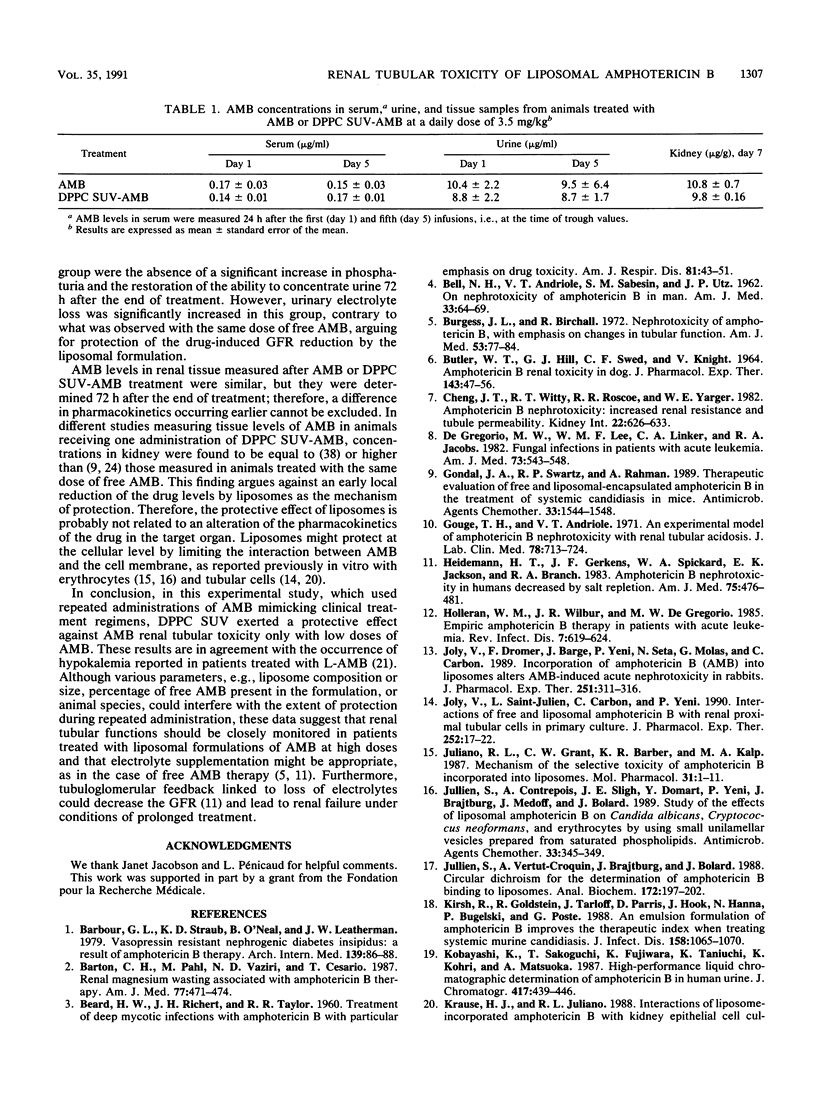
Amphotericin B (AMB), either alone or incorporated into small unilamellar vesicles of pure dipalmitoylphosphatidyl choline (DPPC SUV-AMB), was administered intravenously to male Sprague-Dawley rats once daily for 5 days. Either 1.5 or 3.5 mg of AMB or DPPC SUV-AMB per kg was given, since these concentrations corresponded, respectively, to the lowest nephrotoxic dose and the sublethal dose of AMB in our model. Tubular functions were evaluated daily, and AMB concentrations in plasma, urine, and tissues were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography. AMB at both doses induced tubular toxicity, hyposthenuria being the earliest symptom. DPPC SUV-AMB at 1.5 mg/kg/day was atoxic, but the tubular alterations induced by 3.5 mg of DPPC SUV-AMB per kg were similar to those observed with 3.5 mg of AMB per kg, except that the ability to concentrate urine was partly restored 72 h after the last infusion. Incorporating AMB into DPPC SUV did not influence the pharmacokinetics of the drug. Using this lipidic AMB formulation, we thus observed a beneficial effect toward limiting the renal tubular toxicity of repeated low doses of AMB but, unexpectedly, not that of high doses. These results indicate that tubular renal functions and electrolyte serum values should be closely monitored in patients treated with AMB liposomal formulations, especially high-dose regimens.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEARD H. W., RICHERT J. H., TAYLOR R. R. The treatment of deep mycotic infections with amphotericin B1 with particular emphasis on drug toxicity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1960 Jan;81:43–51. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1960.81.1P1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL N. H., ANDRIOLE V. T., SABESIN S. M., UTZ J. P. On the nephrotoxicity of amphotericin B in man. Am J Med. 1962 Jul;33:64–69. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(62)90277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER W. T., HILL G. J., 2nd, SZWED C. F., KNIGHT V. AMPHOTERICIN B RENAL TOXICITY IN THE DOG. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Jan;143:47–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour G. L., Straub K. D., O'Neal B. L., Leatherman J. W. Vasopressin-resistant nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. A result of amphotericin B therapy. Arch Intern Med. 1979 Jan;139(1):86–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton C. H., Pahl M., Vaziri N. D., Cesario T. Renal magnesium wasting associated with amphotericin B therapy. Am J Med. 1984 Sep;77(3):471–474. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess J. L., Birchall R. Nephrotoxicity of amphotericin B, with emphasis on changes in tubular function. Am J Med. 1972 Jul;53(1):77–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J. T., Witty R. T., Robinson R. R., Yarger W. E. Amphotericin B nephrotoxicity: increased renal resistance and tubule permeability. Kidney Int. 1982 Dec;22(6):626–633. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGregorio M. W., Lee W. M., Linker C. A., Jacobs R. A., Ries C. A. Fungal infections in patients with acute leukemia. Am J Med. 1982 Oct;73(4):543–548. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90334-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gondal J. A., Swartz R. P., Rahman A. Therapeutic evaluation of free and liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B in the treatment of systemic candidiasis in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1544–1548. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouge T. H., Andriole V. T. An experimental model of amphotericin B nephrotoxicity with renal tubular acidosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Nov;78(5):713–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann H. T., Gerkens J. F., Spickard W. A., Jackson E. K., Branch R. A. Amphotericin B nephrotoxicity in humans decreased by salt repletion. Am J Med. 1983 Sep;75(3):476–481. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90353-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holleran W. M., Wilbur J. R., DeGregorio M. W. Empiric amphotericin B therapy in patients with acute leukemia. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Sep-Oct;7(5):619–624. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.5.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly V., Dromer F., Barge J., Yeni P., Seta N., Molas G., Carbon C. Incorporation of amphotericin B (AMB) into liposomes alters AMB-induced acute nephrotoxicity in rabbits. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Oct;251(1):311–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly V., Saint-Julien L., Carbon C., Yeni P. Interactions of free and liposomal amphotericin B with renal proximal tubular cells in primary culture. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Oct;255(1):17–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano R. L., Grant C. W., Barber K. R., Kalp M. A. Mechanism of the selective toxicity of amphotericin B incorporated into liposomes. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;31(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jullien S., Contrepois A., Sligh J. E., Domart Y., Yeni P., Brajtburg J., Medoff G., Bolard J. Study of the effects of liposomal amphotericin B on Candida albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans, and erythrocytes by using small unilamellar vesicles prepared from saturated phospholipids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):345–349. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jullien S., Vertut-Croquin A., Brajtburg J., Bolard J. Circular dichroism for the determination of amphotericin B binding to liposomes. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jul;172(1):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90432-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsh R., Goldstein R., Tarloff J., Parris D., Hook J., Hanna N., Bugelski P., Poste G. An emulsion formulation of amphotericin B improves the therapeutic index when treating systemic murine candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):1065–1070. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Sakoguchi T., Fujiwara K., Taniuchi K., Kohri K., Matsuoka A. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of amphotericin B in human urine. J Chromatogr. 1987 Jul 3;417(2):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(87)80142-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Bodey G. P., Frankel L. S., Mehta K. Treatment of hepatosplenic candidiasis with liposomal-amphotericin B. J Clin Oncol. 1987 Feb;5(2):310–317. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.2.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Fainstein V., Hopfer R., Mehta K., Sullivan M. P., Keating M., Rosenblum M. G., Mehta R., Luna M., Hersh E. M. Liposomal amphotericin B for the treatment of systemic fungal infections in patients with cancer: a preliminary study. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):704–710. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Mehta R., Hopfer R. L., Mills K., Kasi L., Mehta K., Fainstein V., Luna M., Hersh E. M., Juliano R. Treatment and prophylaxis of disseminated infection due to Candida albicans in mice with liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):939–945. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Rosenblum M. G., Mehta R. Altered tissue distribution of amphotericin B by liposomal encapsulation: comparison of normal mice to mice infected with Candida albicans. Cancer Drug Deliv. 1984 Summer;1(3):199–205. doi: 10.1089/cdd.1984.1.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massa T., Sinha D. P., Frantz J. D., Filipek M. E., Weglein R. C., Steinberg S. A., McGrath J. T., Murphy B. F., Szot R. J., Black H. E. Subchronic toxicity studies of N-D-ornithyl amphotericin B methyl ester in dogs and rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1985 Aug;5(4):737–753. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(85)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew J. W., Fiore C., Murray T., Barza M. An internally-standardized assay for amphotericin B in tissues and plasma. J Chromatogr. 1983 May 13;274:271–279. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84430-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCurdy D. K., Frederic M., Elkinton J. R. Renal tubular acidosis due to amphotericin B. N Engl J Med. 1968 Jan 18;278(3):124–130. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196801182780302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medoff G., Brajtburg J., Kobayashi G. S., Bolard J. Antifungal agents useful in therapy of systemic fungal infections. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:303–330. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaidis S., Rowland N., Meile M. J., Marfaing-Jallat P., Pesez A. A flexible technique for long term infusions in unrestrained rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1974 Jan-Feb;2(1):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(74)90147-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi A., Ohnishi T., Stevenhead W., Robinson R. D., Glick A., O'Day D. M., Sabra R., Jackson E. K., Branch R. A. Sodium status influences chronic amphotericin B nephrotoxicity in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1222–1227. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUGH D., LEABACK D. H., WALKER P. G. Studies on glucosaminidase; N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase in rat kidney. Biochem J. 1957 Mar;65(3):464–469. doi: 10.1042/bj0650464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R. M., Ackerman G. L. Renal tubular acidosis due to amphotericin B nephrotoxicity. Arch Intern Med. 1971 Feb;127(2):241–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisarik L., Joly V., Jullien S., Carbon C., Yeni P. Reduction of free amphotericin B acute toxicity in mice after intravenous administration of empty liposomes. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):1042–1044. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculier J. P., Coune A., Meunier F., Brassinne C., Laduron C., Hollaert C., Collette N., Heymans C., Klastersky J. Pilot study of amphotericin B entrapped in sonicated liposomes in cancer patients with fungal infections. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1988 Mar;24(3):527–538. doi: 10.1016/s0277-5379(98)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka F. C., Jr, Milholland D., Barza M. Effect of lipid composition and liposome size on toxicity and in vitro fungicidal activity of liposome-intercalated amphotericin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Mar;31(3):421–429. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.3.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. L., Williams D. M., Craven P. C., Graybill J. R., Drutz D. J., Magee W. E. Amphotericin B in liposomes: a novel therapy for histoplasmosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 May;125(5):610–611. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.5.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay C., Barza M., Fiore C., Szoka F. Efficacy of liposome-intercalated amphotericin B in the treatment of systemic candidiasis in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):170–173. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERTLAKE P. T., BUTLER W. T., HILL G. J., 2nd, UTZ J. P. NEPHROTOXIC TUBULAR DAMAGE AND CALCIUM DEPOSITION FOLLOWING AMPHOTERICIN B THERAPY. Am J Pathol. 1963 Sep;43:449–457. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasan K. M., Vadiei K., Lopez-Berestein G., Luke D. R. Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, and toxicity of free and liposomal amphotericin B in diabetic rats. J Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;161(3):562–566. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.3.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasan K. M., Vadiei K., Lopez-Berestein G., Verani R. R., Luke D. R. Pentoxifylline in amphotericin B toxicity rat model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):241–244. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M., Anthony F. H., Tillack T. W., Thompson T. E. Fusion of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles at 4 degrees C. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):4126–4132. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S. Nosocomial infections in the immunocompromised adult. Am J Med. 1981 Feb;70(2):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90779-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuger A., Louie E., Holzman R. S., Simberkoff M. S., Rahal J. J. Cryptococcal disease in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Diagnostic features and outcome of treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Feb;104(2):234–240. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-104-2-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



