Abstract
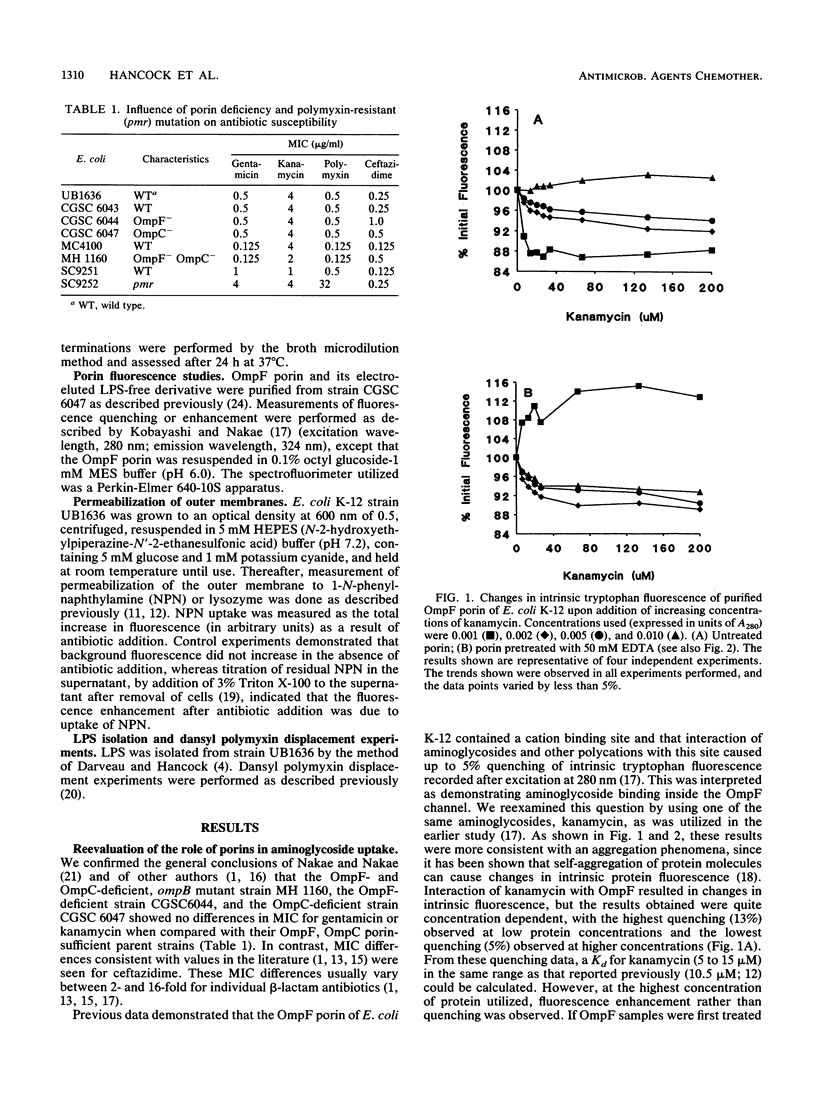
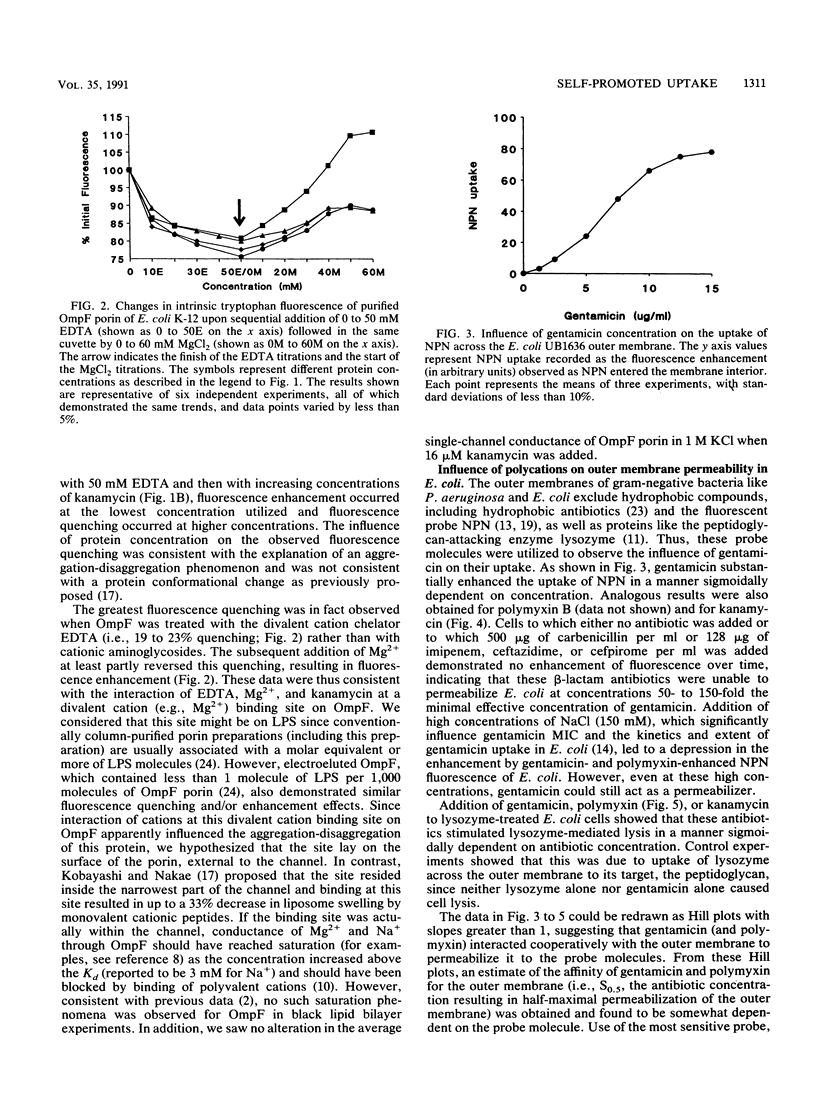
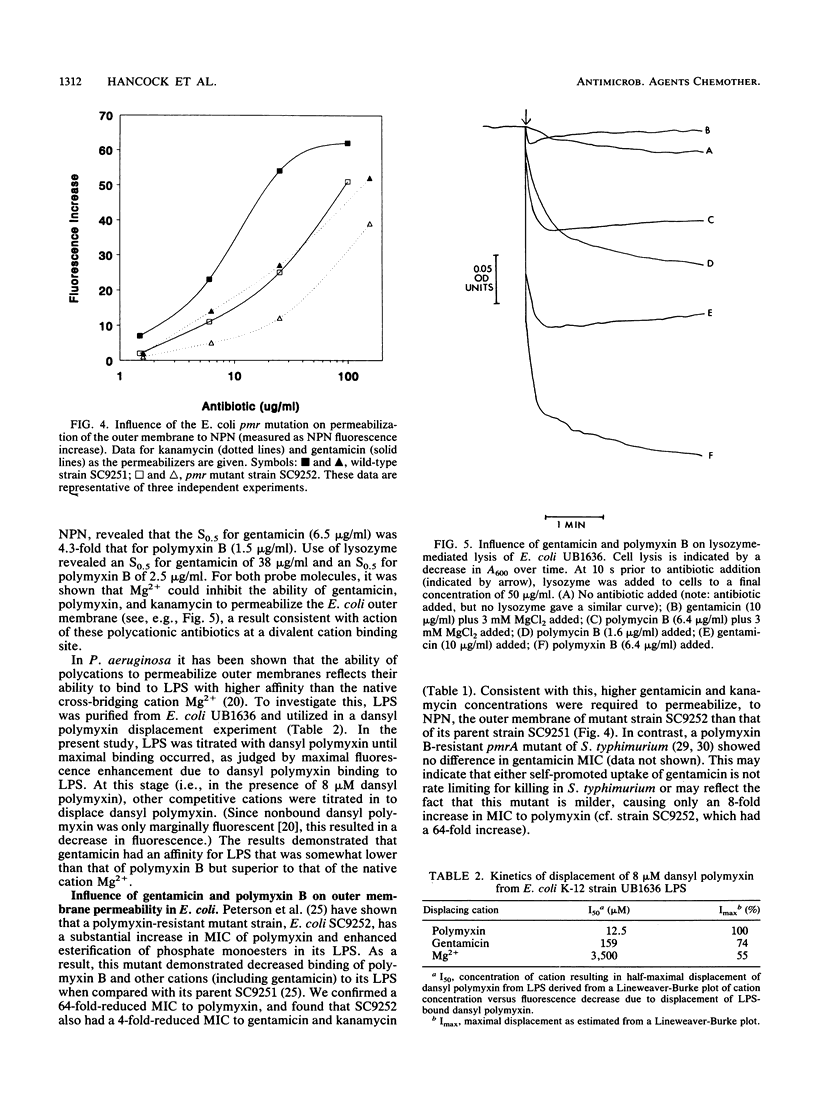
The mechanism of uptake of aminoglycosides across the outer membrane of Escherichia coli was reevaluated. Porin-deficient mutants showed no alteration in gentamicin or kanamycin susceptibility. Furthermore, the influence of kanamycin on intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence of porin OmpF (Y. Kobayashi, and T. Nakae, Eur. J. Biochem. 151:231-236, 1985) was shown to be strongly influenced by protein concentration and EDTA. This led to the hypothesis that aminoglycoside-mediated increases and decreases in intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence were due to aggregation-disaggregation of OmpF mediated by interaction at a divalent cation binding site on OmpF. Gentamicin, kanamycin, and polymyxin B increased E. coli outer membrane permeability to the hydrophobic fluorescent compound 1-N-phenyl-naphthylamine (NPN) and the peptidoglycan-degrading enzyme lysozyme. Addition of Mg2+ blocked these permeabilizing activities. Furthermore, gentamicin and polymyxin B bound to Mg(2+)-binding sites on E. coli lipopolysaccharide, as determined in dansyl polymyxin displacement experiments. A polymyxin-resistant, lipopolysaccharide-altered pmr mutant of E. coli had a fourfold-lower MIC of gentamicin and kanamycin and was more poorly permeabilized to 1-N-phenylnaphthylamine than was its parent strain. These data were consistent with uptake of aminoglycosides across the E. coli outer membrane by the self-promoted uptake mechanism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakken J. S., Sanders C. C., Thomson K. S. Selective ceftazidime resistance in Escherichia coli: association with changes in outer membrane protein. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1220–1225. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Schmid A., Hancock R. E. Ion selectivity of gram-negative bacterial porins. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):722–727. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.722-727.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung L., Kaloyanides G., McDaniel R., McLaughlin A., McLaughlin S. Interaction of gentamicin and spermine with bilayer membranes containing negatively charged phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 15;24(2):442–452. doi: 10.1021/bi00323a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Hancock R. E. Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):831–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.831-838.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulds J., Chai T. Isolation and characterization of isogenic E. coli strains with alterations in the level of one or more major outer membrane proteins. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Mar;25(3):423–427. doi: 10.1139/m79-065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Billot-Klein D., Williamson R., Goldstein F. W., Mounier J., Acar J. F., Collatz E. Mutation of Salmonella paratyphi A conferring cross-resistance to several groups of antibiotics by decreased permeability and loss of invasiveness. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Feb;32(2):195–201. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.2.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. Aminoglycoside uptake and mode of action--with special reference to streptomycin and gentamicin. I. Antagonists and mutants. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Oct;8(4):249–276. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.4.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Bell A. Antibiotic uptake into gram-negative bacteria. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;7(6):713–720. doi: 10.1007/BF01975036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Benz R. Demonstration and chemical modification of a specific phosphate binding site in the phosphate-starvation-inducible outer membrane porin protein P of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 11;860(3):699–707. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Raffle V. J., Nicas T. I. Involvement of the outer membrane in gentamicin and streptomycin uptake and killing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):777–785. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. Role of porins in outer membrane permeability. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):929–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.929-933.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Wong P. G. Compounds which increase the permeability of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):48–52. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder K. J., Nikaido H., Matsuhashi M. Mutants of Escherichia coli that are resistant to certain beta-lactam compounds lack the ompF porin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Oct;20(4):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.4.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller A. H., Spector R., Aalyson M. Effect of sodium chloride on gentamicin accumulation by Escherichia coli: correlation with bacterial growth and viability. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1980 Jun;33(6):604–613. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.33.604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Nakae T. The mechanism of ion selectivity of OmpF-porin pores of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):231–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu Y., Murakami K., Nishikawa T. Penetration of moxalactam into its target proteins in Escherichia coli K-12: comparison of a highly moxalactam resistant mutant with its parent strain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Nov;20(5):613–619. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.5.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh B., Grant C., Hancock R. E. Use of the fluorescent probe 1-N-phenylnaphthylamine to study the interactions of aminoglycoside antibiotics with the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Oct;26(4):546–551. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.4.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. A., Bates N. C., Hancock R. E. Interaction of polycationic antibiotics with Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide and lipid A studied by using dansyl-polymyxin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):496–500. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae R., Nakae T. Diffusion of aminoglycoside antibiotics across the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):554–559. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Hancock R. E. Outer membrane protein H1 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: involvement in adaptive and mutational resistance to ethylenediaminetetraacetate, polymyxin B, and gentamicin. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):872–878. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.872-878.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parr T. R., Jr, Poole K., Crockford G. W., Hancock R. E. Lipopolysaccharide-free Escherichia coli OmpF and Pseudomonas aeruginosa protein P porins are functionally active in lipid bilayer membranes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):523–526. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.523-526.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., Fesik S. W., McGroarty E. J. Decreased binding of antibiotics to lipopolysaccharides from polymyxin-resistant strains of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):230–237. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera M., Hancock R. E., Sawyer J. G., Haug A., McGroarty E. J. Enhanced binding of polycationic antibiotics to lipopolysaccharide from an aminoglycoside-supersusceptible, tolA mutant strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):649–655. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr, Goering R. V., Werner V. Selection of multiple antibiotic resistance by quinolones, beta-lactams, and aminoglycosides with special reference to cross-resistance between unrelated drug classes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):797–801. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawai T., Hiruma R., Kawana N., Kaneko M., Taniyasu F., Inami A. Outer membrane permeation of beta-lactam antibiotics in Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, and Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):585–592. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Outer membrane permeability barrier disruption by polymyxin in polymyxin-susceptible and -resistant Salmonella typhimurium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):578–583. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T., Sarvas M. Decreased binding of polymyxin by polymyxin-resistant mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):664–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.664-667.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S. C., McCashion R. N., Lynch W. H. Multiple low-level antibiotic resistance in Aeromonas salmonicida. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):992–996. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Nikaido H. Diffusion of beta-lactam antibiotics through the porin channels of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):84–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


