Abstract
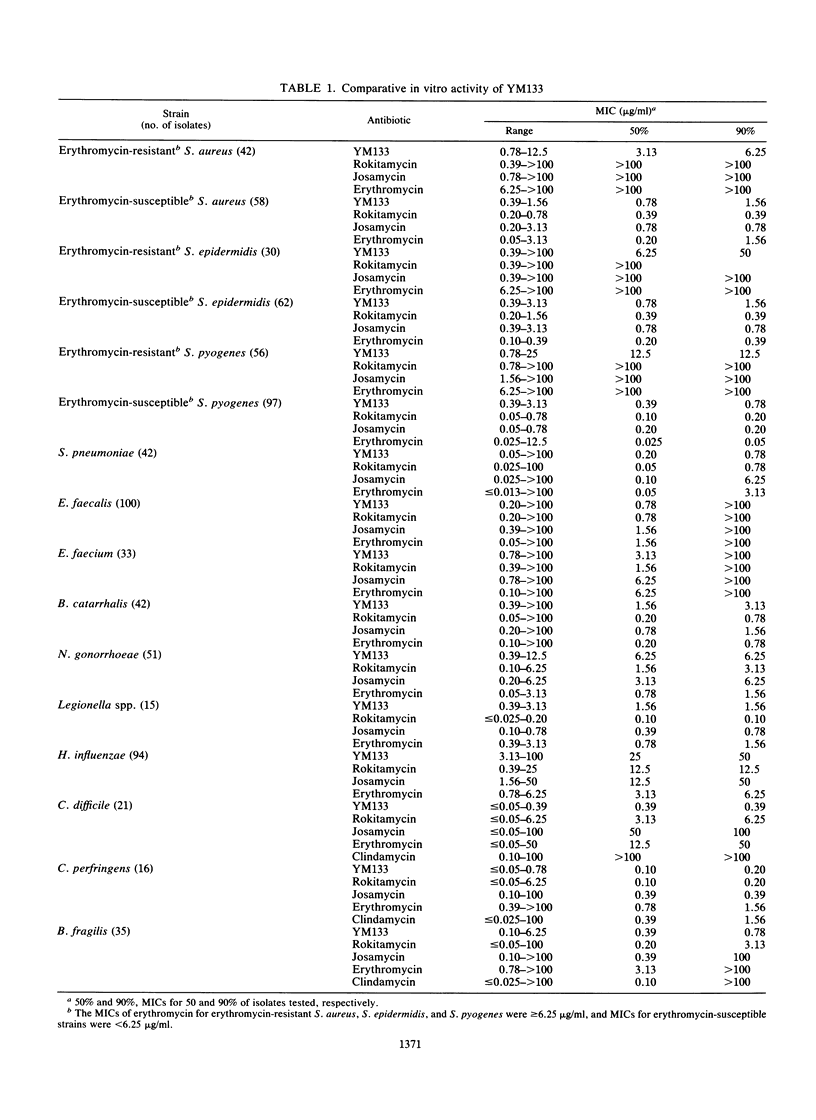
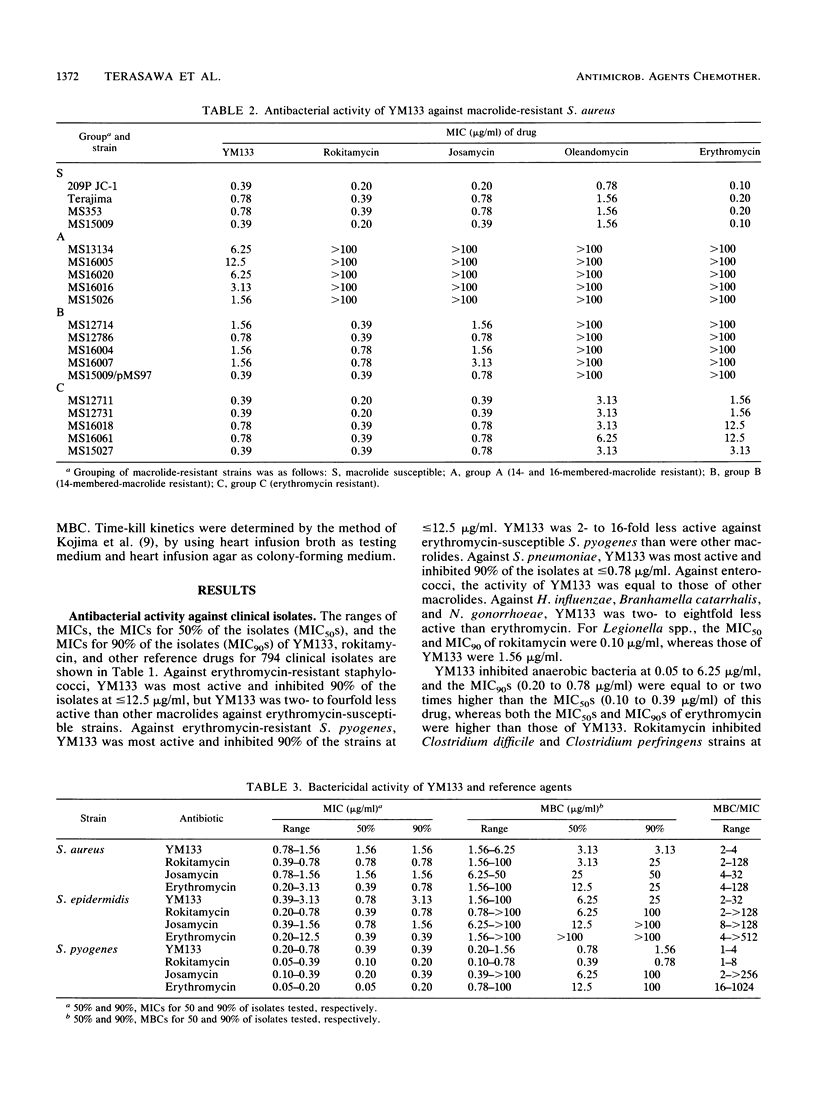
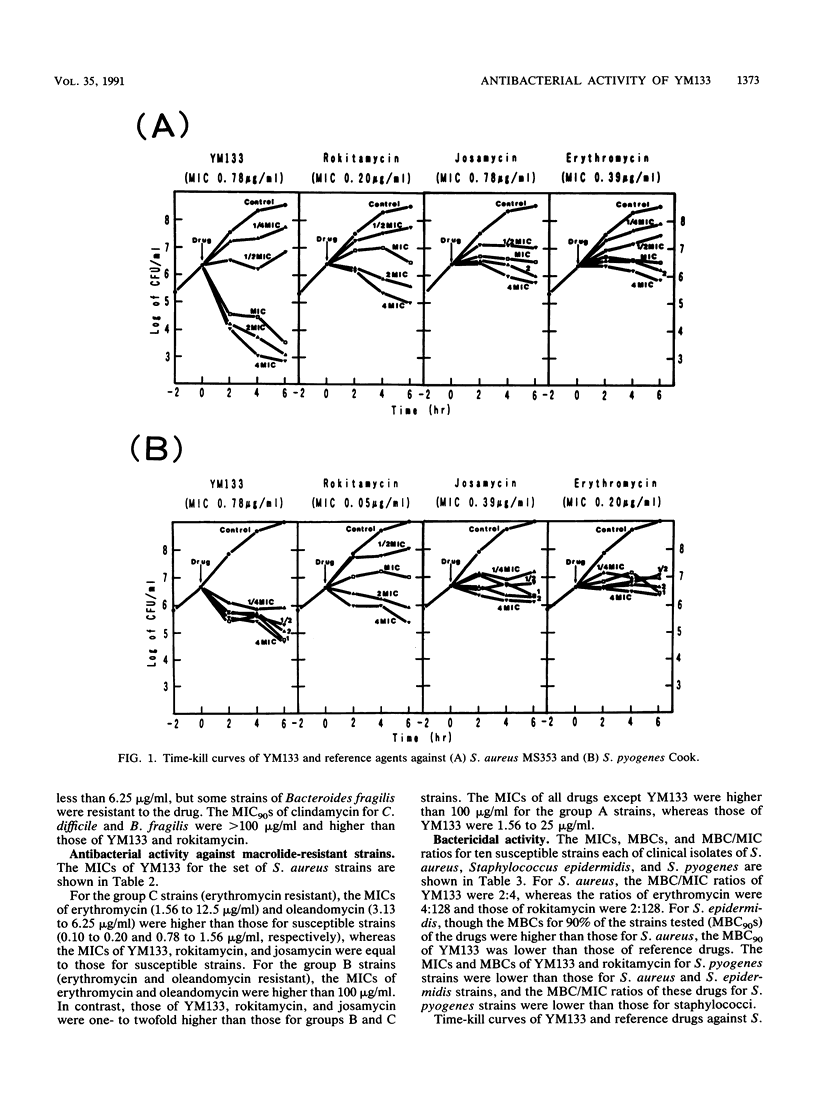
YM133, the 4"-O-(4-methoxyphenyl)acetyltylosin, is a new macrolide. The in vitro activity of YM133 was compared with those of erythromycin, josamycin, and rokitamycin by an agar dilution method. YM133 inhibited 90% of the tested isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Legionella spp., and anaerobic bacteria at less than or equal to 1.56 micrograms/ml. The drug inhibited 90% of erythromycin-resistant staphylococci and Streptococcus pyogenes at less than or equal to 50 micrograms/ml. YM133 showed activity against erythromycin-, josamycin-, and rokitamycin-resistant (MIC greater than or equal to 100 micrograms/ml) strains of staphylococci, streptococci, Bacteroides spp., and Clostridium spp. Enterococci were less susceptible to other YM133-like macrolides. Unlike other macrolides, YM133 showed killing activity, and the MBC/MIC ratios of YM133 for several strains were 1:32, whereas those of erythromycin were 4:1,024. In a time-kill curve study, the reduction of viable cells started within 2 h after the addition of YM133.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chin N. X., Neu N. M., Labthavikul P., Saha G., Neu H. C. Activity of A-56268 compared with that of erythromycin and other oral agents against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Mar;31(3):463–466. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.3.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes P. B., Bailer R., Swanson R., Hanson C. W., McDonald E., Ramer N., Hardy D., Shipkowitz N., Bower R. R., Gade E. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of A-56268 (TE-031), a new macrolide. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):865–873. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy D. J., Hensey D. M., Beyer J. M., Vojtko C., McDonald E. J., Fernandes P. B. Comparative in vitro activities of new 14-, 15-, and 16-membered macrolides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1710–1719. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirst H. A., Sides G. D. New directions for macrolide antibiotics: pharmacokinetics and clinical efficacy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1419–1422. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirst H. A., Sides G. D. New directions for macrolide antibiotics: structural modifications and in vitro activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1413–1418. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyoshima K., Sakamoto M., Ishikura T., Fukagawa Y., Yoshioka T., Naganawa H., Sawa T., Takeuchi T. Application of dibutyltin oxide method to regioselective acylation and alkylation of tylosin at C-4''. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1989 Apr;37(4):861–865. doi: 10.1248/cpb.37.861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima T., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro activity of AT-4140 against clinical bacterial isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1980–1988. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto R., Nomura H., Tsuchiya M., Tsunekawa H., Fukumoto T., Inui T., Sawa T., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. The activity of 4''-acylated tylosin derivatives against macrolide-resistant gram-positive bacteria. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1979 May;32(5):542–544. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.32.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Steigbigel R. T., Davis H. T., Chapman S. W. Method of reliable determination of minimal lethal antibiotic concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):699–708. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., Sawa T., Naganawa H., Hamada M., Umezawa H., Yoshioka T., Kiyoshima K., Iguchi H., Sakamoto M., Shimauchi Y. 4''-O-(4-methoxyphenyl)-acetyltylosin, a new macrolide derivative of therapeutic importance. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1987 Sep;40(9):1358–1360. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.40.1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Okamoto R., Yoshida T., Yamamoto H., Kondo S., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of ME1207, a new oral cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Sep;32(9):1421–1426. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.9.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. C., Schoenknecht F. D., Sherris J. C., Linner E. C. Determination of minimum bactericidal concentrations of oxacillin for Staphylococcus aureus: influence and significance of technical factors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):142–150. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya M., Hamada M., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H., Yamamoto K., Tanaka H., Kiyoshima K., Mori S., Okamoto R. Studies of tylosin derivatives effective against macrolide-resistant strains: synthesis and structure-activity relationships. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Jun;35(6):661–672. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro activity of amifloxacin against outer membrane mutants of the family Enterobacteriaceae and frequency of spontaneous resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1837–1840. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka T., Kiyoshima K., Maeda M., Sakamoto M., Ishikura T., Fukagawa Y., Sawa T., Hamada M., Naganawa H., Takeuchi T. Synthesis and structure-activity studies of new 4''-O-acyltylosin derivatives of therapeutic interest. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1988 Nov;41(11):1617–1628. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.41.1617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


