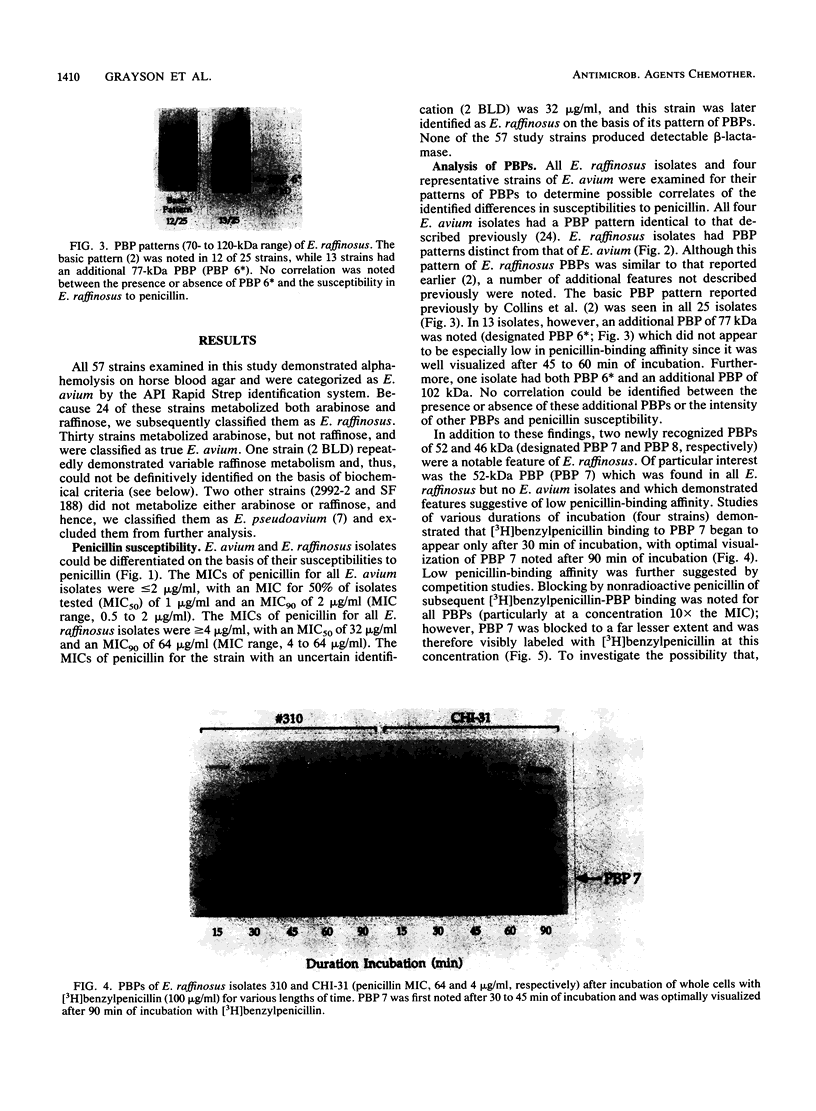
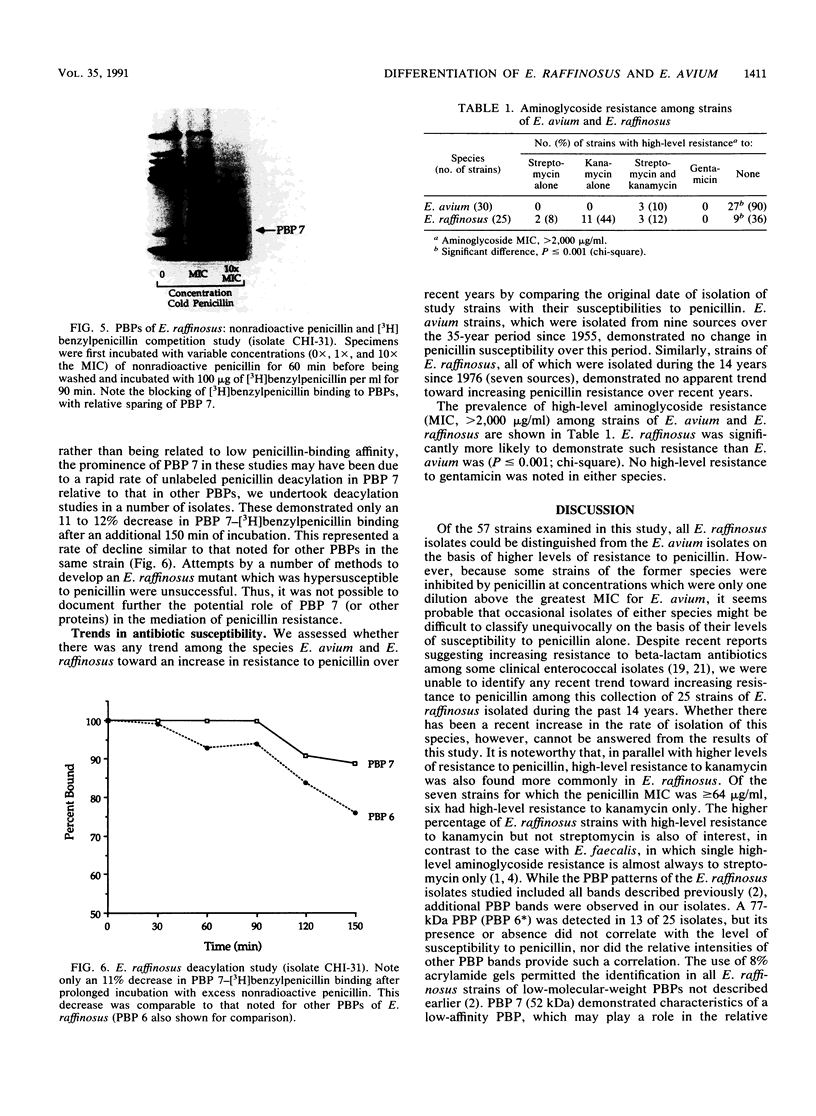
Abstract
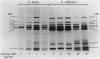
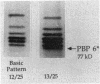
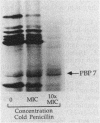
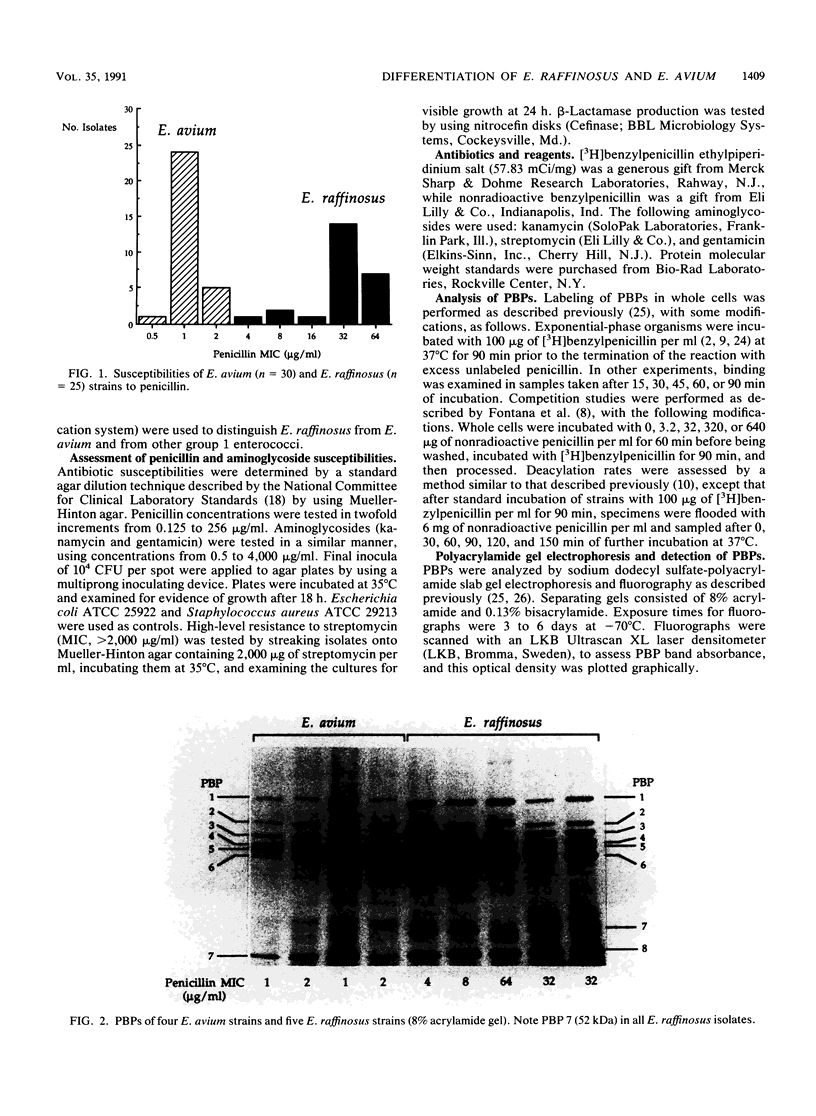
We reidentified our laboratories' collections of 57 enterococcal isolates previously classified as Enterococcus avium by the API Rapid Strep identification system (Analytab Products, Plainview, N.Y.) with the identification criteria recommended by Facklam and Collins (R. R. Facklam and M. D. Collins, J. Clin. Microbiol. 27: 731-734, 1989). Thirty isolates were identified as true E. avium, 25 isolates were identified as E. raffinosus, and 2 isolates were identified as E. pseudoavium. E. raffinosus could be differentiated from E. avium on the basis of penicillin susceptibility, as follows: MIC for 50% of E. raffinosus isolates tested (MIC50), 32 micrograms/ml; MIC90, 64 micrograms/ml (range, 4 to 64 micrograms/ml); E. avium MIC50, 1 microgram/ml; MIC90, 2 micrograms/ml (range, 0.5 to 2 micrograms/ml). No strains produced detectable beta-lactamase. Penicillin-binding protein (PBP) analysis of all E. raffinosus isolates demonstrated the unique pattern reported previously (M. D. Collins, R. R. Facklam, J. A. E. Farrow, and R. Williamson, FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 57:283-288, 1989); however, a number of newly identified PBPs were noted. Of 25 isolates, 13 had an additional PBP of 77 kDa (designated PBP 6*), while all isolates possessed a 52-kDa PBP (PBP 7) and a 46-kDa PBP (PBP 8). The presence or absence of PBP 6* did not correlate with penicillin susceptibility; however, PBP 7 demonstrated many features suggestive of low penicillin-binding affinity and may represent a possible mechanism for the relative resistance of this species to penicillin, although this hypothesis remains speculative since attempts to develop a penicillin-hypersusceptible E. raffinosus mutant were unsuccessful. E. raffinosus isolates were significantly more likely to exhibit high-level resistance to kanamycin than E. avium strains were (P < 0.001; chi-square); however, no strains demonstrated high-level resistance to gentamicin. No trend toward increasing penicillin resistance was noted among this collection of E. avium and E. raffinosus isolates collected over the past 35 and 14 years, respectively. Relative resistance to penicillin may be a helpful differentiating feature between E. avium and E. raffinosus when assessment of raffinose metabolism is not possible or is indeterminant.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calderwood S. A., Wennersten C., Moellering R. C., Jr, Kunz L. J., Krogstad D. J. Resistance to six aminoglycosidic aminocyclitol antibiotics among enterococci: prevalence, evolution, and relationship to synergism with penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):401–405. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. D., Facklam R. R., Farrow J. A., Williamson R. Enterococcus raffinosus sp. nov., Enterococcus solitarius sp. nov. and Enterococcus pseudoavium sp. nov. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Feb;57(3):283–288. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90315-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courvalin P., Carlier C., Collatz E. Plasmid-mediated resistance to aminocyclitol antibiotics in group D streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):541–551. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.541-551.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Farber B. F., Murray B. E., Wennersten C., Moellering R. C., Jr Ribosomal resistance of clinical enterococcal to streptomycin isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):398–399. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Wennersten C., Moellering R. C., Jr Resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Streptococcus faecium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):295–301. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Wennersten C., Zighelboim-Daum S., Reiszner E., Goldmann D., Moellering R. C., Jr High-level resistance to gentamicin in clinical isolates of Streptococcus (Enterococcus) faecium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Oct;32(10):1528–1532. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.10.1528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Collins M. D. Identification of Enterococcus species isolated from human infections by a conventional test scheme. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):731–734. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.731-734.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Cerini R., Longoni P., Grossato A., Canepari P. Identification of a streptococcal penicillin-binding protein that reacts very slowly with penicillin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1343–1350. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1343-1350.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Grossato A., Rossi L., Cheng Y. R., Satta G. Transition from resistance to hypersusceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics associated with loss of a low-affinity penicillin-binding protein in a Streptococcus faecium mutant highly resistant to penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):678–683. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handwerger S., Tomasz A. Alterations in kinetic properties of penicillin-binding proteins of penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann S. A., Moellering R. C., Jr The enterococcus: "putting the bug in our ears". Ann Intern Med. 1987 May;106(5):757–761. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-5-757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horodniceanu T., Bougueleret L., El-Solh N., Bieth G., Delbos F. High-level, plasmid-borne resistance to gentamicin in Streptococcus faecalis subsp. zymogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):686–689. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq R., Derlot E., Duval J., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated resistance to vancomycin and teicoplanin in Enterococcus faecium. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jul 21;319(3):157–161. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198807213190307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki D. G., Agger W. A. Enterococcal bacteremia: clinical features, the risk of endocarditis, and management. Medicine (Baltimore) 1988 Jul;67(4):248–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mederski-Samoraj B. D., Murray B. E. High-level resistance to gentamicin in clinical isolates of enterococci. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):751–757. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Mederski-Samaroj B. Transferable beta-lactamase. A new mechanism for in vitro penicillin resistance in Streptococcus faecalis. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):1168–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI111042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Tsao J., Panida J. Enterococci from Bangkok, Thailand, with high-level resistance to currently available aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):799–802. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oster S. E., Chirurgi V. A., Goldberg A. A., Aiken S., McCabe R. E. Ampicillin-resistant enterococcal species in an acute-care hospital. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1821–1823. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., de la Maza L., Murtagh M. J., Spargo J. D., Ferraro M. J. Species identities of enterococci isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):435–437. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.435-437.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapico F. L., Canawati H. N., Ginunas V. J., Gilmore D. S., Montgomerie J. Z., Tuddenham W. J., Facklam R. R. Enterococci highly resistant to penicillin and ampicillin: an emerging clinical problem? J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2091–2095. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2091-2095.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uttley A. H., Collins C. H., Naidoo J., George R. C. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Lancet. 1988 Jan 2;1(8575-6):57–58. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C. Enterococci from blood cultures during 1980-1989: susceptibility to ampicillin, penicillin and vancomycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Oct;26(4):602–604. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.4.602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Gutmann L., Horaud T., Delbos F., Acar J. F. Use of penicillin-binding proteins for the identification of enterococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jul;132(7):1929–1937. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-7-1929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zighelboim S., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins of multiply antibiotic-resistant South African strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):434–442. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]