Abstract
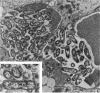
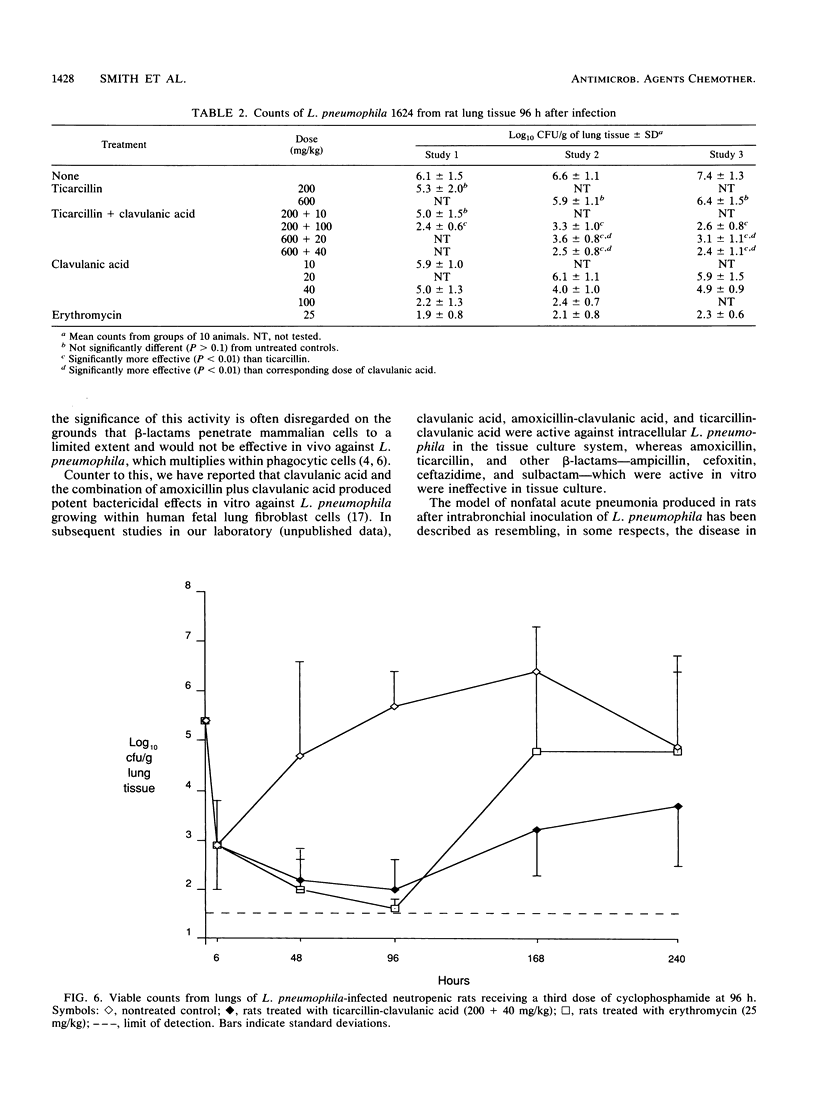
A model of acute Legionella pneumophila pneumonia in neutropenic weanling rats was developed as a means of assessing the efficacies in vivo of the beta-lactams ticarcillin, ticarcillin-clavulanic acid, and clavulanic acid, agents active against the organism in vitro. Weanling rats were dosed with cyclophosphamide 3 days before and immediately prior to infection by intrabronchial intubation with L. pneumophila. The bacteria persisted in the lungs of untreated animals at high counts (5.0 to 7.0 log10 CFU/g of lung tissue) for up to 168 h after infection, and the histological characteristics of the infection were similar to those of the disease in humans. Transmission electron micrography revealed the presence of L. pneumophila multiplying within alveolar macrophages. Therapy with ticarcillin was ineffective in reducing the bacterial numbers in the lung tissue, whereas ticarcillin-clavulanic acid and clavulanic acid were active, producing bactericidal effects similar to those of erythromycin. The ticarcillin-clavulanic acid combination was significantly more efficacious (P less than 0.01) than corresponding doses of clavulanic acid alone. Synergistic activity between ticarcillin and clavulanic acid against L. pneumophila has been demonstrated in vivo, and the combination showed activity similar to that of erythromycin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Edelstein P. H. Improved semiselective medium for isolation of Legionella pneumophila from contaminated clinical and environmental specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):298–303. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.298-303.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. Inactivation of beta-lactam antibiotics by Legionella pneumophila. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):561–564. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glavin F. L., Winn W. C., Jr, Craighead J. E. Ultrastructure of lung in Legionnaires' disease. Observations of three biopsies done during the Vermont epidemic. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):555–559. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., King-Thompson N., Holman J. W. Entry of roxithromycin (RU 965), imipenem, cefotaxime, trimethoprim, and metronidazole into human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1553–1557. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Formation of a novel phagosome by the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1319–1331. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) multiples intracellularly in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):441–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI109874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D., Cockburn A., Cooper D. L., Langley P. F., Tasker T. C., White D. J. Clinical pharmacology and safety evaluation of Timentin. Am J Med. 1985 Nov 29;79(5B):44–55. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. M., Hashemi S. Electron microscopic examination of the inflammatory response to Legionella pneumophila in guinea pigs. Lab Invest. 1982 Jan;46(1):24–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlod D. J., Saravolatz L. D., Quinn E. L., Somerville M. M. Effect of clavulanic acid on minimal inhibitory concentrations of 16 antimicrobial agents tested against Legionella pneumophila. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Aug;18(2):353–354. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.2.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerrett S. J., Schmidt R. A., Martin T. R. Impaired clearance of aerosolized Legionella pneumophila in corticosteroid-treated rats: a model of Legionnaires' disease in the compromised host. J Infect Dis. 1989 Aug;160(2):261–273. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. M., Abbott K. H., Wilkinson M. J., Beale A. S., Sutherland R. Bactericidal effects of amoxycillin/clavulanic acid against a Legionella pneumophila pneumonia in the weanling rat. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Jan;27(1):127–136. doi: 10.1093/jac/27.1.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. M., Boon R. J., Beale A. S. Influence of clavulanic acid on the activity of amoxicillin against an experimental Streptococcus pneumoniae-Staphylococcus aureus mixed respiratory infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):210–214. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Jobanputra V., Zimmermann W. Binding of thienamycin and clavulanic acid to the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):406–409. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes D. H., Slocombe B., Sutherland R. Bactericidal effects of amoxycillin/clavulanic acid against Legionella pneumophila. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Jan;23(1):43–51. doi: 10.1093/jac/23.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes D. H., Wilkinson M. J., Tyler J., Slocombe B., Sutherland R. Bactericidal effects of amoxycillin/clavulanic acid against intracellular Legionella pneumophila in tissue culture studies. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Apr;23(4):547–556. doi: 10.1093/jac/23.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr, Davis G. S., Gump D. W., Craighead J. E., Beaty H. N. Legionnaires' pneumonia after intratracheal inoculation of guinea pigs and rats. Lab Invest. 1982 Dec;47(6):568–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]