Abstract
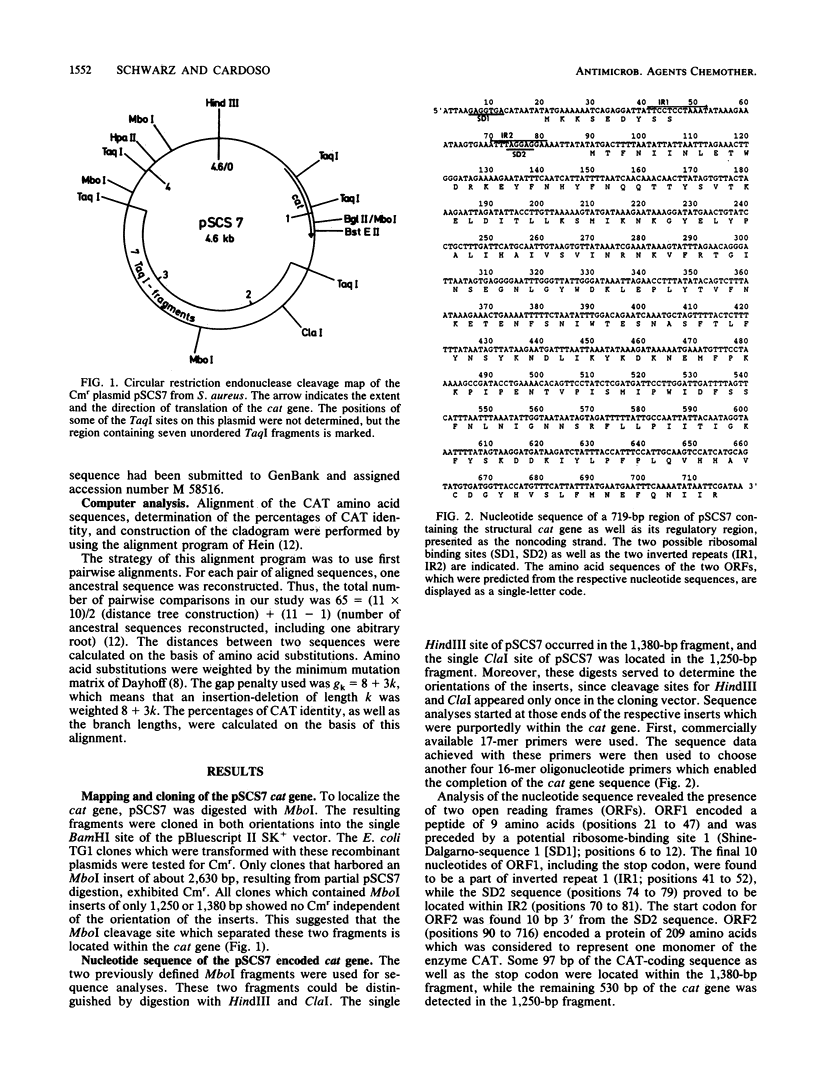
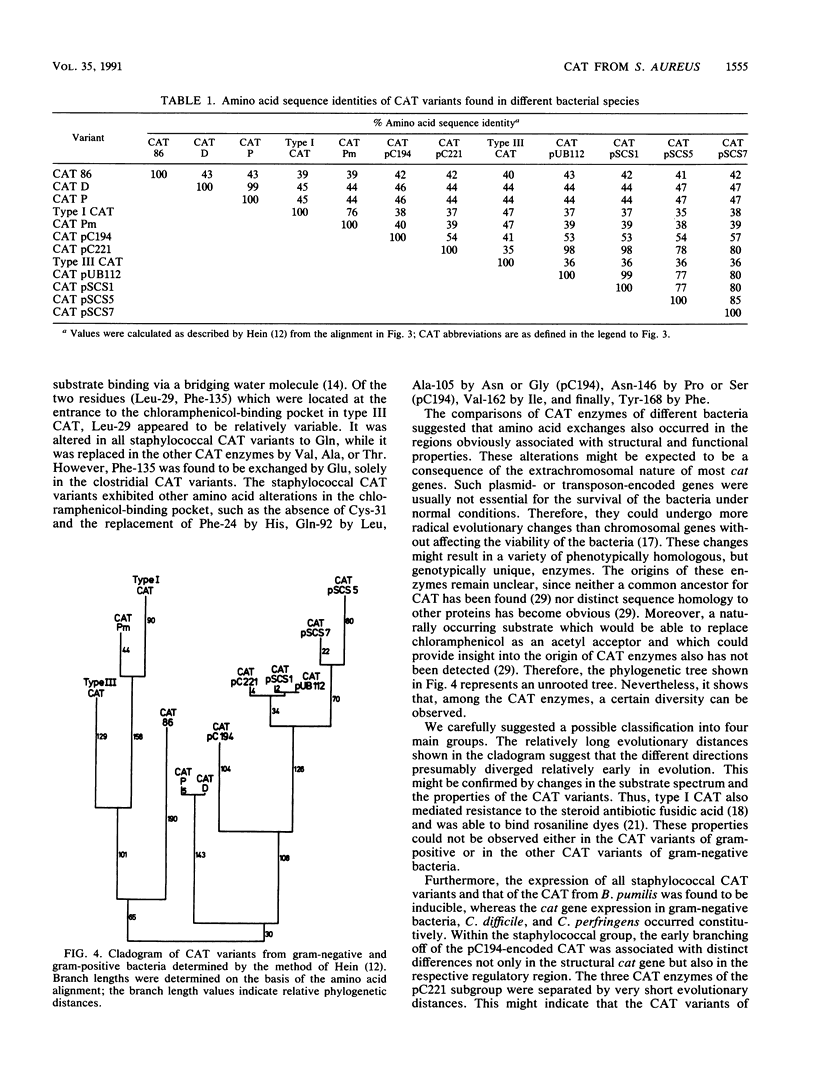
The nucleotide sequence of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene (cat) and its regulatory region, encoded by the plasmid pSCS7 from Staphylococcus aureus, was determined. The structural cat gene encoded a protein of 209 amino acids, which represented one monomer of the enzyme chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT). Comparisons between the amino acid sequences of the pSCS7-encoded CAT from S. aureus and the previously sequenced CAT variants from S. aureus, Staphylococcus intermedius, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Bacillus pumilis, Clostridium difficile, Clostridium perfringens, Escherichia coli, Shigella flexneri, and Proteus mirabilis were performed. An alignment of CAT amino acid sequences demonstrated the presence of 34 conserved amino acids among all CAT variants. These conserved residues were considered for their possible roles in the structure and function of CAT. On the basis of the alignment, a phylogenetic tree was constructed. It demonstrated relatively large evolutionary distances between the CAT variants of enteric bacteria, Clostridium, Bacillus, and Staphylococcus species.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alton N. K., Vapnek D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chloramphenicol resistance transposon Tn9. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):864–869. doi: 10.1038/282864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. G., Shaw W. V. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides with universal templates for rapid DNA sequencing: results with staphylococcal replicon pC221. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):561–568. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03665.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brückner R., Matzura H. Regulation of the inducible chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene of the Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pUB112. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2295–2300. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. L., Mendelman P. M., Levy J., Stull T. L., Smith A. L. A permeability barrier as a mechanism of chloramphenicol resistance in Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):46–54. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles I. G., Keyte J. W., Shaw W. V. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the cat gene of Proteus mirabilis: comparison with the type I (Tn9) cat gene. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):123–129. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.123-129.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehret M., Matzura H. Replication control of the Staphylococcus aureus chloramphenicol resistance plasmids pC223 and pUB112 in Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2045–2062. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood C. R., Williams D. M., Lovett P. S. Nucleotide sequence of a Bacillus pumilus gene specifying chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hein J. Unified approach to alignment and phylogenies. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:626–645. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Nucleotide sequence and functional map of pC194, a plasmid that specifies inducible chloramphenicol resistance. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):815–825. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.815-825.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie A. G., Moody P. C., Shaw W. V. Structure of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase at 1.75-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4133–4137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie A. G. Refined crystal structure of type III chloramphenicol acetyltransferase at 1.75 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1990 May 5;213(1):167–186. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80129-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett P. S. Translational attenuation as the regulator of inducible cat genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.1-6.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon B. R., Skurray R. Antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus: genetic basis. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):88–134. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.88-134.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcoli R., Iida S., Bickle T. A. The DNA sequence of an IS/-flanked transposon coding for resistance to chloramphenicol and fusidic acid. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 28;110(1):11–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray I. A., Hawkins A. R., Keyte J. W., Shaw W. V. Nucleotide sequence analysis and overexpression of the gene encoding a type III chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):173–179. doi: 10.1042/bj2520173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. Plasmid-protein relaxation complexes in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1177–1187. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1177-1187.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor G. N., Rownd R. H. Rosanilins: indicator dyes for chloramphenicol-resistant enterobacteria containing chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1375–1382. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1375-1382.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Projan S. J., Kornblum J., Moghazeh S. L., Edelman I., Gennaro M. L., Novick R. P. Comparative sequence and functional analysis of pT181 and pC221, cognate plasmid replicons from Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(3):452–464. doi: 10.1007/BF00330758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz S., Cardoso M., Blobel H. Detection of a novel chloramphenicol resistance plasmid from "equine" Staphylococcus sciuri. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1990 Nov;37(9):674–679. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1990.tb01113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz S., Cardoso M., Blobel H. Plasmid-mediated chloramphenicol resistance in Staphylococcus hyicus. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Dec;135(12):3329–3336. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-12-3329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz S., Cardoso M. Molecular cloning, purification, and properties of a plasmid-encoded chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from Staphylococcus haemolyticus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jul;35(7):1277–1283. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.7.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz S., Spies U., Cardoso M. Cloning and sequence analysis of a plasmid-encoded chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene from Staphylococcus intermedius. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Apr;137(4):977–981. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-4-977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase: enzymology and molecular biology. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1983;14(1):1–46. doi: 10.3109/10409238309102789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V., Packman L. C., Burleigh B. D., Dell A., Morris H. R., Hartley B. S. Primary structure of a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase specified by R plasmids. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):870–872. doi: 10.1038/282870a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V., Unowsky J. Mechanism of R factor-mediated chloramphenicol resistance. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1976–1978. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1976-1978.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen C., Matzura H. Nucleotide sequence analysis and expression studies of a chloramphenicol-acetyltransferase-coding gene from Clostridium perfringens. Gene. 1989 Feb 20;75(2):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toro C. S., Lobos S. R., Calderón I., Rodríguez M., Mora G. C. Clinical isolate of a porinless Salmonella typhi resistant to high levels of chloramphenicol. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1715–1719. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wren B. W., Mullany P., Clayton C., Tabaqchali S. Nucleotide sequence of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene from Clostridium difficile. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4877–4877. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



