Abstract
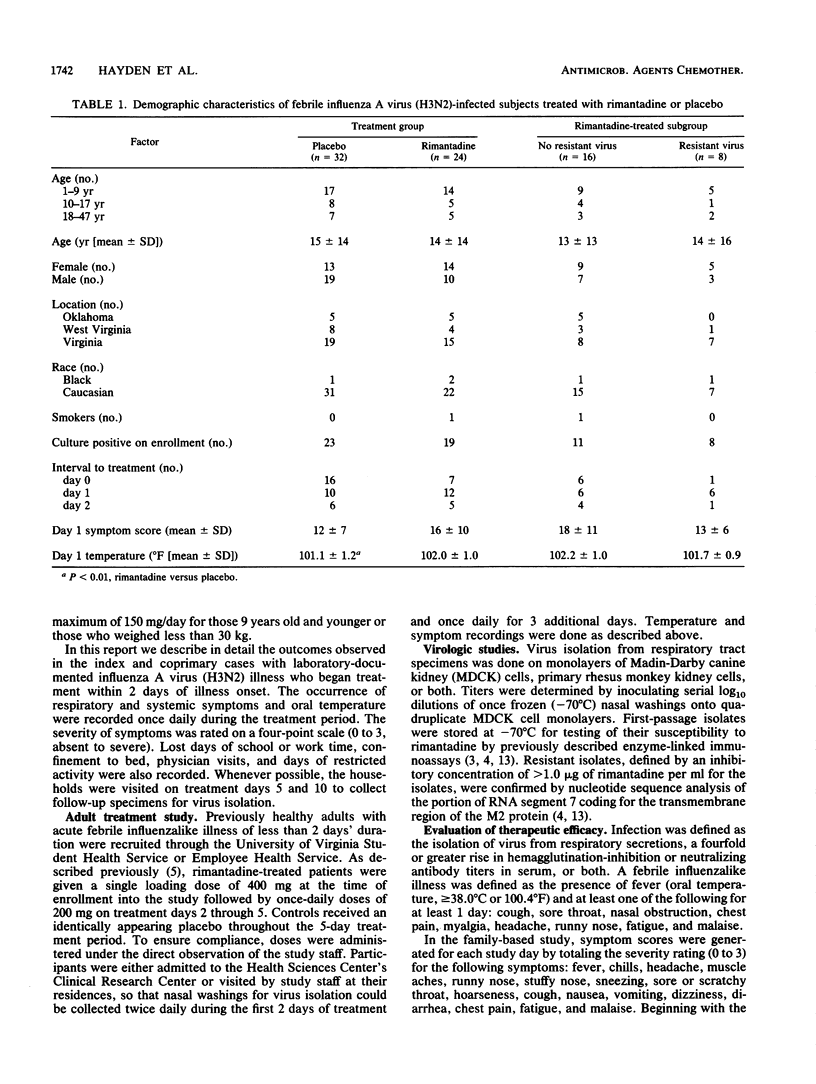
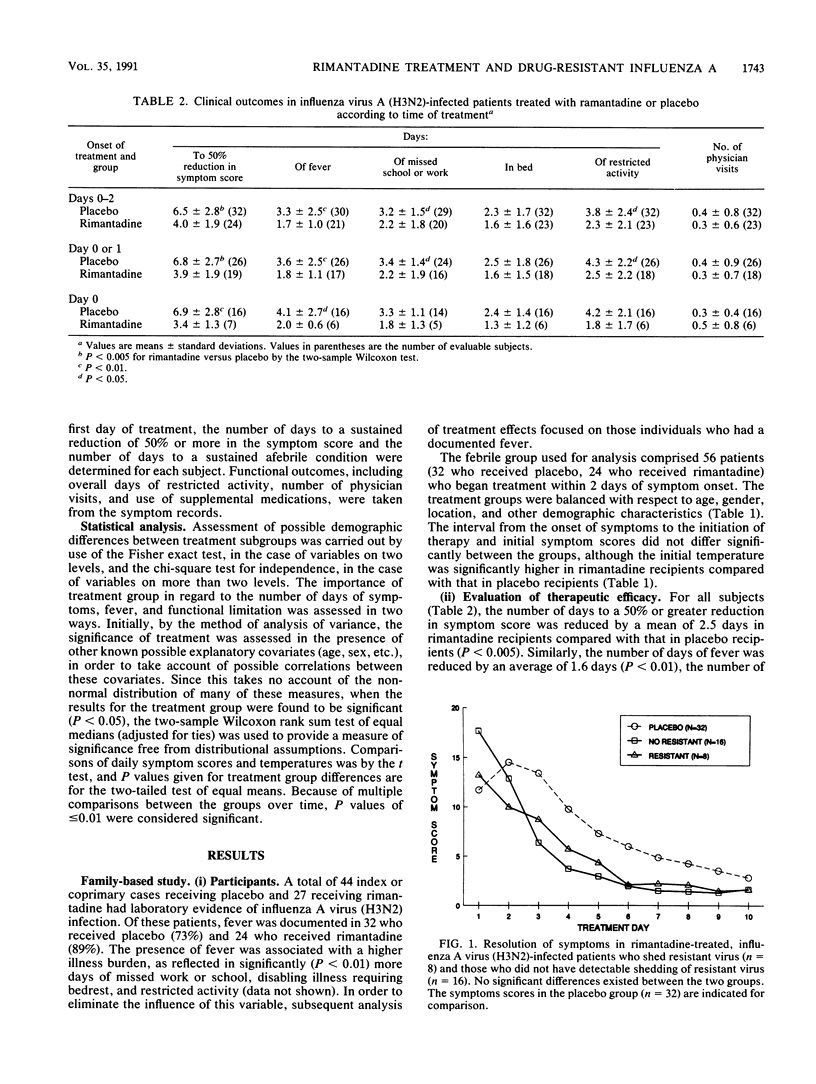
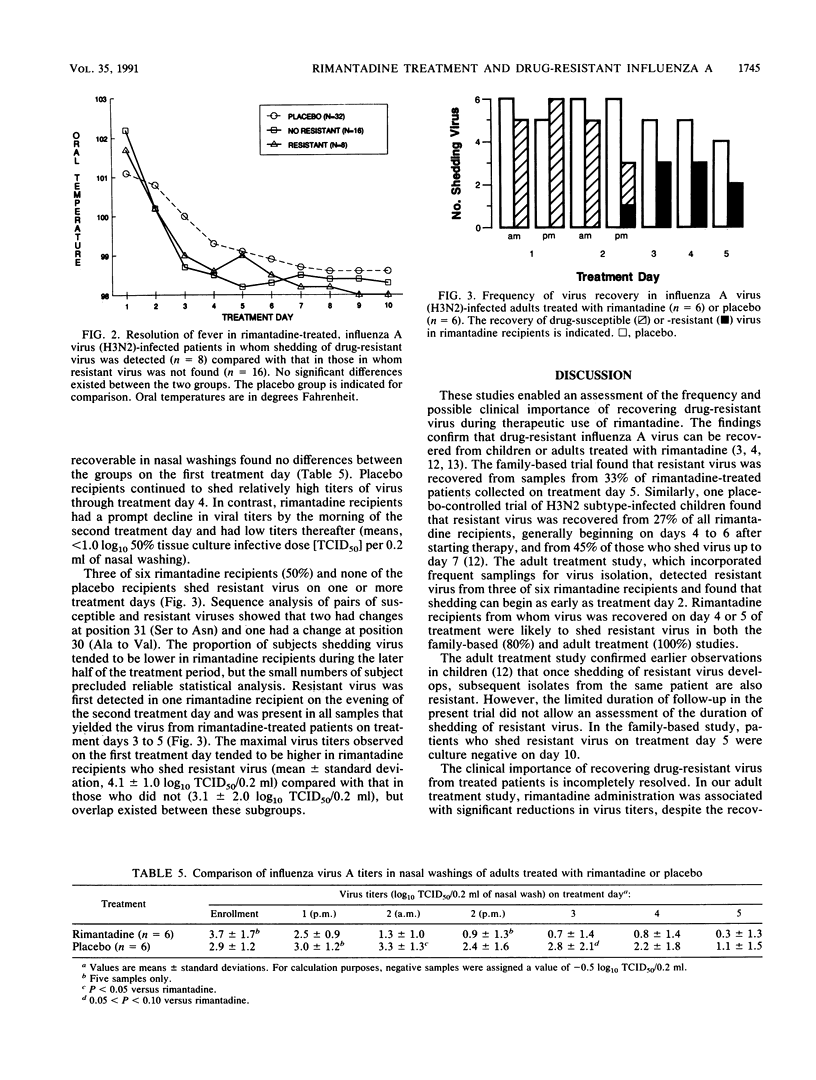
The therapeutic activity of rimantadine and its relationship to the shedding of drug-resistant influenza A virus were assessed in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials involving patients with laboratory-documented influenza A virus (H3N2 subtype) illness of 2 days' duration or less. In a family-based study, rimantadine treatment for 10 days (24 children and adults) was associated with significant decreases in the number of days to a 50% reduction in symptoms (mean difference, 2.5 days), days of fever (1.6 days), and days of restricted activity (1.5 days) compared with the results obtained with placebo-treated patients (32 children and adults). Drug-resistant virus was recovered from eight (33%) of the rimantadine recipients on day 5. No differences in patient demographics or illness severity at the time of enrollment in the study were apparent between those who shed resistant virus and those who did not. Illness resolution tended to be slower in those who shed resistant virus compared with that in those who did not. In a study of adults treated for 5 days (six treated with rimantadine, six treated with placebo), resistant virus was recovered in three rimantadine recipients by day 3 of treatment. The results indicate that drug-resistant influenza A virus (H3N2) can be recovered from rimantadine-treated children and adults as early as 2 days after starting treatment, but that rimantadine retains a net therapeutic benefit compared with that of placebo.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean W. J., Threlkeld S. C., Webster R. G. Biologic potential of amantadine-resistant influenza A virus in an avian model. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jun;159(6):1050–1056. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.6.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard C. W., Brugh M., Webster R. G. Emergence of amantadine-resistant H5N2 avian influenza virus during a simulated layer flock treatment program. Avian Dis. 1987 Jul-Sep;31(3):533–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belshe R. B., Burk B., Newman F., Cerruti R. L., Sim I. S. Resistance of influenza A virus to amantadine and rimantadine: results of one decade of surveillance. J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):430–435. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belshe R. B., Smith M. H., Hall C. B., Betts R., Hay A. J. Genetic basis of resistance to rimantadine emerging during treatment of influenza virus infection. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1508–1512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1508-1512.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith A. W., Oxford J. S., Schild G. C., Watson G. I. Protective effect of 1-adamantanamine hydrochloride on influenza A2 infections in the family environment: a controlled double-blind study. Lancet. 1969 Nov 15;2(7629):1026–1028. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90639-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith A. W., Oxford J. S., Schild G. C., Watson G. I. Study of 1-adamantanamine hydrochloride used prophylactically during the Hong Kong influenza epidemic in the family environment. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;41(3):677–682. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. B., Dolin R., Gala C. L., Markovitz D. M., Zhang Y. Q., Madore P. H., Disney F. A., Talpey W. B., Green J. L., Francis A. B. Children with influenza A infection: treatment with rimantadine. Pediatrics. 1987 Aug;80(2):275–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden F. G., Belshe R. B., Clover R. D., Hay A. J., Oakes M. G., Soo W. Emergence and apparent transmission of rimantadine-resistant influenza A virus in families. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 21;321(25):1696–1702. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912213212502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden F. G., Hoffman H. E., Spyker D. A. Differences in side effects of amantadine hydrochloride and rimantadine hydrochloride relate to differences in pharmacokinetics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Mar;23(3):458–464. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.3.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden F. G., Monto A. S. Oral rimantadine hydrochloride therapy of influenza A virus H3N2 subtype infection in adults. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Feb;29(2):339–341. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. E., West K., Bruns M., Ennis F. A. Effect of rimantadine on cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses and immunity to reinfection in mice infected with influenza A virus. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):180–184. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovich S., Baldini J. T., Bannister R. Treatment of influenza. The therapeutic efficacy of rimantadine HC1 in a naturally occurring influenza A2 outbreak. Am J Med Sci. 1969 May;257(5):328–335. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196905000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Fleet W., Lawrence E., Pierce E., Morris L., Wright P. A comparison of acetaminophen and rimantadine in the treatment of influenza A infection in children. J Med Virol. 1987 Mar;21(3):249–255. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890210308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Voris L. P., Betts R. F., Hayden F. G., Christmas W. A., Douglas R. G., Jr Successful treatment of naturally occurring influenza A/USSR/77 H1N1. JAMA. 1981 Mar 20;245(11):1128–1131. doi: 10.1001/jama.245.11.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Kawaoka Y., Bean W. J., Beard C. W., Brugh M. Chemotherapy and vaccination: a possible strategy for the control of highly virulent influenza virus. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):173–176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.173-176.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



