Abstract
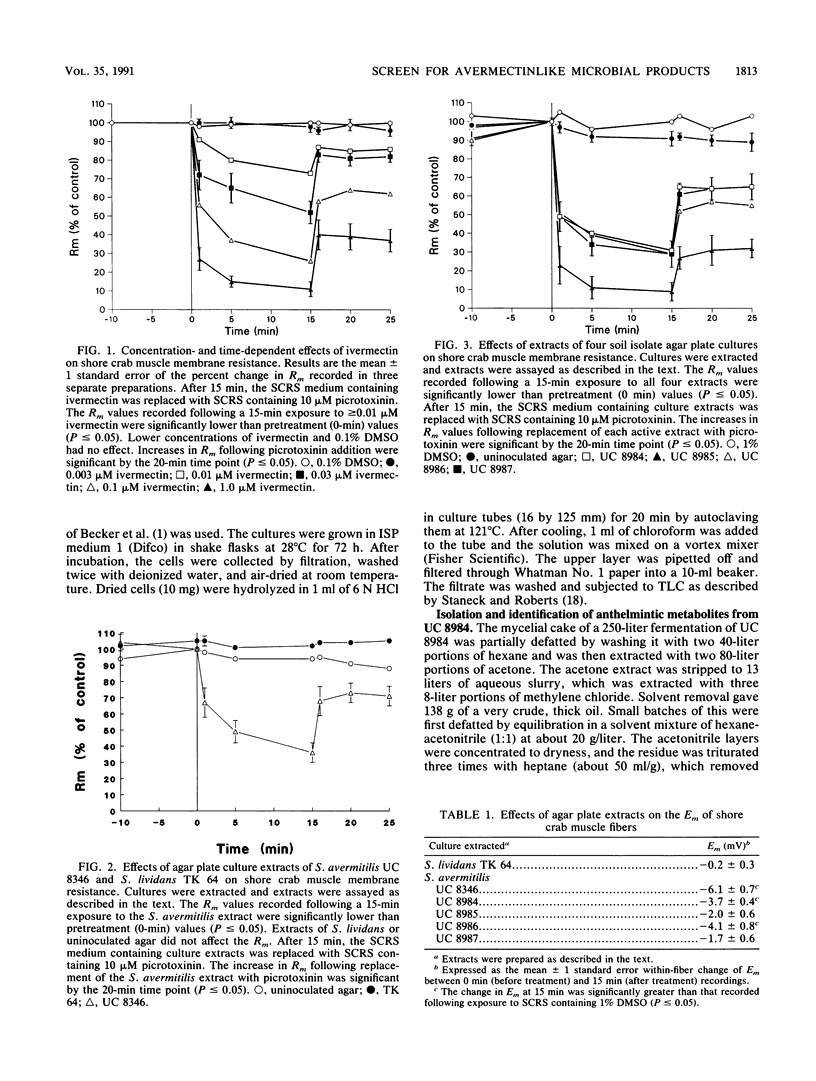
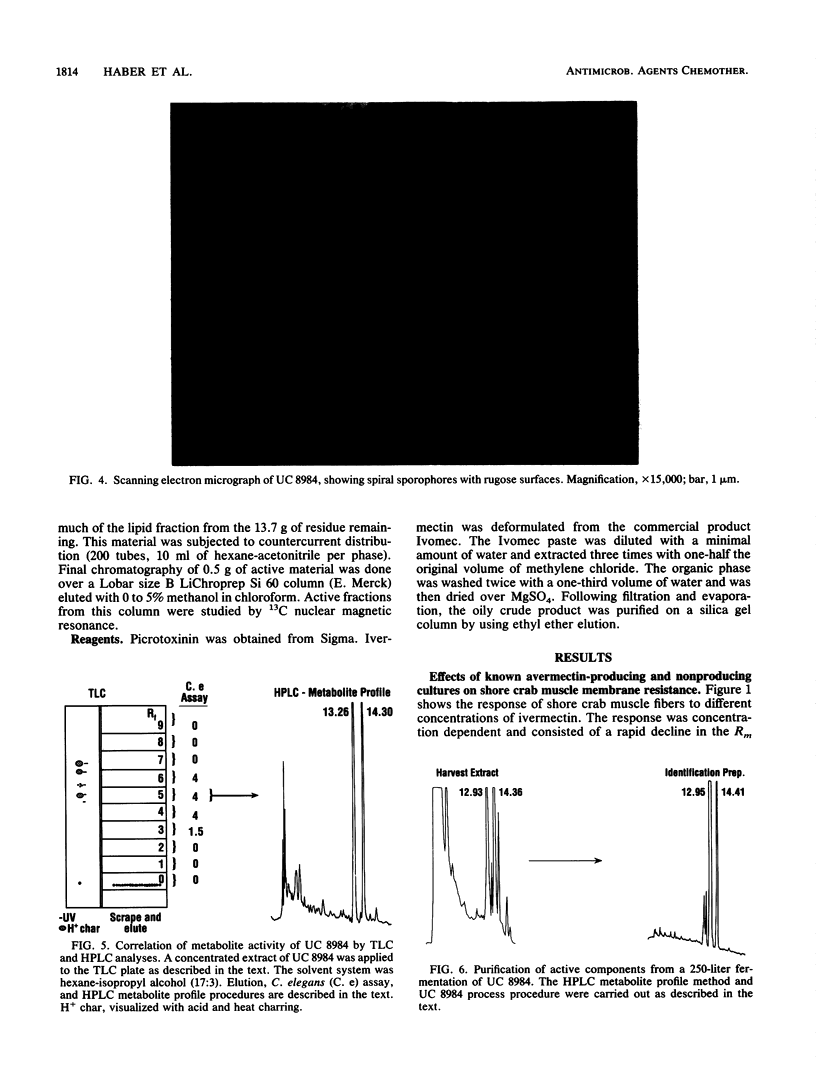
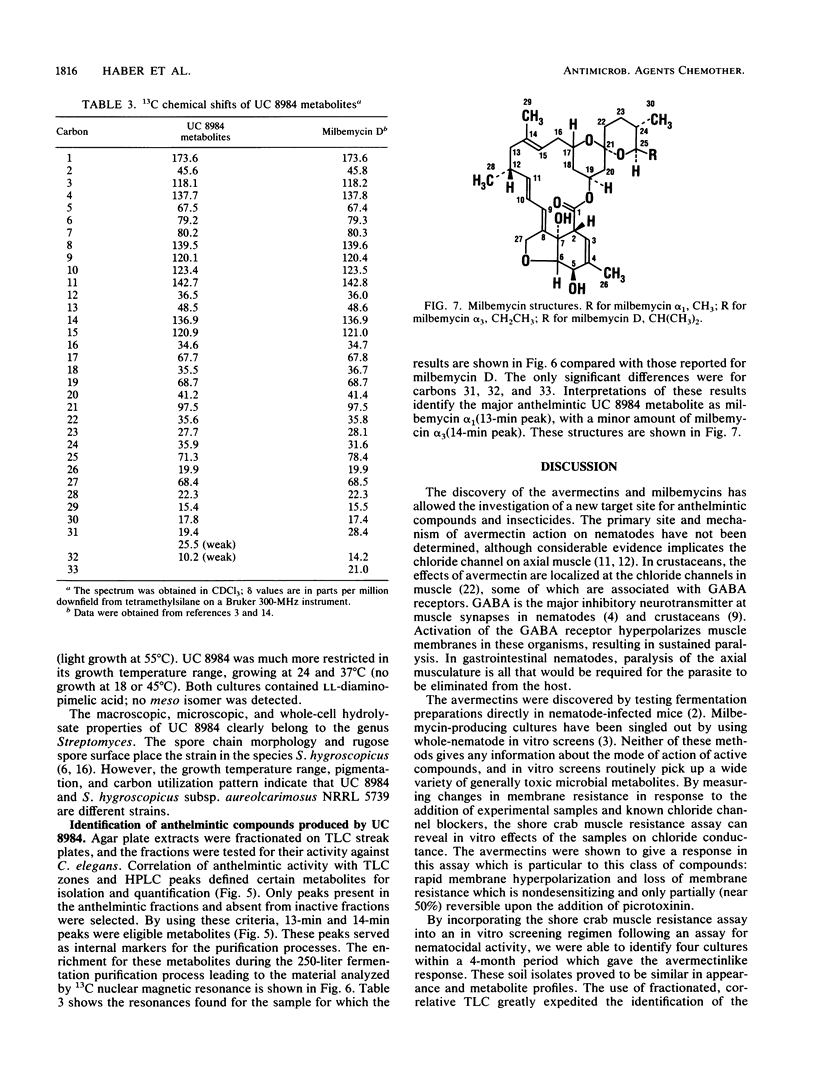
A high-volume screen for anthelmintic microbial metabolites with an avermectinlike mode of action was developed. The primary screen used the free-living nematode Caenorhabditis elegans in a whole-organism assay. The specificity for avermectinlike compounds resides in the secondary screen, which takes advantage of the chloride channel-opening properties of the avermectins. By using standard microelectrode techniques, membrane conductance changes following exposure to extracts of microbial cultures were measured in the walking leg stretcher muscle fibers of the lined shore crab Pachygrapsus crassipes. The avermectins and related milbemycins give a characteristic response of rapid loss of membrane resistance coupled with a slight hyperpolarization of the membrane. This is partially (near 50%) reversible with the chloride channel blocker picrotoxinin. Four morphologically similar cultures that produced avermectinlike activities were identified by this screen. Isolation of the active components from one of these cultures (strain UC 8984) followed by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy resulted in the identification of milbemycins alpha 1 and alpha 3. These metabolites are members of a large family of milbemycins produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus subsp. aureolacrimosus NRRL 5739. Systematic studies revealed that strain UC 8984 is also a S. hygroscopicus strain, but which is taxonomically distinct from NRRL 5739.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKER B., LECHEVALIER M. P., LECHEVALIER H. A. CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF CELL-WALL PREPARATIONS FROM STRAINS OF VARIOUS FORM-GENERA OF AEROBIC ACTINOMYCETES. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:236–243. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.236-243.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg R. W., Miller B. M., Baker E. E., Birnbaum J., Currie S. A., Hartman R., Kong Y. L., Monaghan R. L., Olson G., Putter I. Avermectins, new family of potent anthelmintic agents: producing organism and fermentation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Mar;15(3):361–367. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.3.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter G. T., Nietsche J. A., Hertz M. R., Williams D. R., Siegel M. M., Morton G. O., James J. C., Borders D. B. LL-F28249 antibiotic complex: a new family of antiparasitic macrocyclic lactones. Isolation, characterization and structures of LL-F28249 alpha, beta, gamma, lambda. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1988 Apr;41(4):519–529. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.41.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIETZ A., MATHEWS J. Taxonomy by carbon replication. I. An examination of Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Appl Microbiol. 1962 May;10:258–263. doi: 10.1128/am.10.3.258-263.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Castillo J., De Mello W. C., Morales T. Inhibitory action of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on Ascaris muscle. Experientia. 1964 Mar 15;20(3):141–143. doi: 10.1007/BF02150701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz A., Mathews J. Scanning electron microscopy of selected members of the Streptomyces hygroscopicus group. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Oct;18(4):694–696. doi: 10.1128/am.18.4.694-696.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz L. C., Wang C. C., Gorio A. Avermectin B1a irreversibly blocks postsynaptic potentials at the lobster neuromuscular junction by reducing muscle membrane resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):2062–2066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.2062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W., Bownds M. D., Kravitz E. A. The metabolism of gamma aminobutyric acid in the lobster nervous system. Enzymes in single excitatory and inhibitory axons. J Cell Biol. 1970 Aug;46(2):290–299. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.2.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood J. D., Banks R. M., Brewer M. D., Fish J. P., Manger B. R., Poulton M. E. A novel series of milbemycin antibiotics from Streptomyces strain E225. I. Discovery, fermentation and anthelmintic activity. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1989 Nov;42(11):1593–1598. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.42.1593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass I. S., Larsen D. A., Wang C. C., Stretton A. O. Ascaris suum: differential effects of avermectin B1a on the intact animal and neuromuscular strip preparations. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Oct;54(2):166–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. J., Pennington A. J. A patch-clamp study of effects of dihydroavermectin on Ascaris muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):747–756. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14602.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. W., Chaiet L., Cole D. J., Cole L. J., Flor J. E., Goegelman R. T., Gullo V. P., Joshua H., Kempf A. J., Krellwitz W. R. Avermectins, new family of potent anthelmintic agents: isolation and chromatographic properties. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Mar;15(3):368–371. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.3.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Mishima H., Takiguchi Y., Terao M., Kobayashi H., Iwasaki S., Okuda S. Milbemycins, a new family of macrolide antibiotics. Studies on the biosynthesis of milbemycins alpha 2, alpha 4 and D using 13C labeled precursors. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1983 Aug;36(8):991–1000. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.36.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staneck J. L., Roberts G. D. Simplified approach to identification of aerobic actinomycetes by thin-layer chromatography. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):226–231. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.226-231.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRESNER H. D., BACKUS E. J. System of color wheels for streptomycete taxonomy. Appl Microbiol. 1963 Jul;11:335–338. doi: 10.1128/am.11.4.335-338.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takiguchi Y., Mishima H., Okuda M., Terao M., Aoki A., Fukuda R. Milbemycins, a new family of macrolide antibiotics: fermentation, isolation and physico-chemical properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1980 Oct;33(10):1120–1127. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.33.1120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




