Abstract
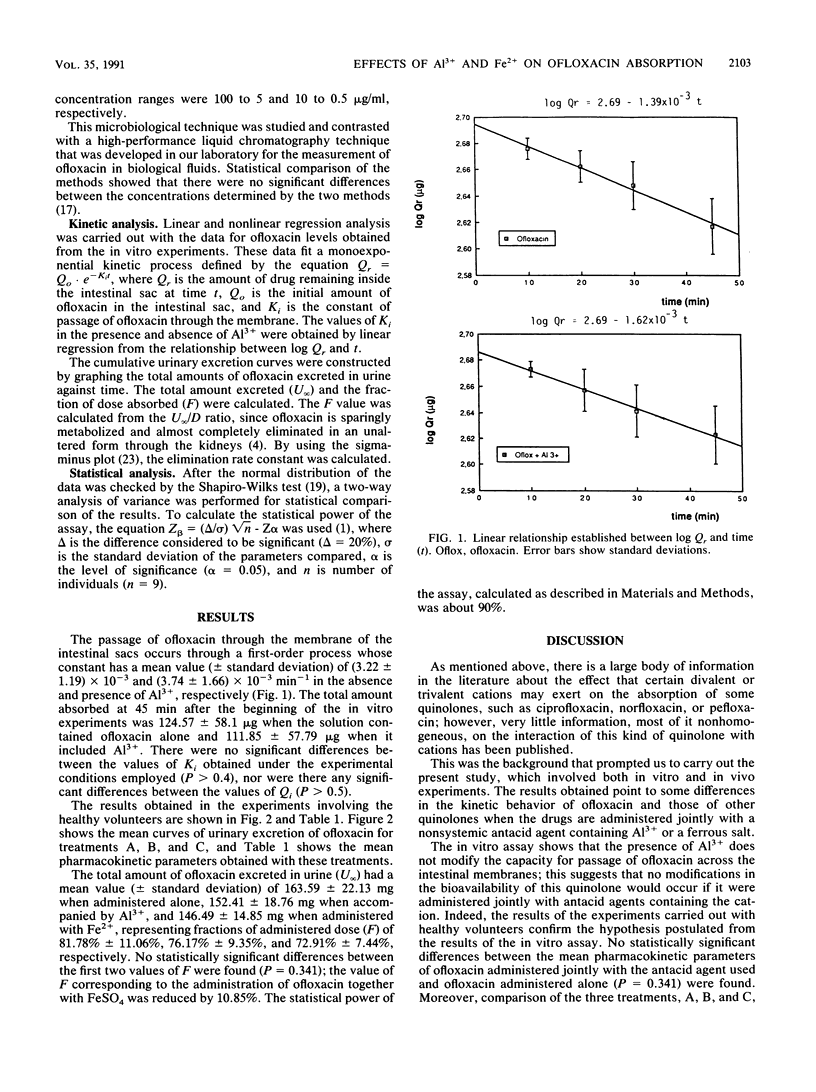
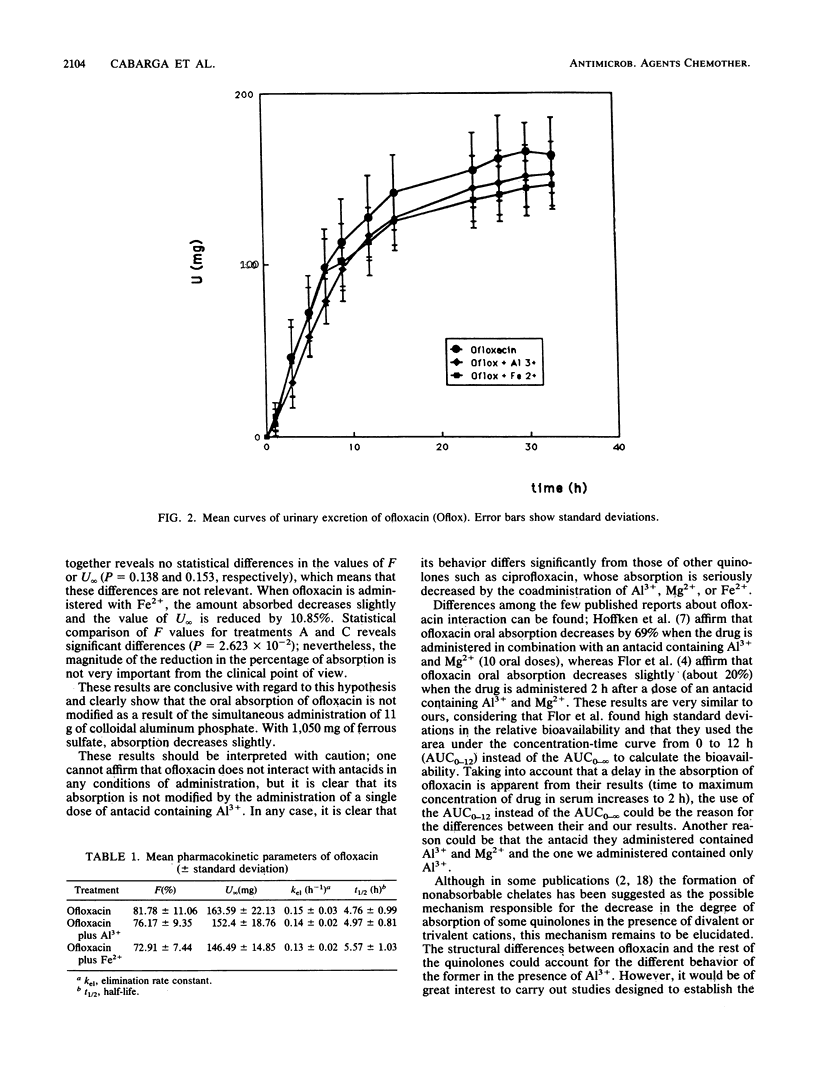
A study was performed to establish the effect of Al3+ and Fe2+ cations on the absorption of ofloxacin when it is administered orally at a dose of 200 mg. The study was carried out with nine volunteers, who each received three treatments (A [200 mg of ofloxacin], B [200 mg of ofloxacin plus 11 g of colloidal aluminum phosphate], and C [200 mg of ofloxacin plus 1,050 mg of FeSO4]) according to a Latin square design; the washout period was 1 week. The analytical technique was a microbiological diffusion method. The pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated from the cumulative urinary excretion data and from a sigma-minus plot. The total amount of ofloxacin excreted in urine had a mean value of 163.59 +/- 22.13 mg when ofloxacin was administered alone, 152.41 +/- 18.76 mg when it was administered with Al3+, and 146.49 +/- 14.85 mg when it was administered with Fe2+. No statistically significant differences were found in the F values (fractions of dose absorbed) obtained with ofloxacin alone and ofloxacin plus Al3+ (P = 0.341). When ofloxacin alone was compared with joint administration with Fe2+ the value of F decreased 10.85%; this difference is statistically significant (P = 2.623 x 10(-2)).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davey P. G. Overview of drug interactions with the quinolones. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Sep;22 (Suppl 100):97–107. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_c.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flor S., Guay D. R., Opsahl J. A., Tack K., Matzke G. R. Effects of magnesium-aluminum hydroxide and calcium carbonate antacids on bioavailability of ofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Dec;34(12):2436–2438. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.12.2436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golper T. A., Hartstein A. I., Morthland V. H., Christensen J. M. Effects of antacids and dialysate dwell times on multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of oral ciprofloxacin in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1787–1790. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S. The fluoroquinolones: pharmacology, clinical uses, and toxicities in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):716–721. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höffken G., Borner K., Glatzel P. D., Koeppe P., Lode H. Reduced enteral absorption of ciprofloxacin in the presence of antacids. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;4(3):345–345. doi: 10.1007/BF02013667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lode H., Höffken G., Olschewski P., Sievers B., Kirch A., Borner K., Koeppe P. Pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin after parenteral and oral administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1338–1342. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuman M. Clinical pharmacokinetics of the newer antibacterial 4-quinolones. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1988 Feb;14(2):96–121. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198814020-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nix D. E., Watson W. A., Lener M. E., Frost R. W., Krol G., Goldstein H., Lettieri J., Schentag J. J. Effects of aluminum and magnesium antacids and ranitidine on the absorption of ciprofloxacin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1989 Dec;46(6):700–705. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1989.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nix D. E., Wilton J. H., Ronald B., Distlerath L., Williams V. C., Norman A. Inhibition of norfloxacin absorption by antacids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Mar;34(3):432–435. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.3.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parpia S. H., Nix D. E., Hejmanowski L. G., Goldstein H. R., Wilton J. H., Schentag J. J. Sucralfate reduces the gastrointestinal absorption of norfloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):99–102. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. H., Reeves D. S. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Microbiology, pharmacokinetics and clinical use. Drugs. 1988 Aug;36(2):193–228. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198836020-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polk R. E., Healy D. P., Sahai J., Drwal L., Racht E. Effect of ferrous sulfate and multivitamins with zinc on absorption of ciprofloxacin in normal volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1841–1844. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson B. N., Boppana V. K., Vlasses P. H., Rotmensch H. H., Ferguson R. K. Norfloxacin disposition after sequentially increasing oral doses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Feb;23(2):284–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.2.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinceneux P., Weber P., Gaudin H., Boussougant Y. Diminution de l'absorption de la péfloxacine par des pansements gastriques. Etude préliminaire. Presse Med. 1986 Oct 18;15(36):1826–1826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON T. H., WISEMAN G. The use of sacs of everted small intestine for the study of the transference of substances from the mucosal to the serosal surface. J Physiol. 1954 Jan;123(1):116–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



