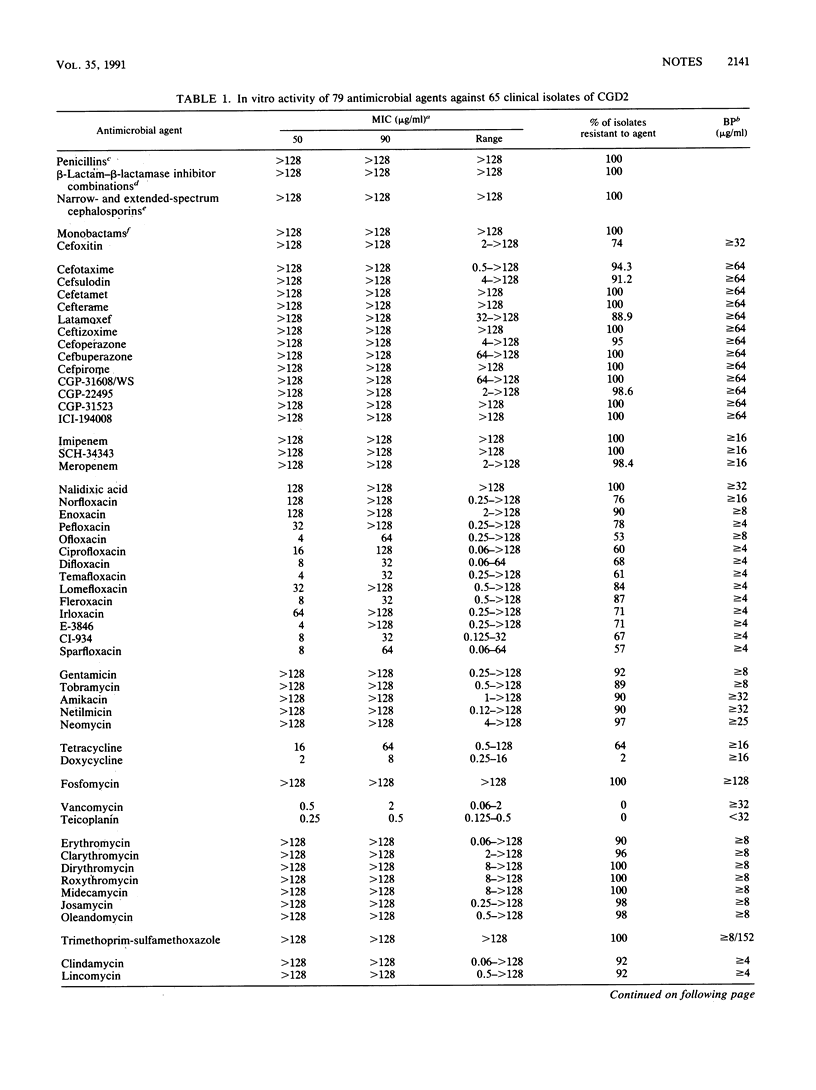
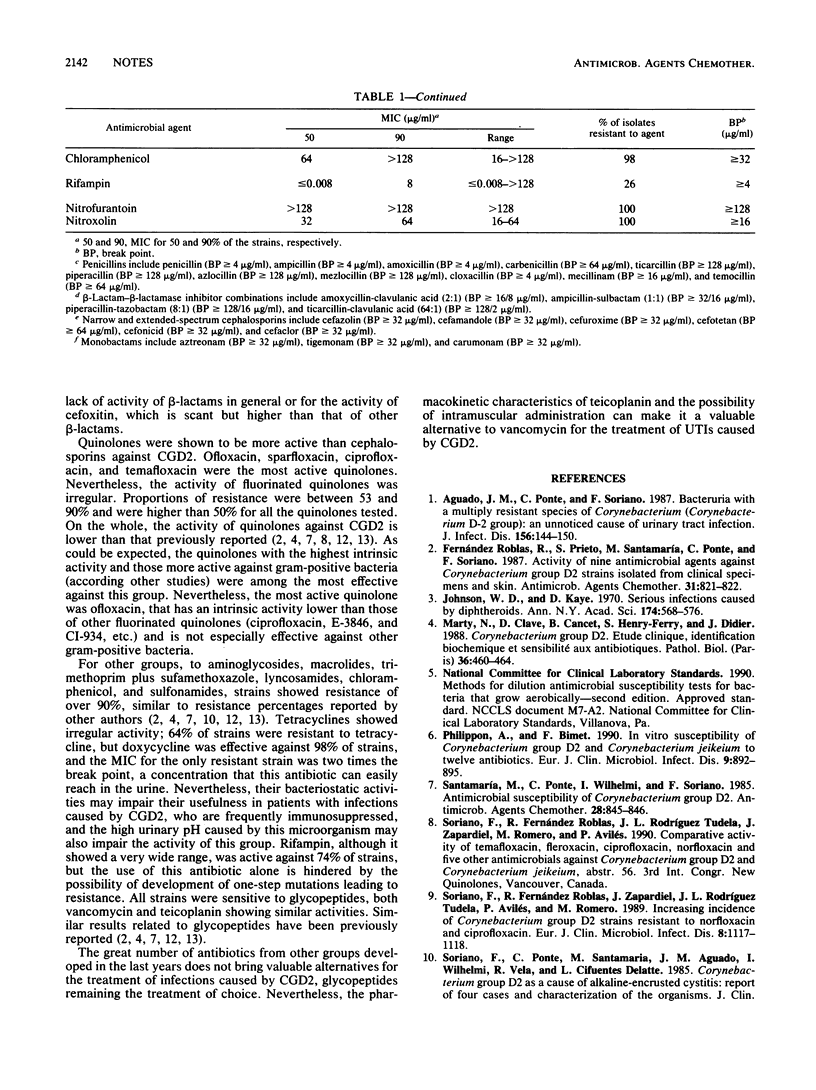
Abstract
Corynebacterium group D2 (CGD2) is involved in urinary tract infections in patients with underlying predisposing factors. This microorganism is highly resistant to a number of antimicrobial agents. We tested the activities of 79 antimicrobial agents against CGD2. beta-Lactams, aminoglycosides, and macrolides were ineffective. Fluorinated quinolones showed irregular activities, ofloxacin being the most active one. Doxycycline, rifampin, and mainly glycopeptides (vancomycin and teicoplanin) were the most active antibiotics against CGD2.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguado J. M., Ponte C., Soriano F. Bacteriuria with a multiply resistant species of Corynebacterium (Corynebacterium group D2): an unnoticed cause of urinary tract infection. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):144–150. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Roblas R., Prieto S., Santamaría M., Ponte C., Soriano F. Activity of nine antimicrobial agents against Corynebacterium group D2 strains isolated from clinical specimens and skin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):821–822. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. D., Kaye D. Serious infections caused by diphtheroids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1970 Oct 30;174(2):568–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1970.tb45582.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty N., Clave D., Cancet B., Henry-Ferry S., Didier J. Corynebacterium groupe D2. Etude clinique, identification biochimique et sensibilité aux antibiotiques. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1988 May;36(5):460–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon A., Bimet F. In vitro susceptibility of Corynebacterium group D2 and Corynebacterium jeikeium to twelve antibiotics. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Dec;9(12):892–895. doi: 10.1007/BF01967505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santamaría M., Ponte C., Wilhelmi I., Soriano F. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Corynebacterium group D2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Dec;28(6):845–846. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.6.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano F., Fernández-Roblas R., Zapardiel J., Rodríguez-Tudela J. L., Avilés P., Romero M. Increasing incidence of Corynebacterium group D2 strains resistant to norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;8(12):1117–1118. doi: 10.1007/BF01975179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano F., Ponte C., Santamaría M., Castilla C., Fernández Roblas R. In vitro and in vivo study of stone formation by Corynebacterium group D2 (Corynebacterium urealyticum). J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):691–694. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.691-694.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano F., Ponte C., Santamaría M., Torres A., Fernández-Roblas R. Susceptibility of urinary isolates of Corynebacterium group D2 to fifteen antimicrobials and acetohydroxamic acid. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Sep;20(3):349–355. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.3.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verschraegen G., Claeys G., Van den Abeele A. M. Comparative in vitro activity of the new quinolone fleroxacin (RO 23-6240). Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;7(1):63–66. doi: 10.1007/BF01962177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



