Abstract
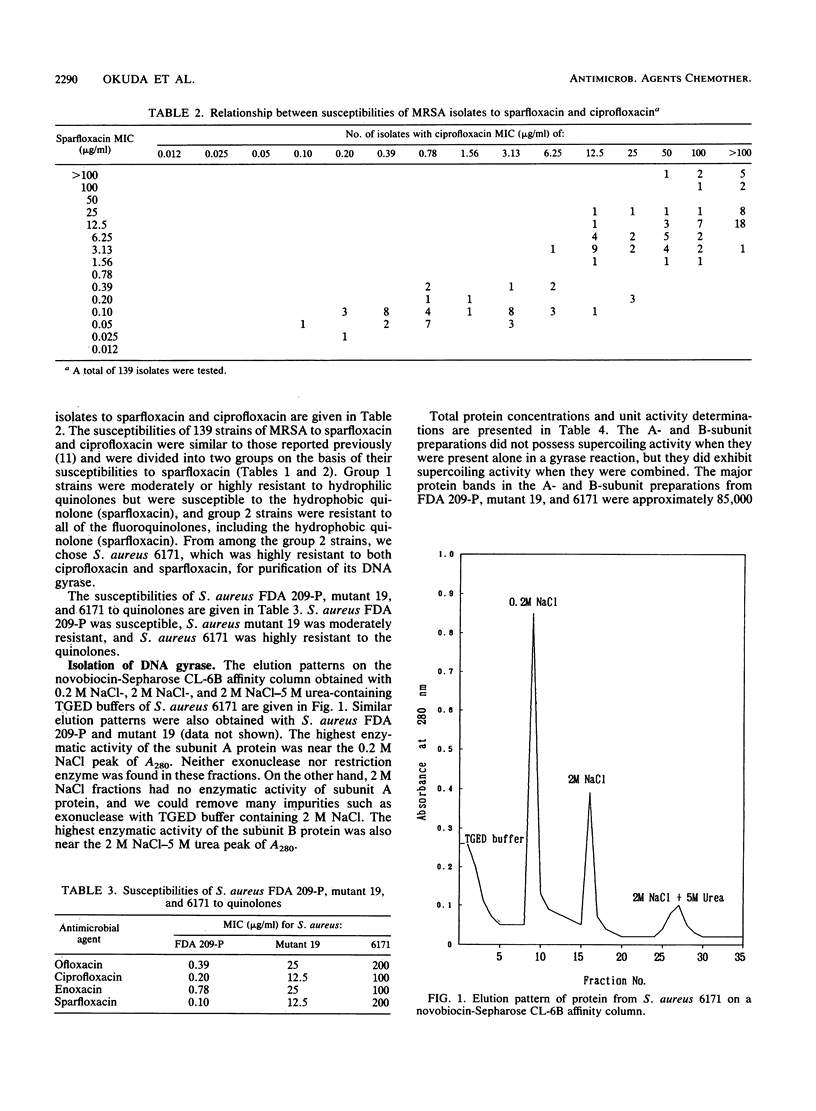
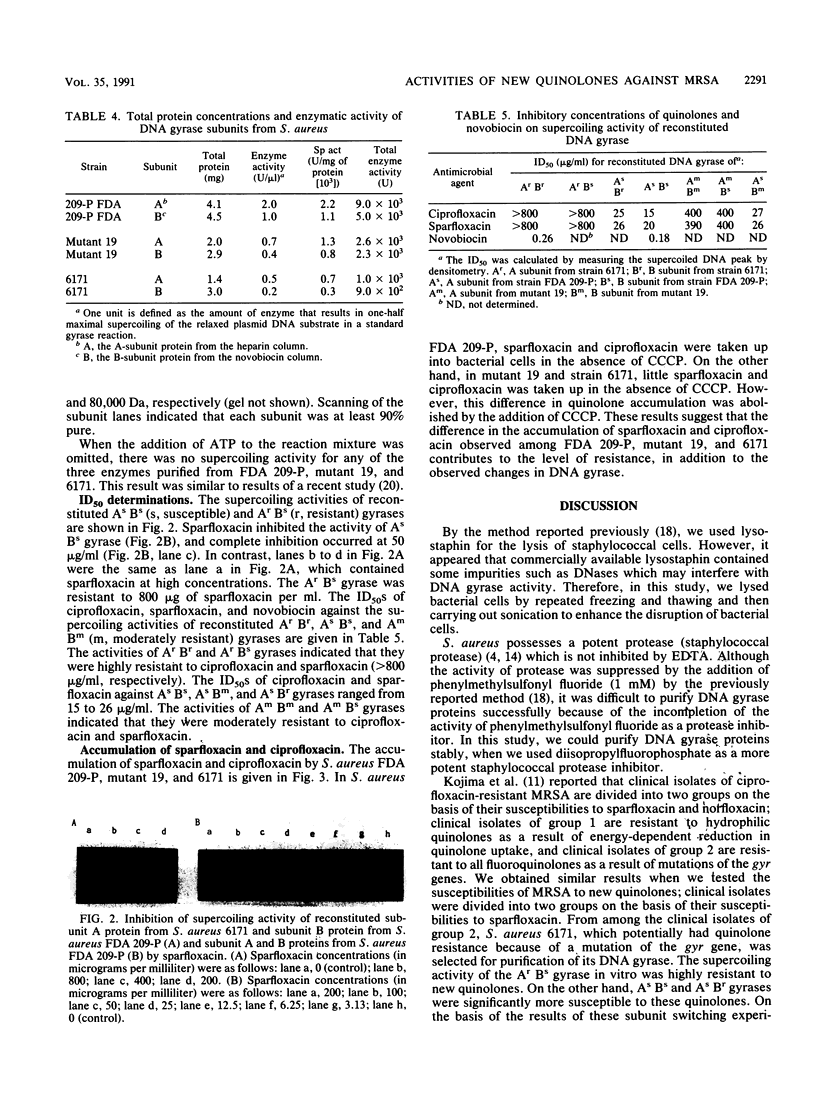
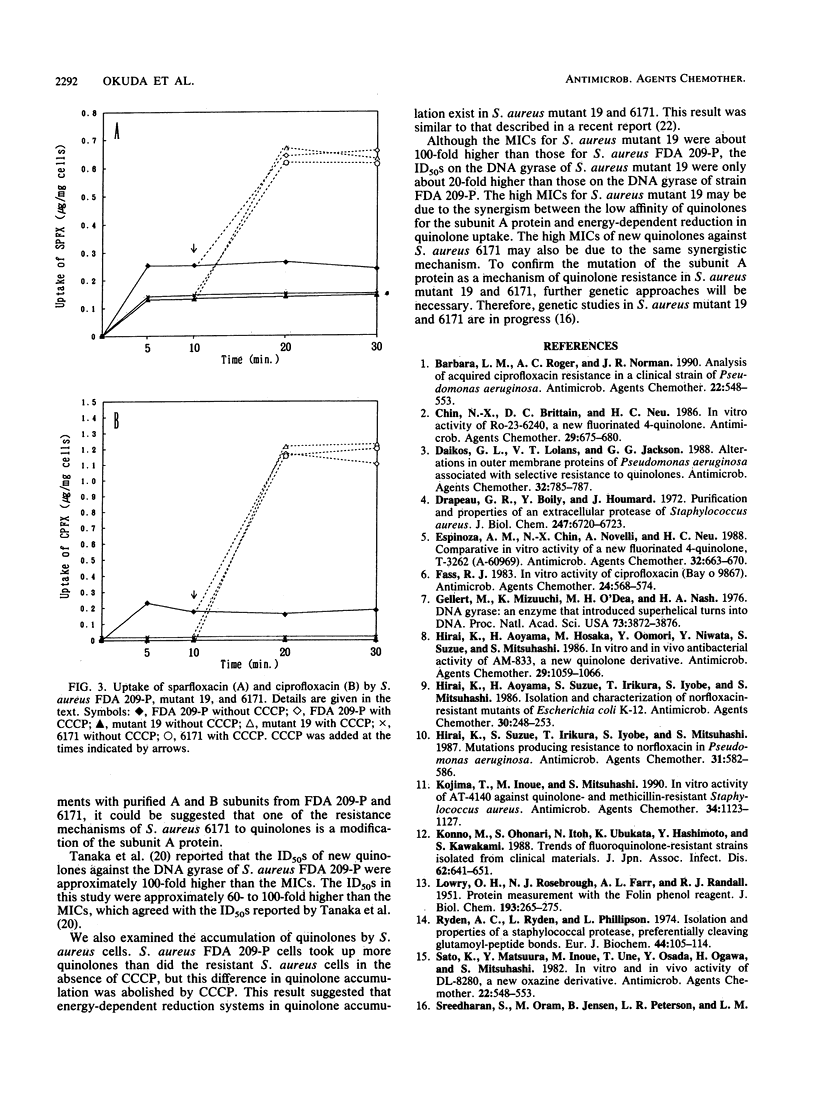
The activities of new quinolones against 140 strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus were determined. From the relationship between the MICs of sparfloxacin and ciprofloxacin, fluoroquinolone-resistant S. aureus 6171 (MIC of sparfloxacin, 200 micrograms/ml; MIC of ciprofloxacin, 100 micrograms/ml) and fluoroquinolone-susceptible S. aureus FDA 209-P were selected for purification of the subunit A and B proteins of their DNA gyrases. The supercoiling activities of reconstituted ArBr (r, resistant) (from strain 6171) and ArBs (s, susceptible) gyrases were 40-fold more resistant to new quinolones than those of AsBs from FDA 209-P and AsBr gyrases. The 50% inhibitory doses of ciprofloxacin and sparfloxacin for AmBm (from mutant 19) and AmBs (m, moderately resistant) gyrases were 15- to 27-fold higher than those for AsBs and AsBm gyrases. These findings indicate that one of the resistance mechanisms of S. aureus against fluoroquinolones is a modification of the gyrase subunit A protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chin N. X., Brittain D. C., Neu H. C. In vitro activity of Ro 23-6240, a new fluorinated 4-quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):675–680. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daikos G. L., Lolans V. T., Jackson G. G. Alterations in outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with selective resistance to quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):785–787. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G. R., Boily Y., Houmard J. Purification and properties of an extracellular protease of Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6720–6726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza A. M., Chin N. X., Novelli A., Neu H. C. Comparative in vitro activity of a new fluorinated 4-quinolone, T-3262 (A-60969). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):663–670. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin (Bay o 9867). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Oct;24(4):568–574. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.4.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Nash H. A. DNA gyrase: an enzyme that introduces superhelical turns into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Aoyama H., Hosaka M., Oomori Y., Niwata Y., Suzue S., Irikura T. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activity of AM-833, a new quinolone derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1059–1066. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Aoyama H., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Isolation and characterization of norfloxacin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):248–253. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Mutations producing resistance to norfloxacin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):582–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima T., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro activity of AT-4140 against quinolone- and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1123–1127. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno M., Ohonari S., Itoh N., Ubukata K., Hashimoto Y., Kawakami S. [Trends of fluoroquinolone-resistant strains isolated from clinical materials]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1988 Jul;62(7):641–651. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.62.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén A. C., Rydén L., Philipson L. Isolation and properties of a staphylococcal protease, preferentially cleaving glutamoyl-peptide bonds. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 2;44(1):105–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Matsuura Y., Inoue M., Une T., Osada Y., Ogawa H., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo activity of DL-8280, a new oxazine derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):548–553. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreedharan S., Oram M., Jensen B., Peterson L. R., Fisher L. M. DNA gyrase gyrA mutations in ciprofloxacin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus: close similarity with quinolone resistance mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7260–7262. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7260-7262.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudenbauer W. L., Orr E. DNA gyrase: affinity chromatography on novobiocin-Sepharose and catalytic properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3589–3603. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahata M., Nishino T. DNA gyrase of Staphylococcus aureus and inhibitory effect of quinolones on its activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1192–1195. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahata M., Otsuki M., Nishino T. In-vitro and in-vivo activities of T-3262, a new pyridone carboxylic acid. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Aug;22(2):143–154. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.2.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Sato K., Kimura Y., Hayakawa I., Osada Y., Nishino T. Inhibition by quinolones of DNA gyrase from Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jul;35(7):1489–1491. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.7.1489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Bogaki M., Nakamura S., Ubukata K., Konno M. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus norA gene, which confers resistance to quinolones. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6942–6949. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6942-6949.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Kojima T., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Uptake of sparfloxacin and norfloxacin by clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):368–370. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



