Abstract
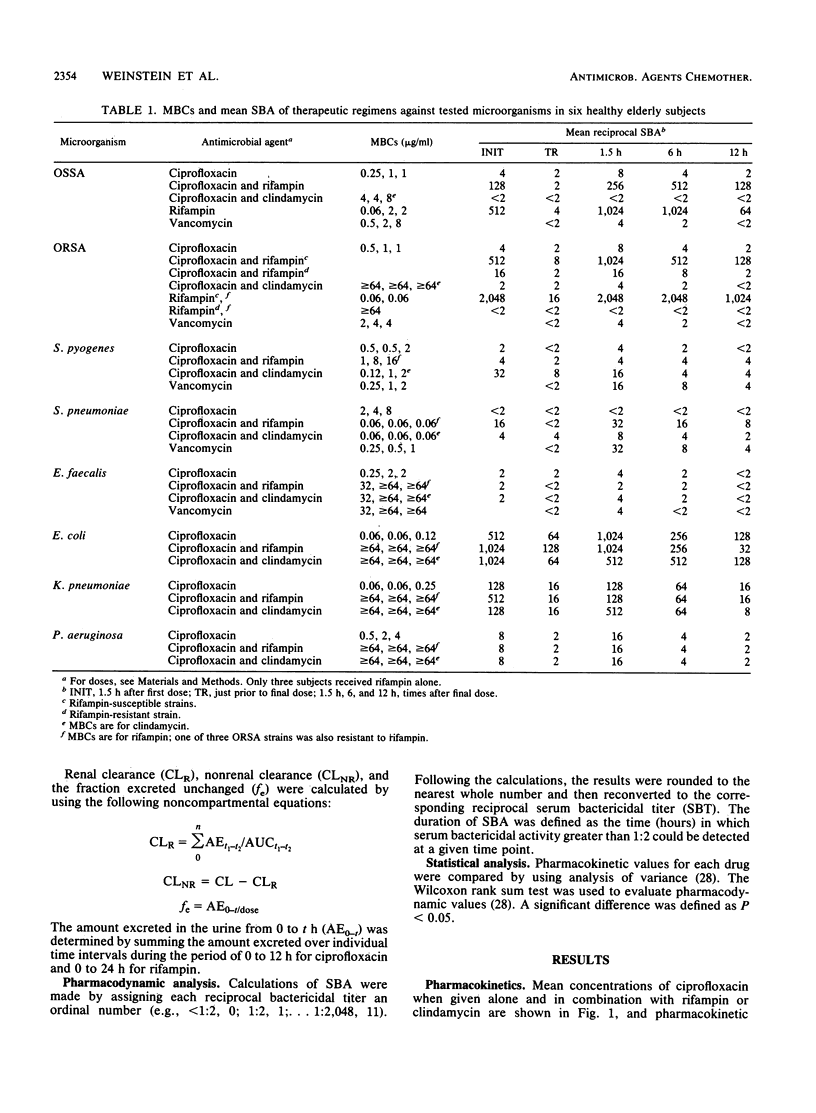
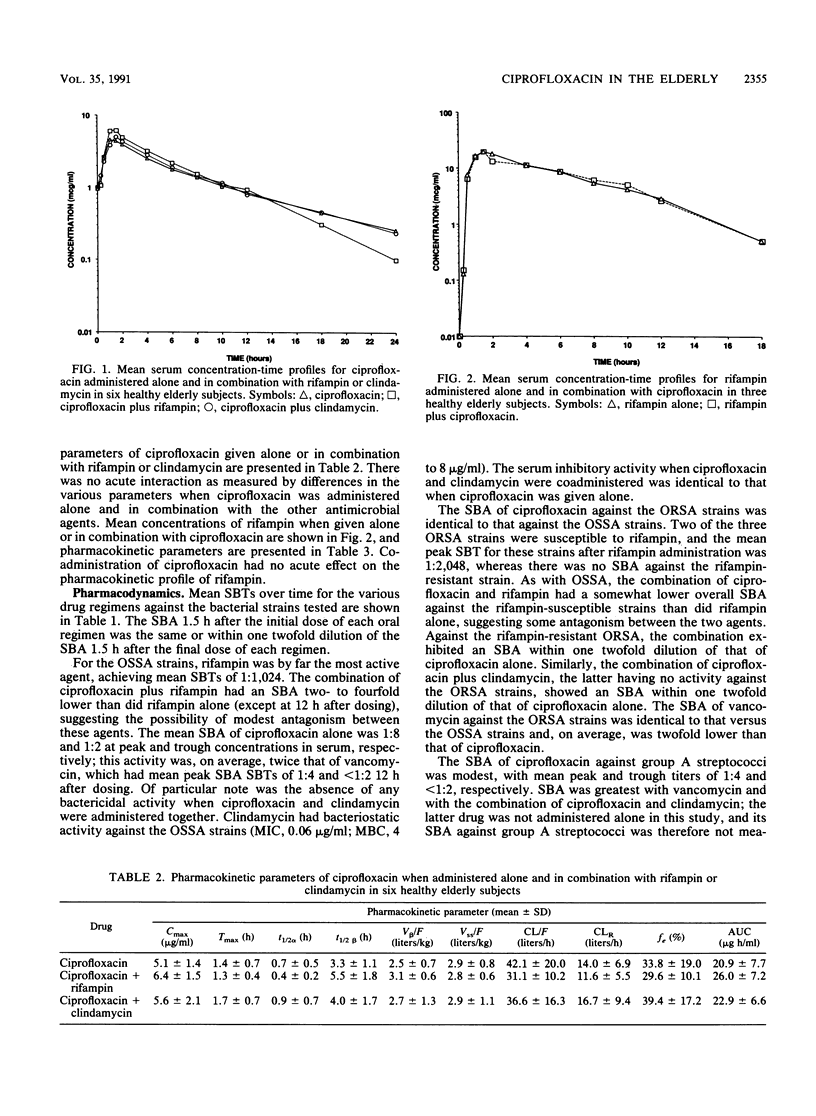
To better define the pharmacokinetics and serum bactericidal activity (SBA) of ciprofloxacin and other antimicrobial agents in the elderly, six healthy (greater than 65 years) volunteers with normal renal function were given ciprofloxacin alone orally, ciprofloxacin plus rifampin orally, ciprofloxacin plus clindamycin orally, rifampin alone orally (three volunteers), and, for comparison of SBA against gram-positive cocci, vancomycin intravenously. Mean peak ciprofloxacin concentrations and other pharmacokinetic parameters were not altered significantly by coadministration of either rifampin or clindamycin. Ciprofloxacin had somewhat greater SBA against the oxacillin-susceptible and oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains tested than did vancomycin, but rifampin was by far the most active single agent tested. The SBA of rifampin against S. aureus was modestly antagonized during combination therapy with ciprofloxacin, but substantial SBA still was present. The ciprofloxacin SBA against S. aureus was completely antagonized by clindamycin if the strains were susceptible to the latter agent. Ciprofloxacin had modest SBA against group A streptococci and no SBA against the three pneumococcal strains tested. All of the regimens had poor to absent SBA against Enterococcus faecalis. By contrast, ciprofloxacin had excellent SBA against Escherchia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae and moderate SBA against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Combination therapy with rifampin or clindamycin in general enhanced the SBA against the nonenterococcal streptococci and had no effect on the SBA against the gram-negative bacilli.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acocella G. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of rifampin in humans. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5 (Suppl 3):S428–S432. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_3.s428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Advenier C., Gobert C., Houin G., Bidet D., Richelet S., Tillement J. P. Pharmacokinetic studies of rifampicin in the elderly. Ther Drug Monit. 1983;5(1):61–65. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198303000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R., Chapman J., Drew W. L. Comparison of bactericidal activity of five antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):1023–1025. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckh M., Lode H., Deppermann K. M., Grineisen S., Shokry F., Held R., Wernicke K., Koeppe P., Wagner J., Krasemann C. Pharmacokinetics and serum bactericidal activities of quinolones in combination with clindamycin, metronidazole, and ornidazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Dec;34(12):2407–2414. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.12.2407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittain D. C., Scully B. E., McElrath M. J., Steinman R., Labthavikul P., Neu H. C. The pharmacokinetics and serum and urine bactericidal activity of ciprofloxacin. J Clin Pharmacol. 1985 Mar;25(2):82–88. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1985.tb02806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler M. H., Toler S. M., Rapp R. P., Muder R. R., Korvick J. A. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of concurrent oral ciprofloxacin and rifampin therapy in elderly patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Mar;34(3):442–447. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.3.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin R. J., Lee B. L., Sande M. A., Chambers H. F. Treatment of right-sided Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis in intravenous drug users with ciprofloxacin and rifampicin. Lancet. 1989 Nov 4;2(8671):1071–1073. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin R., Modin G., Kunz S., Rich R., Zak O., Sande M. Comparative efficacies of ciprofloxacin, pefloxacin, and vancomycin in combination with rifampin in a rat model of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus chronic osteomyelitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1014–1016. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. O., Rodriguez G. G. Oral ciprofloxacin compared with parenteral antibiotics in the treatment of osteomyelitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):40–43. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guay D. R., Awni W. M., Peterson P. K., Obaid S., Breitenbucher R., Matzke G. R. Pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin in acutely ill and convalescent elderly patients. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):124–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackbarth C. J., Chambers H. F., Sande M. A. Serum bactericidal activity of rifampin in combination with other antimicrobial agents against Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):611–613. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry N. K., Rouse M. S., Whitesell A. L., McConnell M. E., Wilson W. R. Treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus experimental osteomyelitis with ciprofloxacin or vancomycin alone or in combination with rifampin. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):73–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata C. A., Guay D. R., Awni W. M., Stein D. J., Peterson P. K. Steady-state pharmacokinetics of intravenous and oral ciprofloxacin in elderly patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1927–1931. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Ng E. Y., Swartz M. N. Mechanisms of action of and resistance to ciprofloxacin. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):12–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Barriere S. L., Schaberg D. R., Fekety R. The emergence of resistance to ciprofloxacin during treatment of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Nov;20(5):753–758. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.5.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Barriere S. L., Albrecht L. M., Rybak M. J. Ciprofloxacin and rifampin, alone and in combination, for therapy of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1184–1187. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton S. J., Shull V. H., Dick J. D. Determination of norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin concentrations in serum and urine by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):325–327. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Synergy of fluoroquinolones with other antimicrobial agents. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jul-Aug;11 (Suppl 5):S1025–S1035. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_5.s1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuman M. Clinical pharmacokinetics of the newer antibacterial 4-quinolones. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1988 Feb;14(2):96–121. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198814020-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piercy E. A., Barbaro D., Luby J. P., Mackowiak P. A. Ciprofloxacin for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):128–130. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J., Stoehr G., Yu V. L., Muder R. R., Matador A., Kamerer D. B. Efficacy of oral ciprofloxacin plus rifampin for treatment of malignant external otitis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1989 Sep;115(9):1063–1069. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1989.01860330053016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalit I., Berger S. A., Gorea A., Frimerman H. Widespread quinolone resistance among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in a general hospital. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):593–594. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford H. C., Drusano G. L., Forrest A., Tatem B., Plaisance K. Bactericidal activity of ciprofloxacin compared with that of cefotaxime in normal volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Aug;31(8):1177–1182. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.8.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera P., Joly P. Comparative in-vitro activities of teicoplanin, vancomycin, coumermycin and ciprofloxacin, alone and in combination with rifampicin or LM 427, against Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Mar;19(3):313–320. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera P., Klastersky J. Bactericidal activity and killing rate of serum in volunteers receiving ciprofloxacin alone or in combination with vancomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):892–895. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. P., Stratton C. W., Ackley A., Hawley H. B., Robinson P. A., Fisher B. D., Alcid D. V., Stephens D. S., Reller L. B. Multicenter collaborative evaluation of a standardized serum bactericidal test as a prognostic indicator in infective endocarditis. Am J Med. 1985 Feb;78(2):262–269. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90436-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. P., Stratton C. W., Hawley H. B., Ackley A., Reller L. B. Multicenter collaborative evaluation of a standardized serum bactericidal test as a predictor of therapeutic efficacy in acute and chronic osteomyelitis. Am J Med. 1987 Aug;83(2):218–222. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90688-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



