Abstract
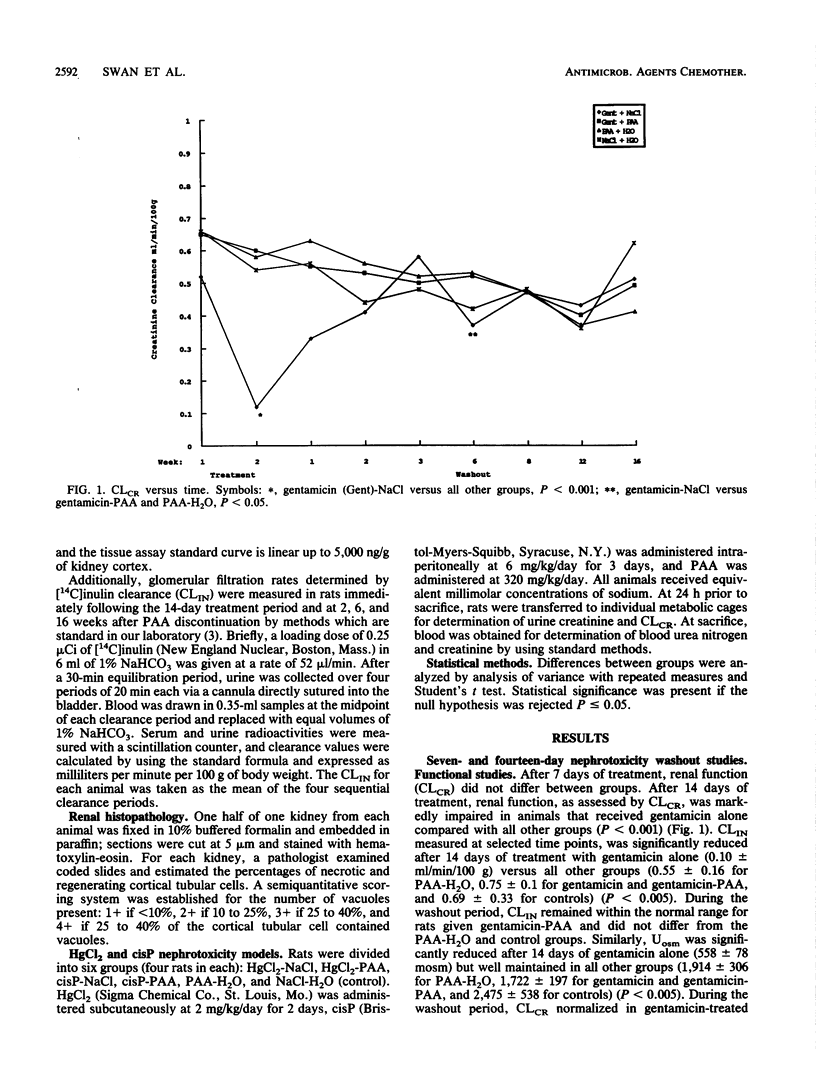
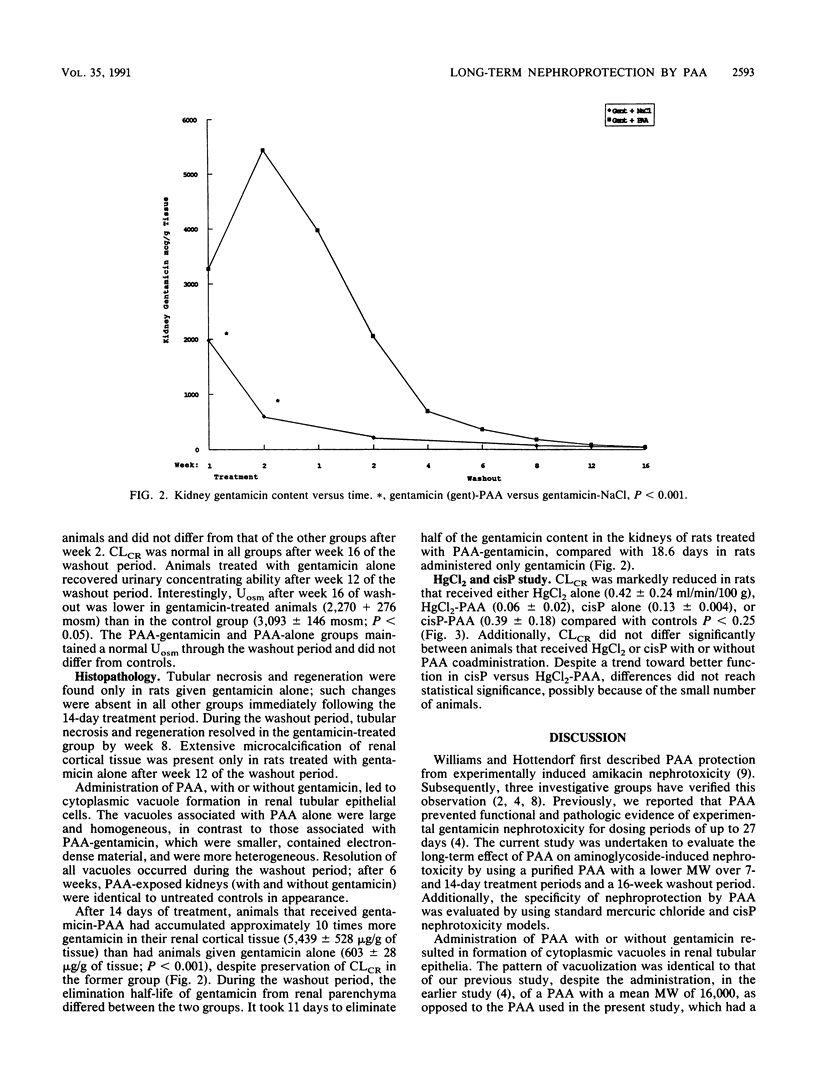
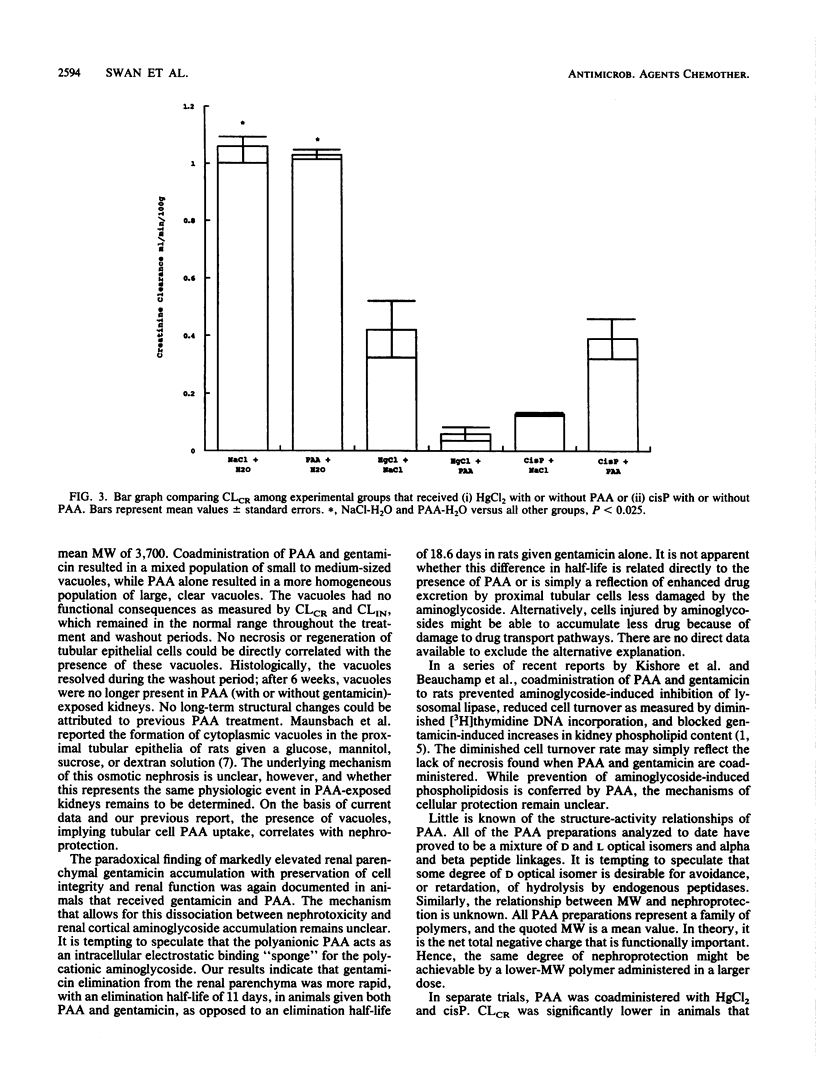
Polyaspartic Acid (PAA) protects the kidney from experimental gentamicin nephrotoxicity despite large increases in renal cortical gentamicin content. In these experiments, prominent cytoplasmic vacuoles were noted in all animals that received PAA with or without gentamicin. The present study showed that there were no renal structural or functional consequences of PAA given alone or with gentamicin for up to 14 days, followed by a 16-week washout period. Creatinine clearance was similar to that of controls in animals that received gentamicin and in those that received PAA alone. Thus, complete functional protection was conferred by PAA and gentamicin, confirming previous reports from our laboratory. There was no protection by PAA from the nephrotoxic effects of mercuric chloride and cis-platinum.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beauchamp D., Laurent G., Maldague P., Abid S., Kishore B. K., Tulkens P. M. Protection against gentamicin-induced early renal alterations (phospholipidosis and increased DNA synthesis) by coadministration of poly-L-aspartic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Nov;255(2):858–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp D., Laurent G., Maldague P., Tulkens P. M. Reduction of gentamicin nephrotoxicity by the concomitant administration of poly-l-aspartic acid and poly-l-asparagine in rats. Arch Toxicol Suppl. 1986;9:306–309. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71248-7_52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English J., Evan A., Houghton D. C., Bennett W. M. Cyclosporine-induced acute renal dysfunction in the rat. Evidence of arteriolar vasoconstriction with preservation of tubular function. Transplantation. 1987 Jul;44(1):135–141. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198707000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. N., Wood C. A., Kohlhepp S. J., Kohnen P. W., Houghton D. C., Finkbeiner H. C., Lindsley J., Bennett W. M. Polyaspartic acid prevents experimental aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):945–953. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishore B. K., Kállay Z., Lambricht P., Laurent G., Tulkens P. M. Mechanism of protection afforded by polyaspartic acid against gentamicin-induced phospholipidosis. I. Polyaspartic acid binds gentamicin and displaces it from negatively charged phospholipid layers in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Nov;255(2):867–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAUNSBACH A. B., MADDEN S. C., LATTA H. Light and electron microscopic changes in proximal tubules of rats after administration of glucose, mannitol, sucrose, or dextran. Lab Invest. 1962 Jun;11:421–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzke G. R., Lucarotti R. L., Shapiro H. S. Controlled comparison of gentamicin and tobramycin nephrotoxicity. Am J Nephrol. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):11–17. doi: 10.1159/000166680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsammy L. S., Josepovitz C., Lane B. P., Kaloyanides G. J. Polyaspartic acid protects against gentamicin nephrotoxicity in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jul;250(1):149–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. D., Hottendorf G. H., Bennett D. B. Inhibition of renal membrane binding and nephrotoxicity of aminoglycosides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jun;237(3):919–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. D., Hottendorf G. H. Inhibition of renal membrane binding and nephrotoxicity of gentamicin by polyasparagine and polyaspartic acid in the rat. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;47(2):317–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


