Abstract
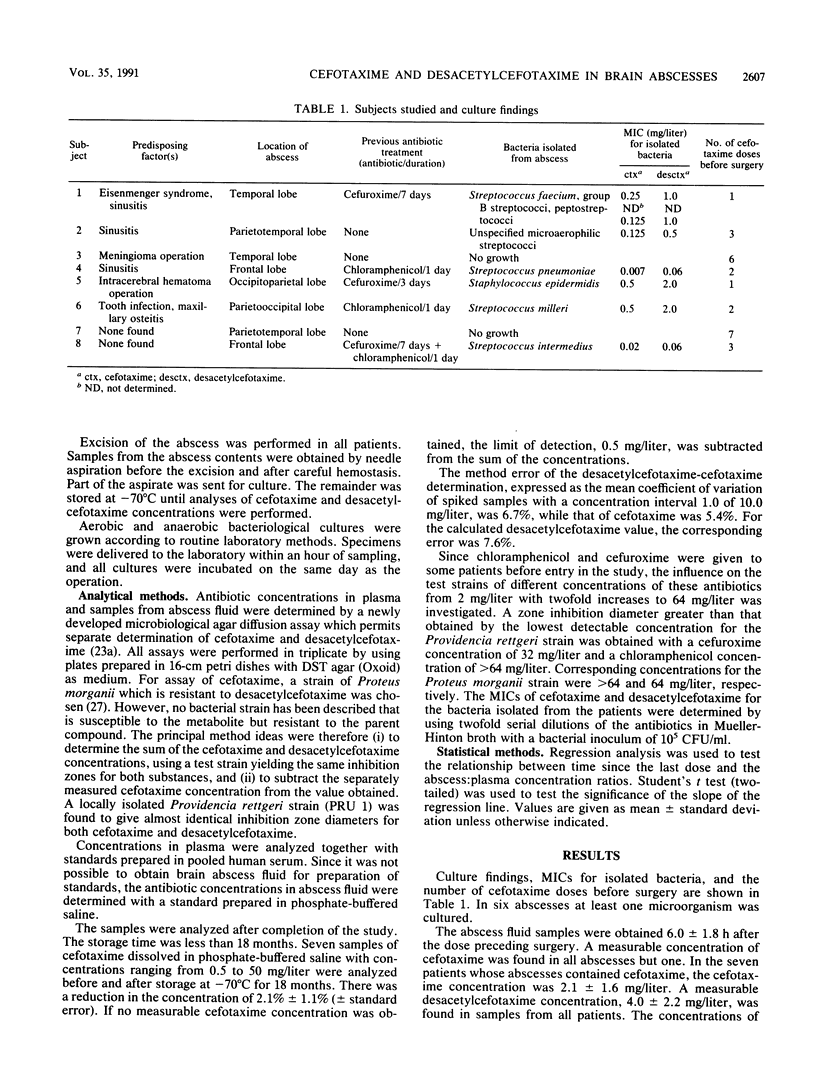
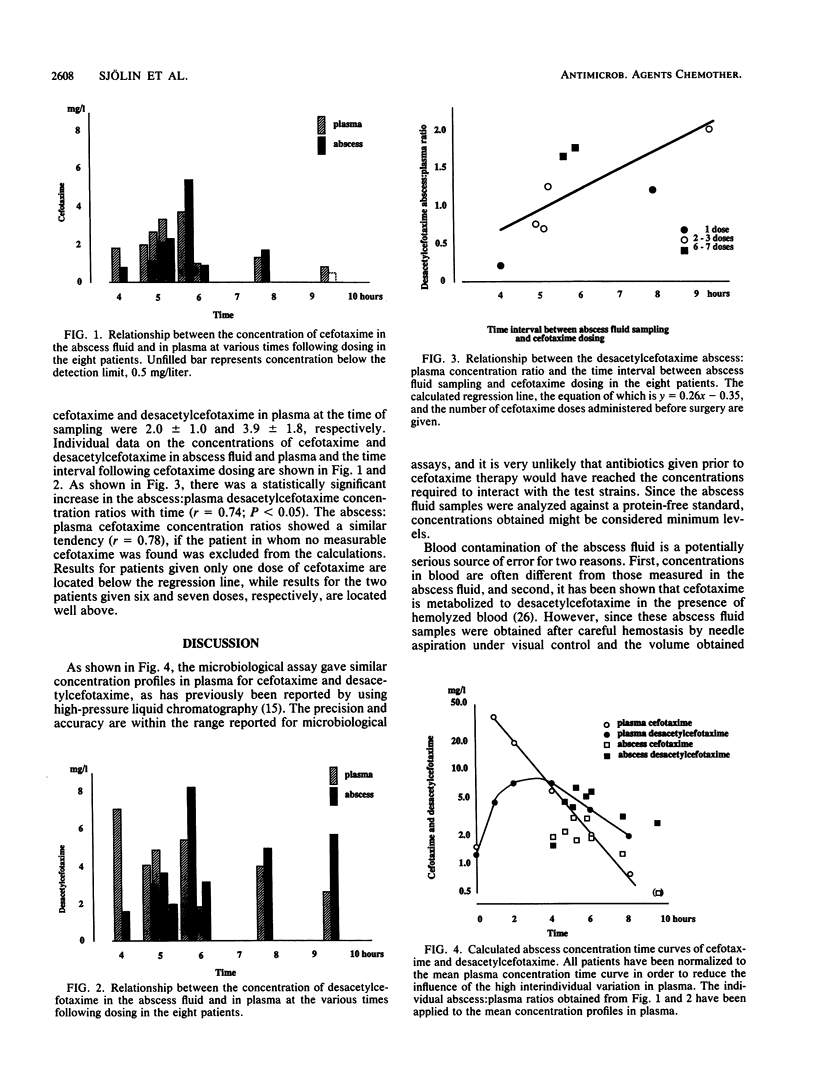
Since clinical trials comparing the efficacies of different antibiotic regimens for treatment of brain abscesses are difficult to perform, the choice of antibiotics must rely on the antibacterial spectrum and the ability of the drug to penetrate into the abscess fluid. The aim of this investigation was to study the ability of cefotaxime and its active metabolite desacetylcefotaxime to penetrate into brain abscesses. Eight patients were given 3 g of cefotaxime intravenously every 8 h. Abscess fluid samples, obtained at surgery at various times after dosing, and blood samples were analyzed for their concentrations of cefotaxime and desacetylcefotaxime by using a newly developed microbiological assay. The brain abscess concentrations of cefotaxime and desacetylcefotaxime were 1.9 +/- 1.7 and 4.0 +/- 2.2 mg/liter, respectively. Simultaneous concentrations in plasma were 2.0 +/- 1.0 and 3.9 +/- 1.8 mg/liter, respectively. With increasing time following cefotaxime dosing there was a significant increase in the abscess:plasma concentration ratio of desacetylcefotaxime. Since both cefotaxime and desacetylcefotaxime penetrate well into the brain abscess, reaching concentrations above the MIC for probable bacteria except gram-negative anaerobes, it is concluded that cefotaxime in combination with metronidazole may be used as an alternative in the treatment of brain abscesses.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderson D., Strong A. J., Ingham H. R., Selkon J. B. Fifteen-year review of the mortality of brain abscess. Neurosurgery. 1981 Jan;8(1):1–6. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198101000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black P., Graybill J. R., Charache P. Penetration of brain abscess by systemically administered antibiotics. J Neurosurg. 1973 Jun;38(6):705–709. doi: 10.3171/jns.1973.38.6.0705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cars O., Ogren S. Antibiotic tissue concentrations: methodological aspects and interpretation of results. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1985;44:7–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cars O. Pharmacokinetics of antibiotics in tissues and tissue fluids: a review. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1990;74:23–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombes J. D. Metabolism of cefotaxime in animals and humans. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Sep-Oct;4 (Suppl):S325–S332. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_2.s325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett E. D., Strausbaugh L. J. Antimicrobial agents and the central nervous system. Neurosurgery. 1980 Jun;6(6):691–714. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198006000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George R. H., Bint A. J. Letter: Treatment of a brain abscess due to Bacteroides fragilis with metronidazole. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Mar;2(1):101–102. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.1.101-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girgis N. I., Yassin M. W., Sanborn W. R., Burdick R. E., el-Ela H. A., Kent D. C., Sorensen K., Nabil I. M. Ampicillin compared with penicillin and chloramphenicol combined in the treatment of bacterial meningitis. J Trop Med Hyg. 1972 Aug;75(8):154–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H. T., O'Donoghue M. A., Shaw M. D., Dowling C. Penetration of ceftazidime into intracranial abscess. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Sep;24(3):431–436. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.3.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham H. R., Slekon J. B., Roxby C. M. Bacteriological study of otogenic cerebral abscesses: chemotherapeutic role of metronidazole. Br Med J. 1977 Oct 15;2(6093):991–993. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6093.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ings R. M., Reeves D. S., White L. O., Bax R. P., Bywater M. J., Holt H. A. The human pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime and its metabolites and the role of renal tubular secretion on their elimination. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1985 Apr;13(2):121–142. doi: 10.1007/BF01059394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAWETZ E., GUNNISON J. B., SPECK R. S., COLEMAN V. R. Studies on antibiotic synergism and antagonism; the interference of chloramphenicol with the action of penicillin. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1951 Mar;87(3):349–359. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1951.03810030022002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kourtópoulos H., Holm S. E., Norrby S. R. The influence of steroids on the penetration of antibiotics into brain tissue and brain abscesses. An experimental study in rats. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Mar;11(3):245–249. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.3.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer P. W., Griffith R. S., Campbell R. L. Antibiotic penetration of the brain. A comparative study. J Neurosurg. 1969 Sep;31(3):295–302. doi: 10.3171/jns.1969.31.3.0295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. M., Gutin P. H., Baskin D. S., Pons V. G. Vancomycin penetration of a brain abscess: case report and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 1986 May;18(5):632–636. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198605000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby R. A review of the penetration of antibiotics into CSF and its clinical significance. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):296–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliamser S. E., Bäckman K., Norrby S. R. Intracranial abscesses in adults: an analysis of 54 consecutive cases. Scand J Infect Dis. 1988;20(1):1–9. doi: 10.3109/00365548809117210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn S., Bakhtiar M. Comparative in vitro studies on cefotaxime and desacetylcefotaxime. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1986;12(12):953–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. D., Bawdon R. E. Cefotaxime metabolism by hemolyzed blood: quantitation and inhibition of the deacetylation reaction. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;4(2):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(86)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Wright N., Wills P. J. Pharmacology of cefotaxime and its desacetyl metabolite in renal and hepatic disease. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):526–531. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wispelwey B., Scheld W. M. Brain abscess. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1987 Dec;10(6):483–510. doi: 10.1097/00002826-198712000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Louvois J., Gortavai P., Hurley R. Bacteriology of abscesses of the central nervous system: a multicentre prospective study. Br Med J. 1977 Oct 15;2(6093):981–984. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6093.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Louvois J., Gortvai P., Hurley R. Antibiotic treatment of abscesses of the central nervous system. Br Med J. 1977 Oct 15;2(6093):985–987. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6093.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Louvois J., Hurley R. Inactivation of penicillin by purulent exudates. Br Med J. 1977 Apr 16;1(6067):998–1000. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6067.998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Louvois J. The bacteriology and chemotherapy of brain abscess. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Sep;4(5):395–413. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.5.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


