Abstract
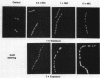
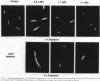
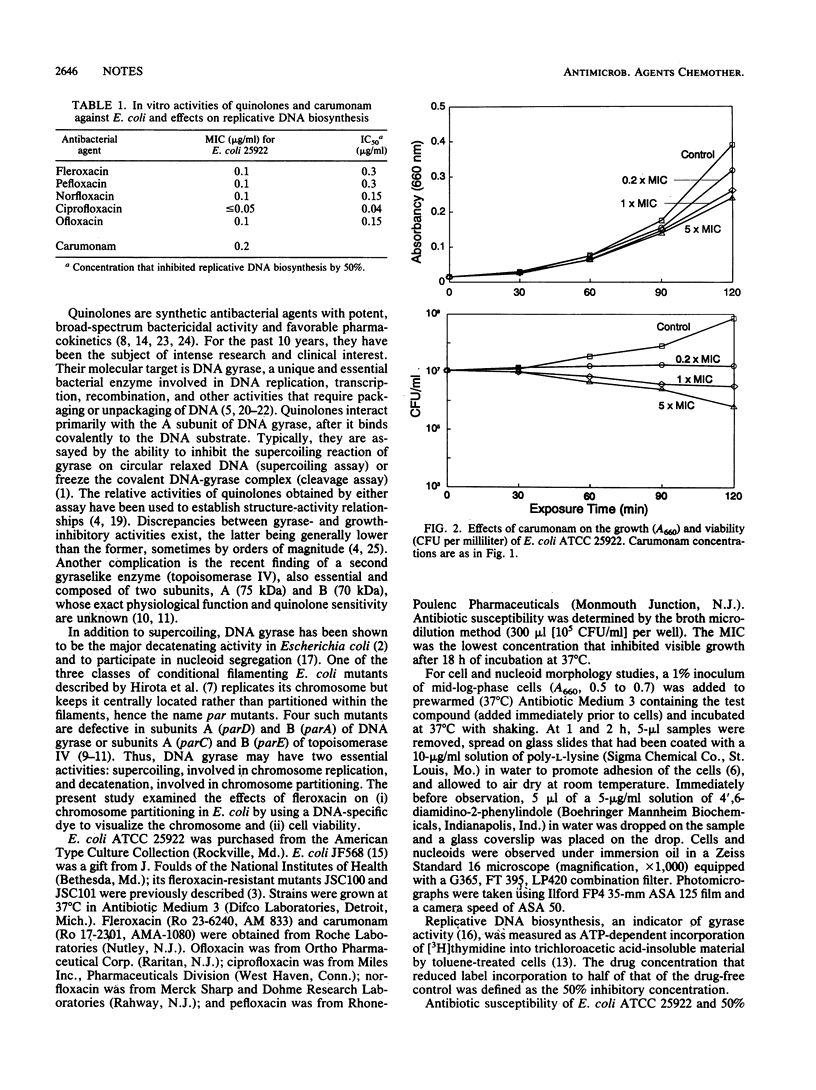
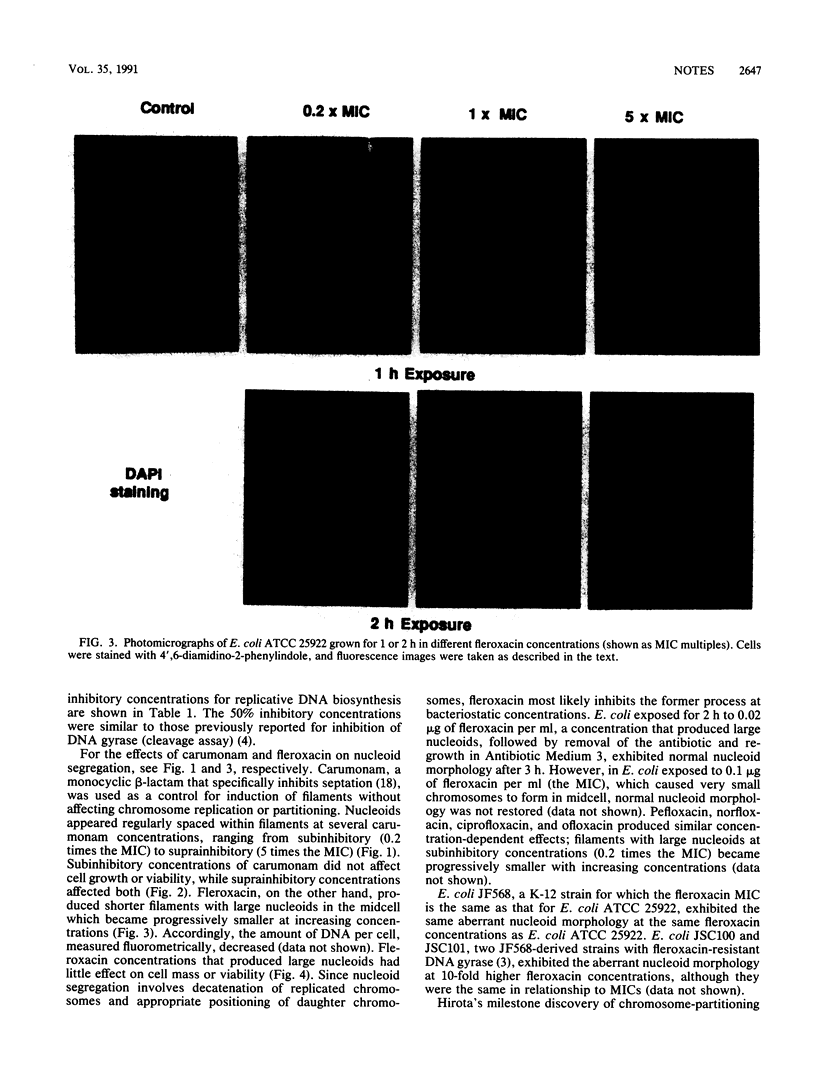
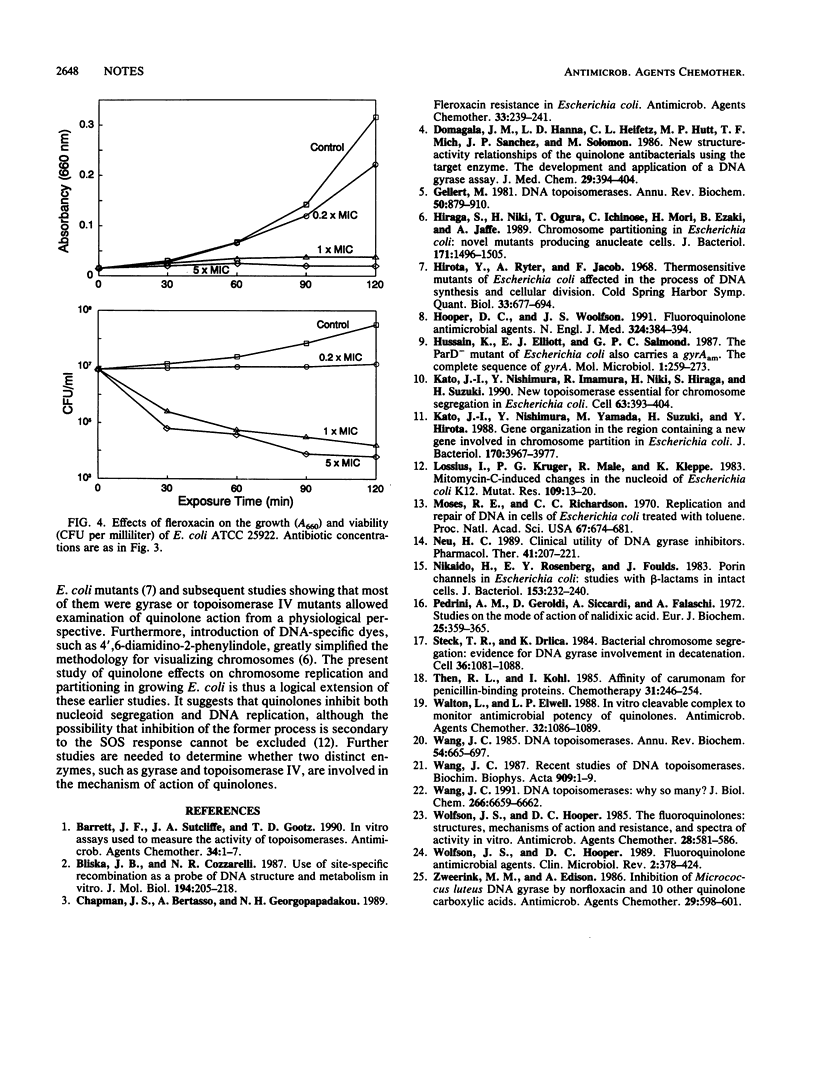
The effects of quinolone antibiotics on nucleoid segregation in growing Escherichia coli were examined by using fleroxacin (Ro 23-6240, AM 833) as a prototype compound. At levels that were close to its MIC and induced growth arrest and filamentation, fleroxacin caused large nucleoids to appear in midcell, suggesting inhibition of nucleoid segregation. With increasing fleroxacin concentrations, nucleoids became progressively smaller, suggesting inhibition of DNA replication. Removal of fleroxacin restored normal cell and nucleoid morphology in filaments with large nucleoids but not in filaments with small nucleoids. The results are consistent with inhibition of chromosome decatenation at low quinolone concentrations (bacteriostatic effect) and DNA supercoiling at high concentrations (bactericidal effect).
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett J. F., Sutcliffe J. A., Gootz T. D. In vitro assays used to measure the activity of topoisomerases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliska J. B., Cozzarelli N. R. Use of site-specific recombination as a probe of DNA structure and metabolism in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 20;194(2):205–218. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90369-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. S., Bertasso A., Georgopapadakou N. H. Fleroxacin resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Feb;33(2):239–241. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.2.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domagala J. M., Hanna L. D., Heifetz C. L., Hutt M. P., Mich T. F., Sanchez J. P., Solomon M. New structure-activity relationships of the quinolone antibacterials using the target enzyme. The development and application of a DNA gyrase assay. J Med Chem. 1986 Mar;29(3):394–404. doi: 10.1021/jm00153a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraga S., Niki H., Ogura T., Ichinose C., Mori H., Ezaki B., Jaffé A. Chromosome partitioning in Escherichia coli: novel mutants producing anucleate cells. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1496–1505. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1496-1505.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota Y., Ryter A., Jacob F. Thermosensitive mutants of E. coli affected in the processes of DNA synthesis and cellular division. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:677–693. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S. Fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agents. N Engl J Med. 1991 Feb 7;324(6):384–394. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199102073240606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain K., Elliott E. J., Salmond G. P. The parD- mutant of Escherichia coli also carries a gyrAam mutation. The complete sequence of gyrA. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Nov;1(3):259–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb01932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Nishimura Y., Imamura R., Niki H., Hiraga S., Suzuki H. New topoisomerase essential for chromosome segregation in E. coli. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):393–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90172-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Nishimura Y., Yamada M., Suzuki H., Hirota Y. Gene organization in the region containing a new gene involved in chromosome partition in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3967–3977. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3967-3977.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lossius I., Krüger P. G., Male R., Kleppe K. Mitomycin-C-induced changes in the nucleoid of Escherichia coli K12. Mutat Res. 1983 Apr;109(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(83)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses R. E., Richardson C. C. Replication and repair of DNA in cells of Escherichia coli treated with toluene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):674–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Clinical utility of DNA gyrase inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;41(1-2):207–221. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Rosenberg E. Y., Foulds J. Porin channels in Escherichia coli: studies with beta-lactams in intact cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):232–240. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.232-240.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrini A. M., Geroldi D., Siccardi A., Falaschi A. Studies on the mode of action of nalidixic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Feb 15;25(2):359–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. R., Drlica K. Bacterial chromosome segregation: evidence for DNA gyrase involvement in decatenation. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1081–1088. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Then R. L., Kohl I. Affinity of carumonam for penicillin-binding proteins. Chemotherapy. 1985;31(4):246–254. doi: 10.1159/000238343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton L., Elwell L. P. In vitro cleavable-complex assay to monitor antimicrobial potency of quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jul;32(7):1086–1089. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.7.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases: why so many? J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6659–6662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Recent studies of DNA topoisomerases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 6;909(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. Fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agents. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Oct;2(4):378–424. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.4.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. The fluoroquinolones: structures, mechanisms of action and resistance, and spectra of activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):581–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink M. M., Edison A. Inhibition of Micrococcus luteus DNA gyrase by norfloxacin and 10 other quinolone carboxylic acids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):598–601. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]