Abstract
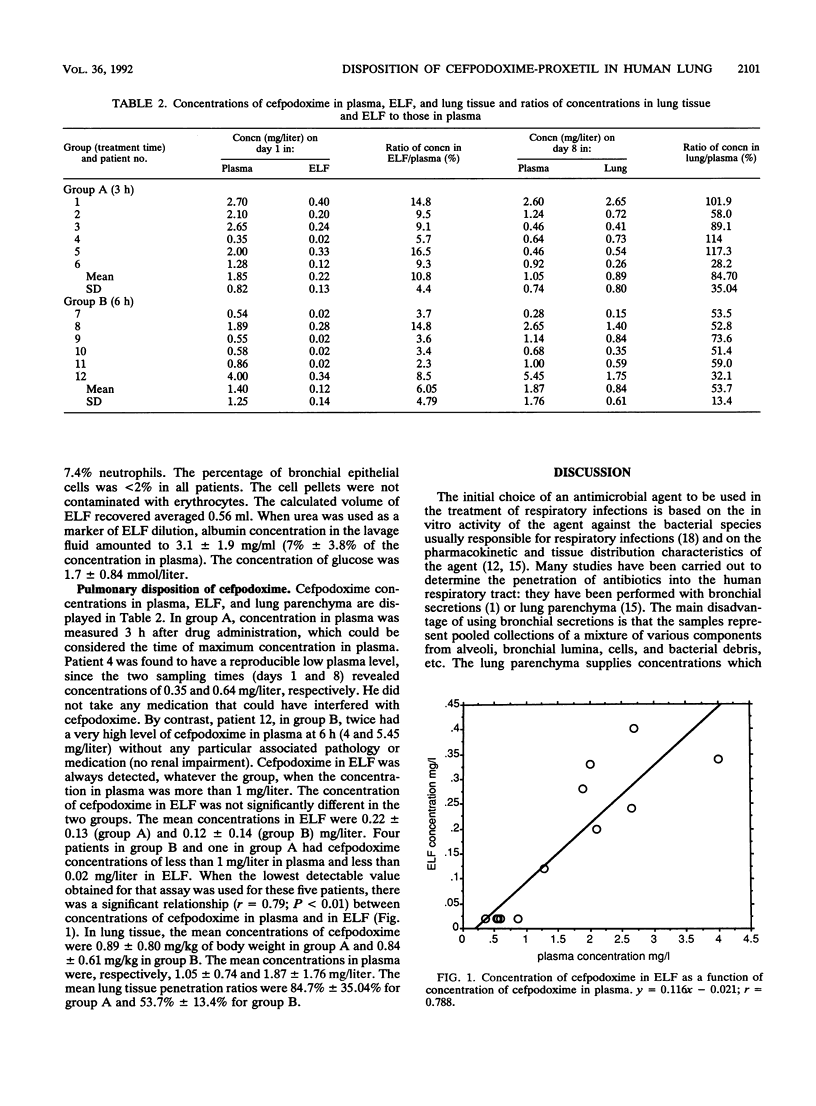
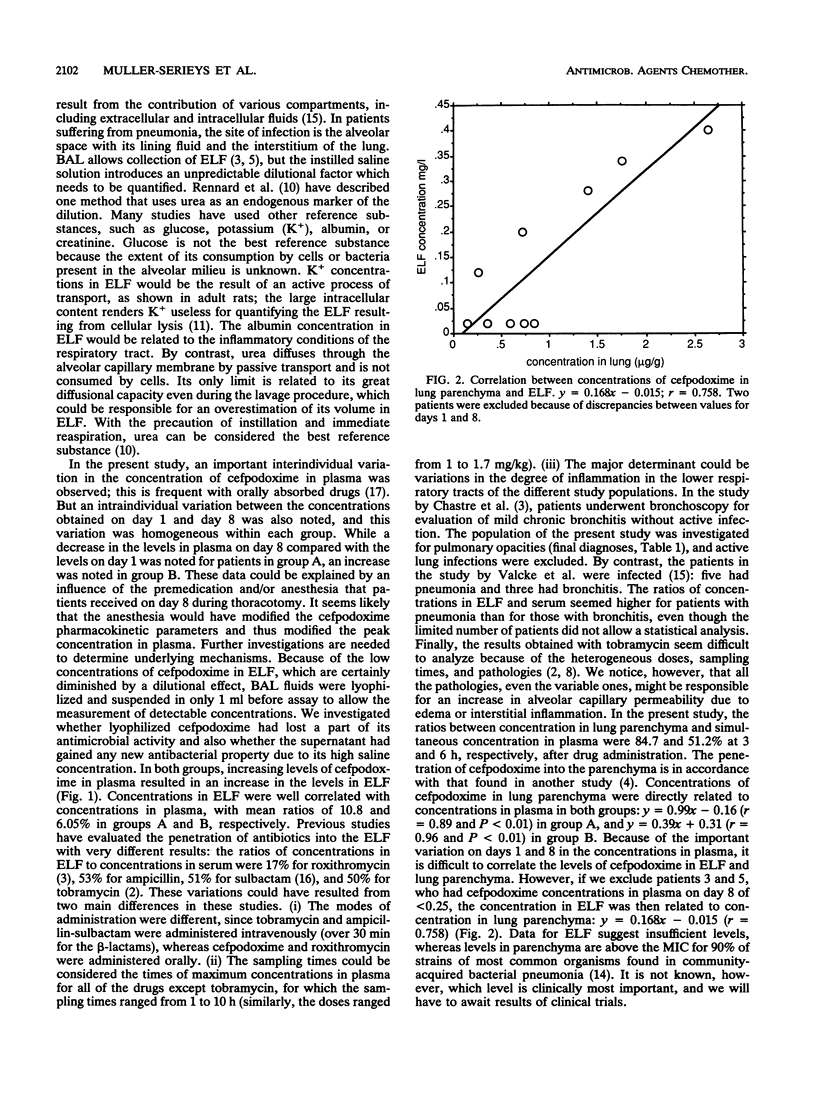
The pulmonary disposition of cefpodoxime was studied in 12 patients with pulmonary opacities after a single oral dose of 260 mg of cefpodoxime-proxetil, which is equivalent to 200 mg of cefpodoxime. Blood and lung tissue samples were collected during surgery, and bronchoalveolar lavage was carried out 3 h (group A) or 6 h (group B) after drug administration. Urea was used as an endogenous marker for measurement of the volume of epithelial lining fluid (ELF). Concentrations were measured by using a microbiological assay. The mean concentrations of cefpodoxime in plasma, ELF, and lung tissue were, respectively, 1.85 +/- 0.82 mg/liter, 0.22 +/- 0.13 mg/liter, and 0.89 +/- 0.80 mg/kg of body weight in group A and 1.40 +/- 1.25 mg/liter, 0.12 +/- 0.14 mg/liter, and 0.84 +/- 0.61 mg/kg in group B. Concentrations in lung parenchyma 6 h after dosing were at least equal to or above the MICs for 90% of the strains of most organisms commonly found in respiratory tract infections, whereas data for ELF suggest levels of drug insufficient to inhibit bacteria.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braude A. C., Hornstein A., Klein M., Vas S., Rebuck A. S. Pulmonary disposition of tobramycin. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5):563–565. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chastre J., Brun P., Fourtillan J. B., Soler P., Basset G., Manuel C., Trouillet J. L., Gibert C. Pulmonary disposition of roxithromycin (RU 28965), a new macrolide antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1312–1316. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couraud L., Andrews J. M., Lecoeur H., Sultan E., Lenfant B. Concentrations of cefpodoxime in plasma and lung tissue after a single oral dose of cefpodoxime proxetil. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Dec;26 (Suppl E):35–40. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.suppl_e.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., Corwin R. W., Steinberg T. H., Grossman G. D. Uptake of antibiotics by human alveolar macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Jun;129(6):933–937. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.6.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Inflammatory and immune processes in the human lung in health and disease: evaluation by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am J Pathol. 1979 Oct;97(1):149–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp C. C., Sierra-Madero J., Washington J. A. Antibacterial activities of cefpodoxime, cefixime, and ceftriaxone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Dec;32(12):1896–1898. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.12.1896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroening U., Liebig S., Wundschock M. Tobramycin-Spiegel im menschlichen Lungengewebe. Infection. 1978;6(5):231–235. doi: 10.1007/BF01642315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill P., Nye K., Douce G., Andrews J., Wise R. Pharmacokinetics and inflammatory fluid penetration of cefpodoxime proxetil in volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):232–234. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Basset G., Lecossier D., O'Donnell K. M., Pinkston P., Martin P. G., Crystal R. G. Estimation of volume of epithelial lining fluid recovered by lavage using urea as marker of dilution. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Feb;60(2):532–538. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.2.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y. Bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):250–263. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taulier A., Levillain P., Lemonnier A. Intérêt de la spectrophotométrie dérivée pour le dosage de l'hémoglobine plasmatique et urinaire. Comparaison avec la méthode utilisant la correction d'Allen. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1986;44(3):242–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsui Y., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of CS-807, a new oral cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1085–1092. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valcke Y. J., Rosseel M. T., Pauwels R. A., Bogaert M. G., Van der Straeten M. E. Penetration of ampicillin and sulbactam in the lower airways during respiratory infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):958–962. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valcke Y., Pauwels R., Van der Straeten M. Pharmacokinetics of antibiotics in the lungs. Eur Respir J. 1990 Jun;3(6):715–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Ashby J. P., Thornber D. The in-vitro activity of cefpodoxime: a comparison with other oral cephalosporins. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Apr;25(4):541–550. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.4.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. The pharmacokinetics of the oral cephalosporins--a review. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Dec;26 (Suppl E):13–20. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.suppl_e.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



