Abstract
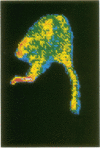
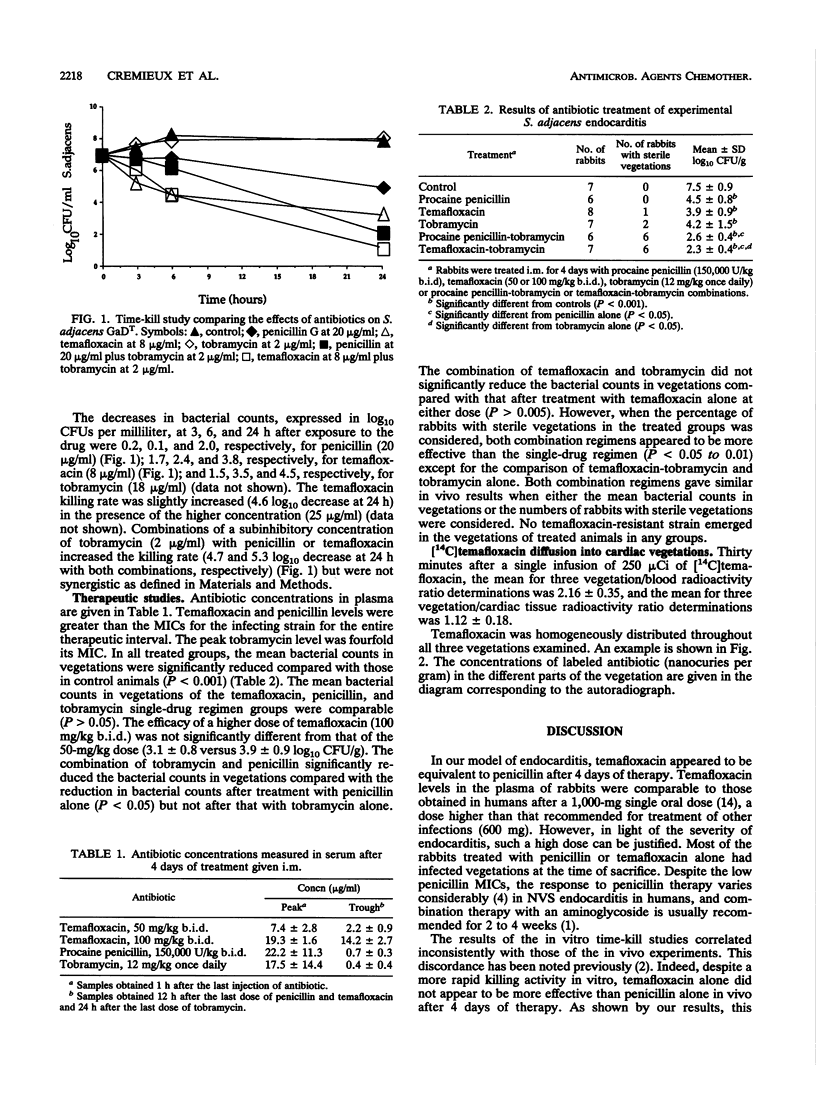
Temafloxacin, a new fluoroquinolone, alone or in combination with tobramycin, was compared with penicillin, tobramycin, and their combination in the therapy of rabbits with endocarditis caused by Streptococcus adjacens GaDT, a new species of nutritionally variant streptococci. Animals were injected intramuscularly for 4 days with temafloxacin (50 mg/kg of body weight twice daily [b.i.d.]) alone or combined with tobramycin (12 mg/kg once daily), with procaine penicillin (150,000 U/kg b.i.d.) alone or combined with tobramycin (12 mg/kg once daily), or with tobramycin (12 mg/kg once daily) alone. Another group of animals was treated with a higher dose of temafloxacin (100 mg/kg b.i.d.). Temafloxacin, penicillin, and tobramycin MICs and MBCs were 1 and 2, 0.015 and 1, and 8 and 16 micrograms/ml, respectively. Time-kill curves showed that the addition of tobramycin to penicillin or temafloxacin increased the killing rate. In vivo, treatment with temafloxacin (50 and 100 mg/kg b.i.d.) alone reduced the bacterial counts in vegetations (3.9 +/- 0.9 and 3.1 +/- 0.8 log10 CFU/g of vegetation) compared with those in the vegetations of control animals (7.5 +/- 0.9 log10 CFU/g of vegetation). This result was similar to that obtained with penicillin alone (4.5 +/- 0.8 log10 CFU/g of vegetation). The combination of temafloxacin (50 mg/kg) and tobramycin was as effective as penicillin plus tobramycin (2.5 +/- 0.3 versus 2.3 +/- 0.4 log10 CFU/g of vegetation, respectively). The autoradiographic pattern of [14C]temafloxacin diffusion into infected cardiac vegetations was studied. Thirty minutes after the end of infusion of 250 microCi of [14C]temafloxacin, the [14C]temafloxacin was homogeneously distributed throughout the vegetations. These data support further evaluation of quinolones in experimental endocarditis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bisno A. L., Dismukes W. E., Durack D. T., Kaplan E. L., Karchmer A. W., Kaye D., Rahimtoola S. H., Sande M. A., Sanford J. P., Watanakunakorn C. Antimicrobial treatment of infective endocarditis due to viridans streptococci, enterococci, and staphylococci. JAMA. 1989 Mar 10;261(10):1471–1477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet A., Cremieux A. C., Contrepois A., Vallois J. M., Lamesch C., Carbon C. Comparison of penicillin and vancomycin, individually and in combination with gentamicin and amikacin, in the treatment of experimental endocarditis induced by nutritionally variant streptococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):607–611. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet A., van de Rijn I., McCarty M. Nutritionally variant streptococci from patients with endocarditis: growth parameters in a semisynthetic medium and demonstration of a chromophore. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):1075–1082. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.1075-1082.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey R. B., Brause B. D., Roberts R. B. Antimicrobial therapy of vitamin B6-dependent streptococcal endocarditis. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Aug;87(2):150–154. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-2-150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cayeux P., Acar J. F., Chabbert Y. A. Bacterial persistence in streptococcal endocarditis due to thiol-requiring mutants. J Infect Dis. 1971 Sep;124(3):247–254. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.3.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremieux A. C., Maziere B., Vallois J. M., Ottaviani M., Azancot A., Raffoul H., Bouvet A., Pocidalo J. J., Carbon C. Evaluation of antibiotic diffusion into cardiac vegetations by quantitative autoradiography. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):938–944. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crémieux A. C., Mazière B., Vallois J. M., Ottaviani M., Bouvet A., Pocidalo J. J., Carbon C. Ceftriaxone diffusion into cardiac fibrin vegetation. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation by autoradiography. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1991;5(1):53–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1991.tb00701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T. Experimental bacterial endocarditis. IV. Structure and evolution of very early lesions. J Pathol. 1975 Feb;115(2):81–89. doi: 10.1002/path.1711150204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frehel C., Hellio R., Cremieux A. C., Contrepois A., Bouvet A. Nutritionally variant streptococci develop ultrastructural abnormalities during experimental endocarditis. Microb Pathog. 1988 Apr;4(4):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. N. Once-daily aminoglycoside therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Mar;35(3):399–405. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. N., Wood C. A., Kimbrough R. C. Failure of treatment with teicoplanin at 6 milligrams/kilogram/day in patients with Staphylococcus aureus intravascular infection. The Infectious Diseases Consortium of Oregon. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman G. R., Carpentier P., Morrison P. J., Pernet A. G. Pharmacokinetics of temafloxacin in humans after single oral doses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Mar;35(3):436–441. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry N. K., Wilson W. R., Roberts R. B., Acar J. F., Geraci J. E. Antimicrobial therapy of experimental endocarditis caused by nutritionally variant viridans group streptococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Sep;30(3):465–467. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessen M. T., Pitsakis P. G., Kaye D. Oral temafloxacin versus vancomycin for therapy of experimental endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1143–1145. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly V., Bergeron Y., Bergeron M. G., Carbon C. Endotoxin-tobramycin additive toxicity on renal proximal tubular cells in culture. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):351–357. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly V., Pangon B., Vallois J. M., Abel L., Brion N., Bure A., Chau N. P., Contrepois A., Carbon C. Value of antibiotic levels in serum and cardiac vegetations for predicting antibacterial effect of ceftriaxone in experimental Escherichia coli endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1632–1639. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Niles A. C. Inactivation of penicillins by Thiol broth. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):982–984. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.982-984.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman B. B., Freedman L. R. Experimental endocarditis. II. Staphylococcal infection of the aortic valve following placement of a polyethylene catheter in the left side of the heart. Yale J Biol Med. 1971 Oct;44(2):206–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. B., Krieger A. G., Schiller N. L., Gross K. C. Viridans streptococcal endocarditis: the role of various species, including pyridoxal-dependent streptococci. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Nov-Dec;1(6):955–966. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.6.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullam P. M., Täuber M. G., Hackbarth C. J., Sande M. A. Antimicrobial activity of gentamicin in experimental enterococcal endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Feb;27(2):224–226. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.2.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. A., Kohlhepp S. J., Kohnen P. W., Houghton D. C., Gilbert D. N. Vancomycin enhancement of experimental tobramycin nephrotoxicity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):20–24. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]