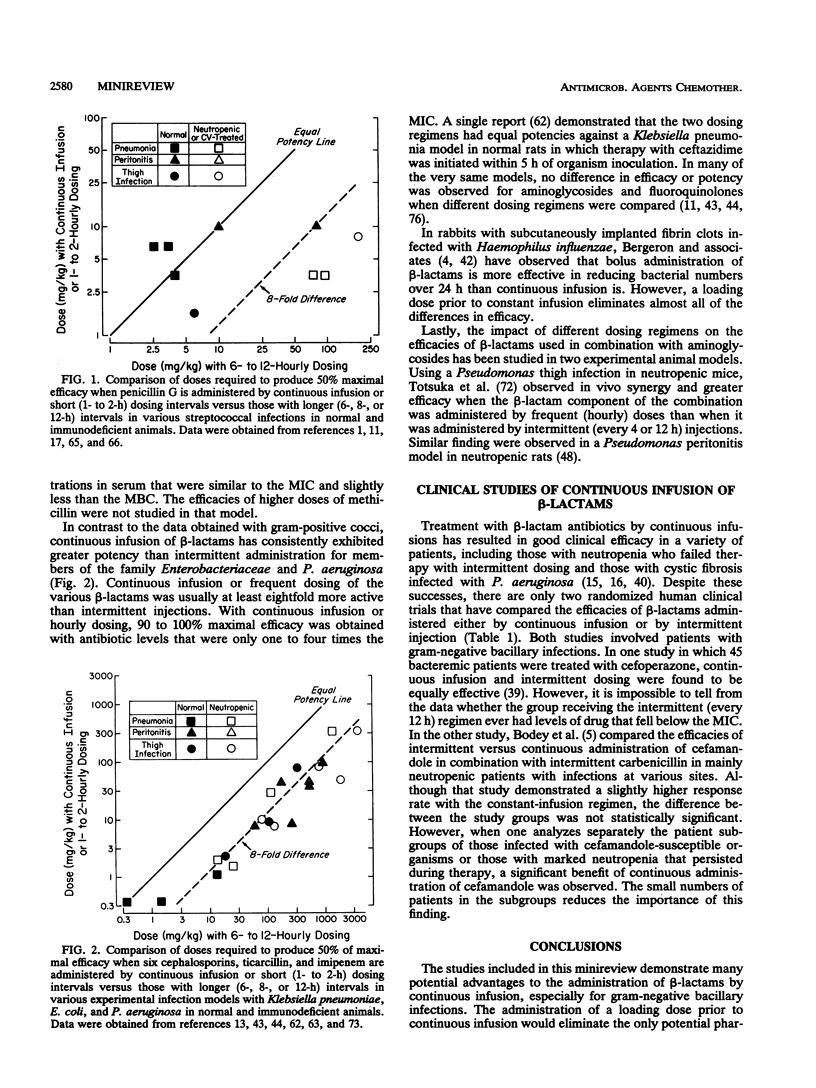
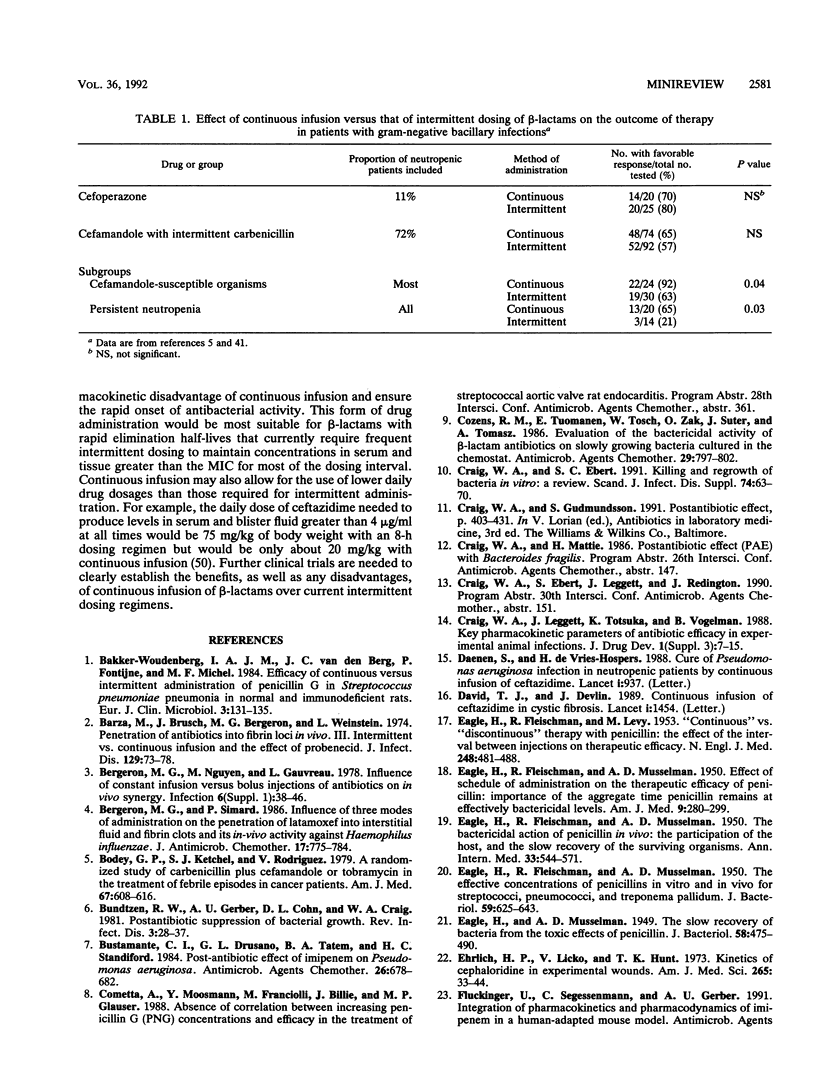
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., van den Berg J. C., Fontijne P., Michel M. F. Efficacy of continuous versus intermittent administration of penicillin G in Streptococcus pneumoniae pneumonia in normal and immunodeficient rats. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;3(2):131–135. doi: 10.1007/BF02014330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M., Brusch J., Bergeron M. G., Weinstein L. Penetration of antibiotics into fibrin loci in vivo. 3. Intermittent vs. continuous infusion and the effect of probenecid. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):73–78. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Simard P. Influence of three modes of administration on the penetration of latamoxef into interstitial fluid and fibrin clots and its in-vivo activity against Haemophilus influenzae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Jun;17(6):775–784. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.6.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Ketchel S. J., Rodriguez V. A randomized study of carbenicillin plus cefamandole or tobramycin in the treatment of febrile episodes in cancer patients. Am J Med. 1979 Oct;67(4):608–616. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundtzen R. W., Gerber A. U., Cohn D. L., Craig W. A. Postantibiotic suppression of bacterial growth. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):28–37. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante C. I., Drusano G. L., Tatem B. A., Standiford H. C. Postantibiotic effect of imipenem on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Nov;26(5):678–682. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.5.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozens R. M., Tuomanen E., Tosch W., Zak O., Suter J., Tomasz A. Evaluation of the bactericidal activity of beta-lactam antibiotics on slowly growing bacteria cultured in the chemostat. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):797–802. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig W. A., Ebert S. C. Killing and regrowth of bacteria in vitro: a review. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1990;74:63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daenen S., de Vries-Hospers H. Cure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in neutropenic patients by continuous infusion of ceftazidime. Lancet. 1988 Apr 23;1(8591):937–937. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91741-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David T. J., Devlin J. Continuous infusion of ceftazidime in cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1989 Jun 24;1(8652):1454–1455. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90164-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H., FLEISCHMAN R., LEVY M. "Continuous" vs. "discontinuous" therapy with penicillin; the effect of the interval between injections on therapeutic efficacy. N Engl J Med. 1953 Mar 19;248(12):481–488. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195303192481201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H., FLEISCHMAN R., MUSSELMAN A. D. Effect of schedule of administration on the therapeutic efficacy of penicillin; importance of the aggregate time penicillin remains at effectively bactericidal levels. Am J Med. 1950 Sep;9(3):280–299. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(50)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H., FLEISCHMAN R., MUSSELMAN A. D. The bactericidal action of penicillin in vivo: the participation of the host, and the slow recovery of the surviving organisms. Ann Intern Med. 1950 Sep;33(3):544–571. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-33-3-544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H., FLEISCHMAN R., MUSSELMAN A. D. The effective concentrations of penicillin in vitro and in vivo for streptococci, pneumococci, and Treponema pallidum. J Bacteriol. 1950 May;59(5):625–643. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.5.625-643.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagle H., Musselman A. D. THE SLOW RECOVERY OF BACTERIA FROM THE TOXIC EFFECTS OF PENICILLIN. J Bacteriol. 1949 Oct;58(4):475–490. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.4.475-490.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. P., Licko V., Hunt T. K. Kinetics of cephaloridine in experimental wounds. Am J Med Sci. 1973 Jan;265(1):33–44. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197301000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuursted K. Comparative killing activity and postantibiotic effect of streptomycin combined with ampicillin, ciprofloxacin, imipenem, piperacillin or vancomycin against strains of Streptococcus faecalis and Streptococcus faecium. Chemotherapy. 1988;34(3):229–234. doi: 10.1159/000238574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gengo F. M., Mannion T. W., Nightingale C. H., Schentag J. J. Integration of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of methicillin in curative treatment of experimental endocarditis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Dec;14(6):619–631. doi: 10.1093/jac/14.6.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber A. U., Feller C., Brugger H. P. Time course of the pharmacological response to beta-lactam antibiotics in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;3(6):592–597. doi: 10.1007/BF02013630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths L. R., Green H. T. Paradoxical effect of penicillin in-vivo. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Apr;15(4):507–508. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.4.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudmundsson S., Vogelman B., Craig W. A. The in-vivo postantibiotic effect of imipenem and other new antimicrobials. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Dec;18 (Suppl E):67–73. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_e.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanberger H., Nilsson L. E., Kihlström E., Maller R. Postantibiotic effect of beta-lactam antibiotics on Escherichia coli evaluated by bioluminescence assay of bacterial ATP. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):102–106. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanberger H., Nilsson L. E., Maller R., Nilsson M. Pharmacodynamics of beta-lactam antibiotics on gram-negative bacteria: initial killing, morphology and postantibiotic effect. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1990;74:118–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessen M. T., Pitsakis P. G., Levison M. E. Absence of a postantibiotic effect in experimental Pseudomonas endocarditis treated with imipenem, with or without gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1988 Sep;158(3):542–548. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.3.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessen M. T., Pitsakis P. G., Levison M. E. Postantibiotic effect of penicillin plus gentamicin versus Enterococcus faecalis in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):608–611. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm S. E., Tornqvist I. O., Cars O. Paradoxical effects of antibiotics. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1990;74:113–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern W., Kennedy S. L., Sachdeva M., Sande E. R., Gunderson D., Täuber M. G. Evaluation of piperacillin-tazobactam in experimental meningitis caused by a beta-lactamase-producing strain of K1-positive Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 May;34(5):697–701. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.5.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby W. M. BACTERIOSTATIC AND LYTIC ACTIONS OF PENICILLIN ON SENSITIVE AND RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCI. J Clin Invest. 1945 Mar;24(2):165–169. doi: 10.1172/JCI101593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzemko J., Crawford C. Continuous infusion of ceftazidime in cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1989 Aug 12;2(8659):385–385. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90561-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagast H., Meunier-Carpentier F., Klastersky J. Treatment of gram-negative bacillary septicemia with cefoperazone. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;2(6):554–558. doi: 10.1007/BF02016564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie G. Y., Bergeron M. G. Influence of four modes of administration on penetration of aztreonam, cefuroxime, and ampicillin into interstitial fluid and fibrin clots and on in vivo efficacy against Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):404–412. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leggett J. E., Ebert S., Fantin B., Craig W. A. Comparative dose-effect relations at several dosing intervals for beta-lactam, aminoglycoside and quinolone antibiotics against gram-negative bacilli in murine thigh-infection and pneumonitis models. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1990;74:179–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leggett J. E., Fantin B., Ebert S., Totsuka K., Vogelman B., Calame W., Mattie H., Craig W. A. Comparative antibiotic dose-effect relations at several dosing intervals in murine pneumonitis and thigh-infection models. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):281–292. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmo E., Coppola L., Pempinello R., Di Nicuolo G., Lampa E. Levels of amoxycillin in the liquor during continuous intravenous administration. Chemotherapy. 1982;28(3):171–175. doi: 10.1159/000238072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald P. J., Craig W. A., Kunin C. M. Persistent effect of antibiotics on Staphylococcus aureus after exposure for limited periods of time. J Infect Dis. 1977 Feb;135(2):217–223. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald P. J., Wetherall B. L., Pruul H. Postantibiotic leukocyte enhancement: increased susceptibility of bacteria pretreated with antibiotics to activity of leukocytes. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):38–44. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordenti J. J., Quintiliani R., Nightingale C. H. Combination antibiotic therapy: comparison of constant infusion and intermittent bolus dosing in an experimental animal model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):313–321. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreillon P., Tomasz A. Penicillin resistance and defective lysis in clinical isolates of pneumococci: evidence for two kinds of antibiotic pressure operating in the clinical environment. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;157(6):1150–1157. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.6.1150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton J. W., Horrevorts A. M., Mulder P. G., Prens E. P., Michel M. F. Pharmacokinetics of ceftazidime in serum and suction blister fluid during continuous and intermittent infusions in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Dec;34(12):2307–2311. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.12.2307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton J. W., Michel M. F. Pharmacokinetics of meropenem in serum and suction blister fluid during continuous and intermittent infusion. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Dec;28(6):911–918. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.6.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neftel K. A., Wälti M., Schulthess H. K., Gubler J. Adverse reactions following intravenous penicillin-G relate to degradation of the drug in vitro. Klin Wochenschr. 1984 Jan 2;62(1):25–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01725189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neftel K. A., Wälti M., Spengler H., de Weck A. L. Effect of storage of penicillin-G solutions on sensitisation to penicillin-G after intravenous administration. Lancet. 1982 May 1;1(8279):986–988. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91991-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neftel K. A., Wälti M., Spengler H., von Felten A., Weitzman S. A., Bürgi H., de Weck A. L. Neutropenia after penicillins: toxic or immune-mediated? Klin Wochenschr. 1981 Aug 17;59(16):877–888. doi: 10.1007/BF01721921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida M., Murakawa T., Kamimura T., Okada N. Bactericidal activity of cephalosporins in an in vitro model simulating serum levels. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jul;14(1):6–12. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino T., Nakazawa S. Bacteriological study on effects of beta-lactam group antibiotics in high concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):1033–1042. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenholt I., Holm S. E., Cars O. Effects of benzylpenicillin on Streptococcus pyogenes during the postantibiotic phase in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Aug;24(2):147–156. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLORDE J. J., GARCIA M., PETERSDORF R. G. STUDIES ON THE PATHOGENESIS OF MENINGITIS. IV. PENICILLIN LEVELS IN THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID IN EXPERIMENTAL MENINGITIS. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Dec;64:960–969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. F., Luse S. The Action of Penicillin on Staphylococcus: Further Observations on the Effect of a Short Exposure. J Bacteriol. 1948 Jul;56(1):75–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.56.1.75-81.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N., Fasching C. E. Effects of method of antibiotic administration on extravascular penetration: cross-over study of cefazolin given by intermittent injection or constant infusion. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jan;7(1):71–79. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roosendaal R., Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., van den Berg J. C., Michel M. F. Therapeutic efficacy of continuous versus intermittent administration of ceftazidime in an experimental Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia in rats. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):373–378. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roosendaal R., Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., van den Berghe-van Raffe M., Michel M. F. Continuous versus intermittent administration of ceftazidime in experimental Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia in normal and leukopenic rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Sep;30(3):403–408. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.3.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT L. H., WALLEY A. The influence of the dosage regimen on the therapeutic effectiveness of penicillin G in experimental lobar pneumonia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1951 Dec;103(4):479–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Korzeniowski O. M., Allegro G. M., Brennan R. O., Zak O., Scheld W. M. Intermittent or continuous therapy of experimental meningitis due to Streptococcus pneumoniae in rabbits: preliminary observations on the postantibiotic effect in vivo. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):98–109. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.1.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah P. M., Junghanns, Stille W. Dosis-Wirkungs-Beziehung der Bakterizidie bei E. coli, K. pneumoniae und Staphylococcus aureus. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1976 Feb 27;101(9):325–328. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1104083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrogiannopoulos G. A., Al-Sabbagh A., Olsen K. D., McCracken G. H., Jr Pharmacokinetics and bacteriological efficacy of ticarcillin-clavulanic acid (timentin) in experimental Escherichia coli K-1 and Haemophilus influenzae type b meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1296–1300. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauvin C., Eliopoulos G. M., Willey S., Wennersten C., Moellering R. C., Jr Continuous-infusion ampicillin therapy of enterococcal endocarditis in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):139–143. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornqvist I. O., Holm S. E., Cars O. Pharmacodynamic effects of subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1990;74:94–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Täuber M. G., Doroshow C. A., Hackbarth C. J., Rusnak M. G., Drake T. A., Sande M. A. Antibacterial activity of beta-lactam antibiotics in experimental meningitis due to Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):568–574. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Täuber M. G., Zak O., Scheld W. M., Hengstler B., Sande M. A. The postantibiotic effect in the treatment of experimental meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):575–583. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etta L. L., Kravitz G. R., Russ T. E., Fasching C. E., Gerding D. N., Peterson L. R. Effect of method of administration on extravascular penetration of four antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):873–880. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelman B., Craig W. A. Kinetics of antimicrobial activity. J Pediatr. 1986 May;108(5 Pt 2):835–840. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80754-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelman B., Gudmundsson S., Leggett J., Turnidge J., Ebert S., Craig W. A. Correlation of antimicrobial pharmacokinetic parameters with therapeutic efficacy in an animal model. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):831–847. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelman B., Gudmundsson S., Turnidge J., Leggett J., Craig W. A. In vivo postantibiotic effect in a thigh infection in neutropenic mice. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):287–298. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. A., Toothaker R. D., Smith A. L., Slattery J. T. In vitro evaluation of the determinants of bactericidal activity of ampicillin dosing regimens against Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jul;33(7):1046–1051. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.7.1046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. A., Rolinson G. N. The recovery period following exposure of bacteria to penicillins. Chemotherapy. 1979;25(1):14–22. doi: 10.1159/000237817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


