Abstract
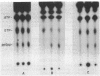
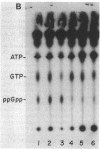
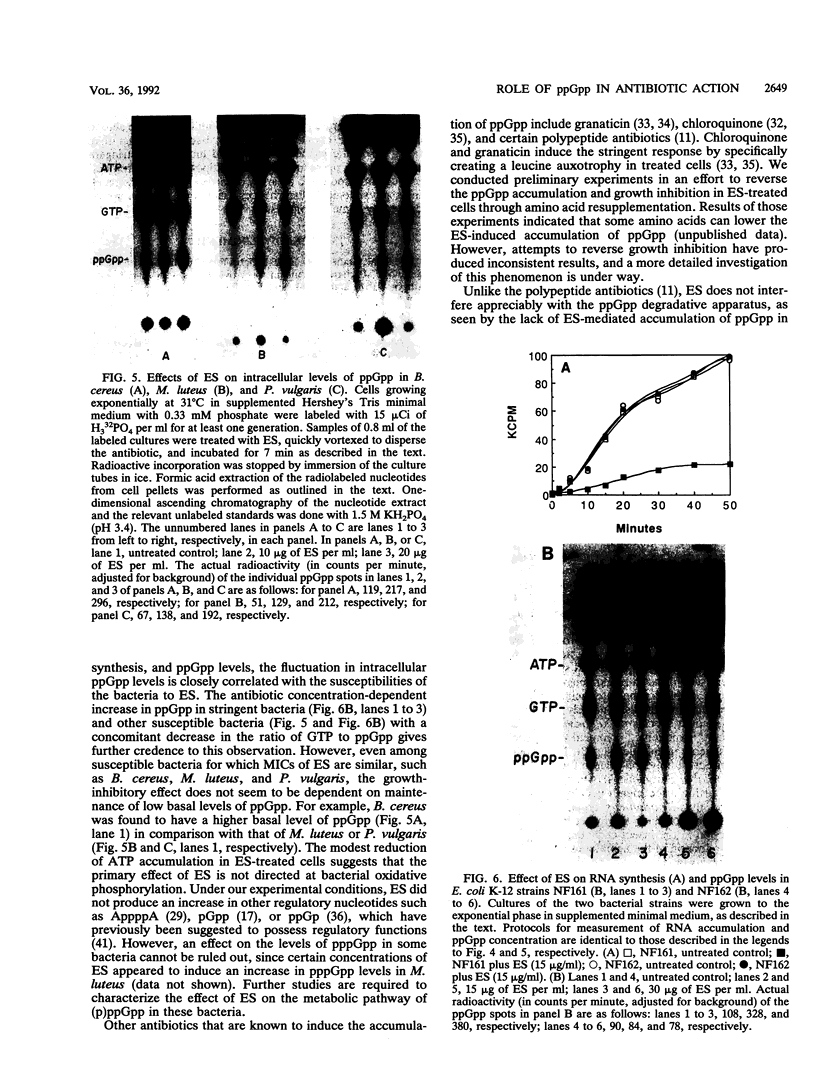
The mode of action of 3,5-dihydroxy-4-ethyl-trans-stilbene (ES), an antibiotic produced by Xenorhabdus luminescens symbiotically associated with an entomopathogenic nematode, was investigated. ES was active against gram-positive and a number of gram-negative bacteria. In susceptible bacteria this antibiotic caused the inhibition of total RNA synthesis and, to a lesser extent, protein synthesis. At or above MICs, ES triggered a substantial accumulation of an intracellular regulatory compound, guanosine-3',5'-bis-pyrophosphate (ppGpp). This response was also noticed in species of bacteria which have previously not been shown to use ppGpp as a regulatory molecule. The involvement of ppGpp in antibiotic action was confirmed by using an isogenic stringent and a relaxed pair of Escherichia coli strains. The fact that the accumulation of ppGpp was correlated with the susceptibility of various gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria to ES suggests that this nucleotide is involved in the regulation of RNA synthesis and growth in all these microorganisms. Thus, inhibition of RNA synthesis via an increase in ppGpp concentrations may represent a mechanism that is prevalent among most bacteria and one that could be exploited for achieving a rapid inhibition of bacterial growth.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- An G., Justesen J., Watson R. J., Friesen J. D. Cloning the spoT gene of Escherichia coli: identification of the spoT gene product. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1100–1110. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1100-1110.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOREK E., ROCKENBACH J., RYAN A. Studies on a mutant of Escherichia coli with unbalanced ribonucleic acid synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1956 Mar;71(3):318–323. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.3.318-323.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Ames B. N. Complete analysis of cellular nucleotides by two-dimensional thin layer chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9759–9769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquet P. L., Devynck M. A., Monnier C., Fromageot P. Inhibition of stable RNA synthesis by levallorphan in Escherichia coli. Implication of compounds MS I and MS II. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Dec 3;40(1):31–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashel M., Gallant J. Two compounds implicated in the function of the RC gene of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):838–841. doi: 10.1038/221838a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashel M. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. IV. Relevance of unusual phosphorylated compounds from amino acid-starved stringent strains. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3133–3141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaloner-Larsson G., Yamazaki H. Adjustment of RNA content during temperature upshift in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):503–508. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Chang C. N., Paik W. K. Methylation of ribosomal proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):651–656. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.651-656.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortay J. C., Cozzone A. J. Accumulation of guanosine tetraphosphate induced by polymixin and gramicidin in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 22;755(3):467–473. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90251-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donini P. Turnover of ribosomal RNA during the stringent response in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):553–569. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90174-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlin G., Donini P. Synthesis of guanosine 5'-diphosphate, 2'-(or 3'-) diphosphate and related nucleotides in a variety of physiological conditions. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4371–4373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehr S., Richter D. Stringent response of Bacillus stearothermophilus: evidence for the existence of two distinct guanosine 3',5'-polyphosphate synthetases. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):68–73. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.68-73.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallant J., Shell L., Bittner R. A novel nucleotide implicated in the response of E. coli to energy source downshift. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90257-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., Takebe Y., Sharrock R. A., Nomura M. Feedback regulation of rRNA and tRNA synthesis and accumulation of free ribosomes after conditional expression of rRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1069–1073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman R. B., Yamazaki H. MSI accumulation induced by sodium chloride. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 15;11(4):615–618. doi: 10.1021/bi00754a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Block R. Synthesis of guanosine tetra- and pentaphosphate requires the presence of a codon-specific, uncharged transfer ribonucleic acid in the acceptor site of ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1564–1568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemeyer E. A., Richter D. In vitro degradation of guanosine tetraphosphate (ppGpp) by an enzyme associated with the ribosomal fraction from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1977 Dec 15;84(2):357–361. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80724-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez V. J., Bremer H. Escherichia coli ppGpp synthetase II activity requires spoT. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5991–5999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. S., Adler C. R., Collins J. J., Court D. Role of the spoT gene product and manganese ion in the metabolism of guanosine 5'-diphosphate 3'-diphosphate in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5483–5487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laffler T., Gallant J. A. Stringent control of protein synthesis in E. coli. Cell. 1974 Sep;3(1):47–49. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagosky P. A., Chang F. N. Correlation between RNA synthesis and basal level guanosine 5'-diphosphate 3'-diphosphate in relaxed mutants of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11651–11656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagosky P. A., Chang F. N. Influence of amino acid starvation on guanosine 5'-diphosphate 3'-diphosphate basal-level synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):499–508. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.499-508.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagosky P. A., Chang F. N. The extraction of guanosine 5'-diphosphate, 3'-diphosphate (ppGpp) from Escherichia coli using low pH reagents: a reevaluation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 30;84(4):1016–1024. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91685-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzarini R. A., Cashel M., Gallant J. On the regulation of guanosine tetraphosphate levels in stringent and relaxed strains of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4381–4385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. C., Bochner B. R., Ames B. N. AppppA, heat-shock stress, and cell oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7496–7500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger S., Schreiber G., Aizenman E., Cashel M., Glaser G. Characterization of the relA1 mutation and a comparison of relA1 with new relA null alleles in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21146–21152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. J., Lucas-Lenard J. M. The effect of alcohols on guanosine 5'-diphosphate-3'-diphosphate metabolism in stringent and relaxed Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6307–6313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie A., Lämmerman M., Wiebauer K., Kersten W. Quinone induced stringent control. Accumulation of ppGpp and inhibition of RNA synthesis in stringent Escherichia coli by 5,8-dioxo-6-amino-7-chloroquinoline. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 16;395(2):136–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie A., Wiebauer K., Kersten W. Inhibition of leucyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetasymol. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):511–515. doi: 10.1042/bj1520511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie A., Wiebauer K., Kersten W. Stringent control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in Bacillus subtilis treated with granaticin. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):517–522. doi: 10.1042/bj1520517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie A., Wiebauer K., Spitzbarth P., Kersten W. Inhibition of leucyl-tRNA synthetase in Escherichia coli by the cytostatic 5,8-dioxo-6-amino-7-chloroquinoline. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 15;407(3):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pao C. C., Gallant J. A new nucleotide involved in the stringent response in Escherichia coli. Guanosine 5'-diphosphate-3'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):688–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price V. L., Brown L. R. Transcriptional inhibition and production of guanosine polyphosphates in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):752–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.752-756.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel K. Nucleosidpolyphosphate: Vorkommen, Metabolismus und Funktion. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1983;23(2):103–141. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630230206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. C., Artz S. W., Ames B. N. Guanosine 5'-diphosphate 3'-diphosphate (ppGpp): positive effector for histidine operon transcription and general signal for amino-acid deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4389–4393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A., Buckland R. Heterogeneity of E. coli RNA polymerase. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 27;243(130):257–260. doi: 10.1038/newbio243257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. Modulation of RNA polymerase specificity by ppGpp. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Aug 19;147(2):225–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00267575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Kalman M., Ikehara K., Zemel S., Glaser G., Cashel M. Residual guanosine 3',5'-bispyrophosphate synthetic activity of relA null mutants can be eliminated by spoT null mutations. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5980–5990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]