Abstract
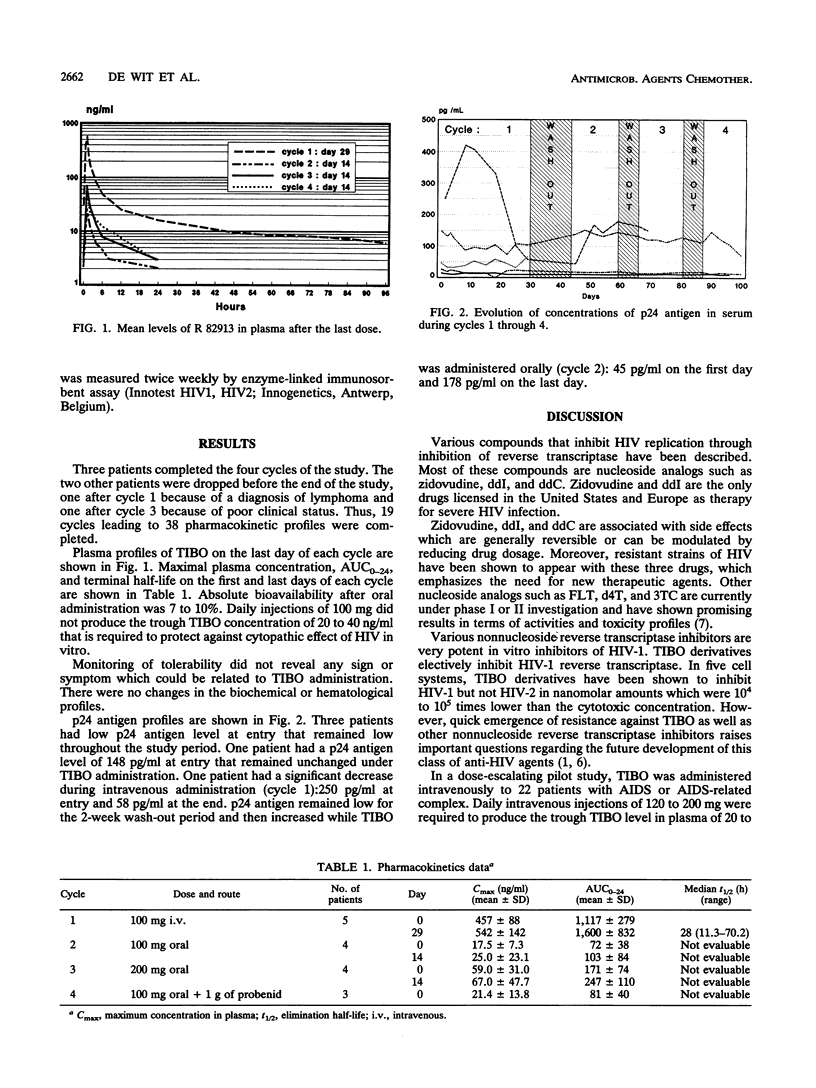
The pharmacokinetics of oral administration of R 82913, or tetrahydroimidazol [4,5,1-jk]-benzodiazepin-2(1H)-one or -thione (TIBO), was compared with those of intravenous administration in five AIDS patients. TIBO was administered as a single daily 1-h infusion of 100 mg for 29 days and orally as a single daily dose for 14 days with three consecutive regimens of 100, 200, and 100 mg with probenecid (1 g) daily. Each cycle was followed by a wash-out period. Oral bioavailability of TIBO appears to be low and is not improved by the adjunction of probenecid. Trough levels obtained with oral administration systematically remained far below the 90% inhibitory concentration of TIBO against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). Tolerance of TIBO was excellent. No clinical efficacy could be demonstrated. p24 antigenemia decreased significantly in one patient under intravenous therapy. TIBO derivatives are promising anti-HIV-1 agents in vitro, but improvement of oral bioavailability is needed before implementation of long-term efficacy and tolerability studies. Moreover, rapid emergence of resistance, which has been recently documented, constitutes a major problem with most nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Nunberg J. H., Schleif W. A., Boots E. J., O'Brien J. A., Quintero J. C., Hoffman J. M., Emini E. A., Goldman M. E. Viral resistance to human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific pyridinone reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4887–4892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4887-4892.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels R., Andries K., Desmyter J., Schols D., Kukla M. J., Breslin H. J., Raeymaeckers A., Van Gelder J., Woestenborghs R., Heykants J. Potent and selective inhibition of HIV-1 replication in vitro by a novel series of TIBO derivatives. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):470–474. doi: 10.1038/343470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pialoux G., Youle M., Dupont B., Gazzard B., Cauwenbergh G. F., Stoffels P. A., Davies S., de Saint Martin J., Janssen P. A. Pharmacokinetics of R 82913 in patients with AIDS or AIDS-related complex. Lancet. 1991 Jul 20;338(8760):140–143. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90135-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D., Shih C. K., Lowy I., Rose J., Prodanovich P., Goff S., Griffin J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mutants resistant to nonnucleoside inhibitors of reverse transcriptase arise in tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11241–11245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarchoan R., Pluda J. M., Perno C. F., Mitsuya H., Broder S. Anti-retroviral therapy of human immunodeficiency virus infection: current strategies and challenges for the future. Blood. 1991 Aug 15;78(4):859–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


