Abstract
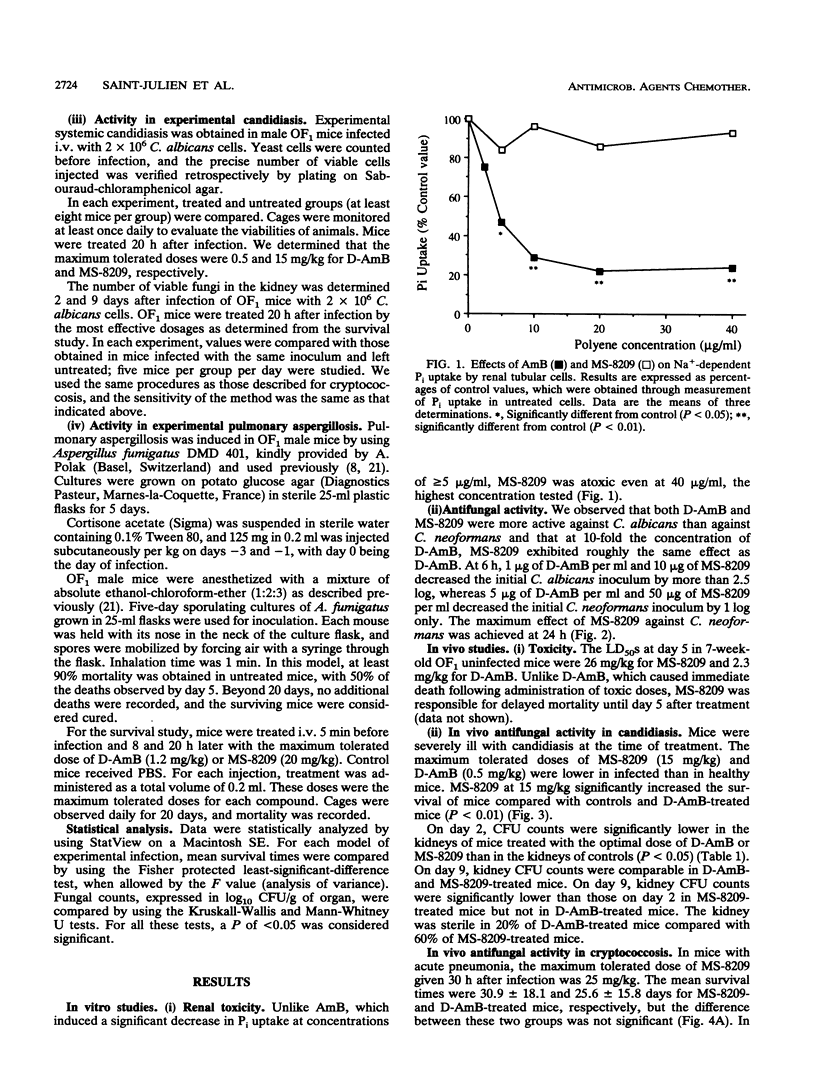
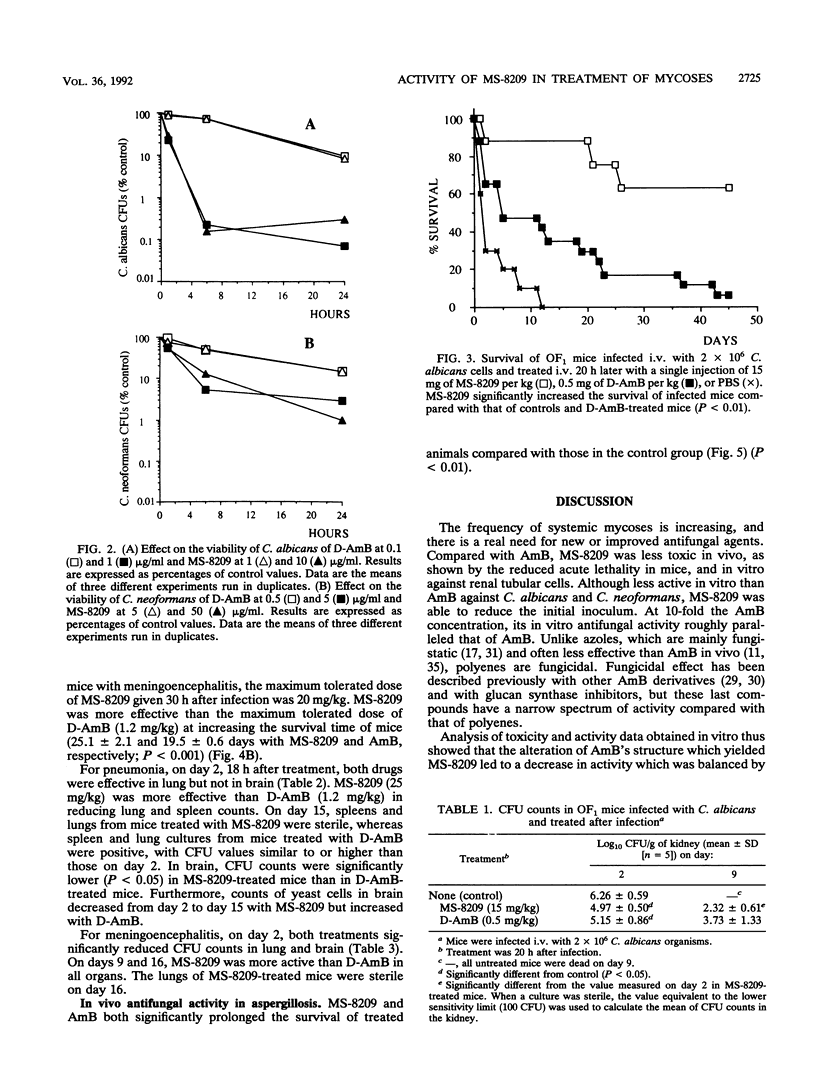
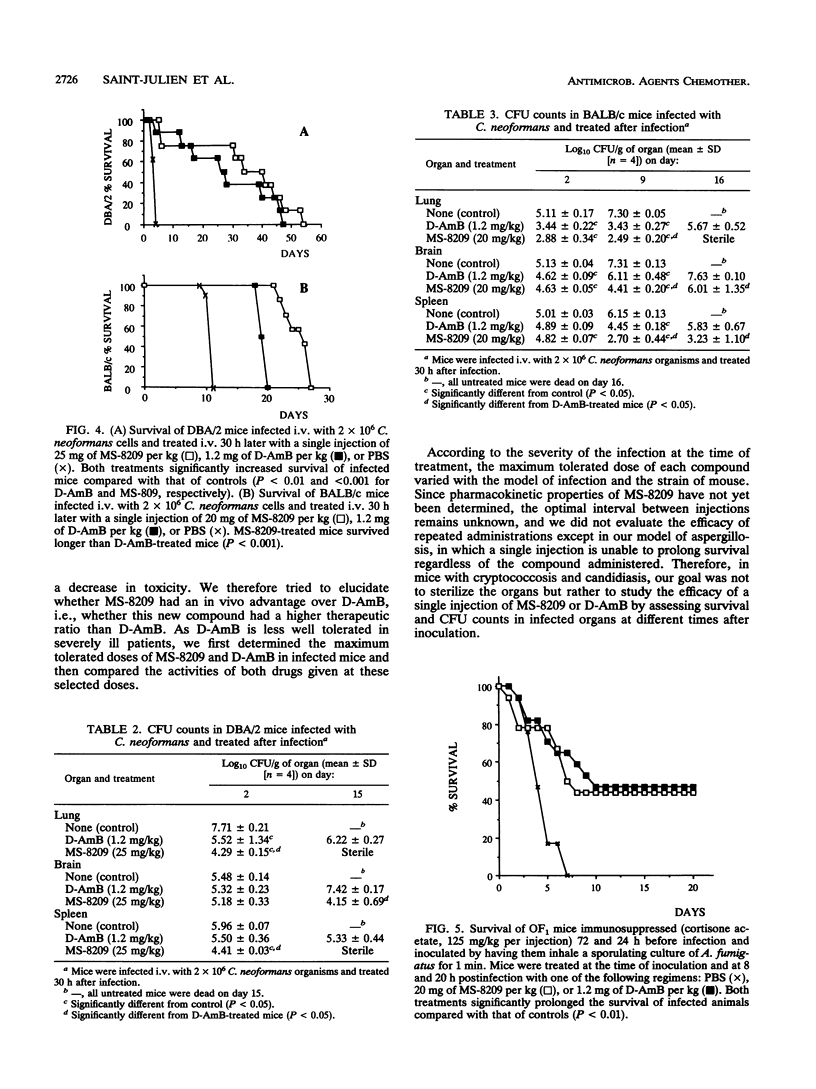
The in vitro and in vivo toxicities and activities of MS-8209, a new hydrosoluble amphotericin B (deoxycholate-amphotericin B [D-AmB]; Fungizone) derivative, were studied. In vitro, MS-8209 was less toxic than AmB against renal tubular cells in primary culture and less active against Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans. However, at 10-fold the AmB concentration, MS-8209 in vitro antifungal activity paralleled that of AmB. Fifty-percent lethal doses of MS-8209 and D-AmB in OF1 noninfected mice were 26 and 2.3 mg/kg, respectively. Therapeutic efficacy of MS-8209 was assessed in murine candidiasis, cryptococcosis, and aspergillosis. In each model of infection, we determined the maximum tolerated dosages of MS-8209 and D-AmB, i.e., the dosage inducing less than 15% mortality due to toxicity; the efficacies of MS-8209 and D-AmB at their respective maximum tolerated dosages were compared. In candidiasis, MS-8209 (15 mg/kg) significantly increased the survival time compared with D-AmB (0.5 mg/kg). Both compounds were equally effective at reducing CFU counts in the kidney. MS-8209 was the most effective agent for increasing the survival time in cryptococcal meningoencephalitis and for reducing CFU counts in spleen, brain, and lung during both cryptococcal pneumonia and meningoencephalitis. In aspergillosis, MS-8209 and D-AmB similarly prolonged the survival of treated mice compared with controls. These results show that when MS-8209 and D-AmB were used at the maximum tolerated dosage, MS-8209 was as effective as or more effective than D-AmB for the treatment of systemic mycoses. These findings warrant further experiments to study the pharmacokinetic properties and toxicity of MS-8209 under conditions of chronic administration.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess J. L., Birchall R. Nephrotoxicity of amphotericin B, with emphasis on changes in tubular function. Am J Med. 1972 Jul;53(1):77–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron M. L., Bartlett J. A., Gallis H. A., Waskin H. A. Manifestations of pulmonary cryptococcosis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jan-Feb;13(1):64–67. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordonnier C., Bernaudin J. F., Bierling P., Huet Y., Vernant J. P. Pulmonary complications occurring after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. A study of 130 consecutive transplanted patients. Cancer. 1986 Sep 1;58(5):1047–1054. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19860901)58:5<1047::aid-cncr2820580512>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Céfai D., Hadida F., Jung M., Debre P., Vernin J. G., Seman M. MS-8209, a new Amphotericin B derivative that inhibits HIV-1 replication in vitro and restores T-cell activation via the CD3/TcR in HIV-infected CD4+ cells. AIDS. 1991 Dec;5(12):1453–1461. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199112000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGregorio M. W., Lee W. M., Linker C. A., Jacobs R. A., Ries C. A. Fungal infections in patients with acute leukemia. Am J Med. 1982 Oct;73(4):543–548. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90334-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dismukes W. E. Cryptococcal meningitis in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):624–628. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon D. M., Polak A., Walsh T. J. Fungus dose-dependent primary pulmonary aspergillosis in immunosuppressed mice. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1452–1456. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1452-1456.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dromer F., Perronne C., Barge J., Vilde J. L., Yeni P. Role of IgG and complement component C5 in the initial course of experimental cryptococcosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Dec;78(3):412–417. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis W. G., Sobel R. A., Nielsen S. L. Leukoencephalopathy in patients treated with amphotericin B methyl ester. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):125–137. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M. A., Lee P. G., Tarry W. F. Fluconazole (UK-49,858) treatment of candidiasis in normal and diabetic rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jul;33(7):1042–1045. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.7.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadebusch H. H., Pansy F., Klepner C., Schwind R. Amphotericin B and amphotericin B methyl ester ascorbate. I. Chemotherapeutic activity against Candida albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans, and Blastomyces dermatitidis in mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Nov;134(5):423–427. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.5.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerson S. L., Talbot G. H., Hurwitz S., Strom B. L., Lusk E. J., Cassileth P. A. Prolonged granulocytopenia: the major risk factor for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with acute leukemia. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Mar;100(3):345–351. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-3-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Kaster S. R. Experimental murine aspergillosis. Comparison of amphotericin B and a new polyene antifungal drug, SCH 28191. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Feb;129(2):292–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holleran W. M., Wilbur J. R., DeGregorio M. W. Empiric amphotericin B therapy in patients with acute leukemia. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Sep-Oct;7(5):619–624. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.5.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. E., Bennett R. L., Tuna I. C., Beggs W. H. Activities of fluconazole (UK 49,858) and ketoconazole against ketoconazole-susceptible and -resistant Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Feb;32(2):209–212. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly V., Saint-Julien L., Carbon C., Yeni P. Interactions of free and liposomal amphotericin B with renal proximal tubular cells in primary culture. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Oct;255(1):17–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen R. A., Leal M. A., Chan L. S. Fluconazole compared with amphotericin B plus flucytosine for cryptococcal meningitis in AIDS. A randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Aug 1;113(3):183–187. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-3-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R. M., Hoeprich P. D. Comparison of amphotericin B and amphotericin B methyl ester: efficacy in murine coccidioidomycosis and toxicity. J Infect Dis. 1976 Feb;133(2):168–174. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.2.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Conte P., Joly V., Saint-Julien L., Gillardin J. M., Carbon C., Yeni P. Tissue distribution and antifungal effect of liposomal itraconazole in experimental cryptococcosis and pulmonary aspergillosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Feb;145(2 Pt 1):424–429. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.2_Pt_1.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Bodey G. P., Frankel L. S., Mehta K. Treatment of hepatosplenic candidiasis with liposomal-amphotericin B. J Clin Oncol. 1987 Feb;5(2):310–317. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.2.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Fainstein V., Hopfer R., Mehta K., Sullivan M. P., Keating M., Rosenblum M. G., Mehta R., Luna M., Hersh E. M. Liposomal amphotericin B for the treatment of systemic fungal infections in patients with cancer: a preliminary study. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):704–710. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Mehta R., Hopfer R. L., Mills K., Kasi L., Mehta K., Fainstein V., Luna M., Hersh E. M., Juliano R. Treatment and prophylaxis of disseminated infection due to Candida albicans in mice with liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):939–945. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massa T., Sinha D. P., Frantz J. D., Filipek M. E., Weglein R. C., Steinberg S. A., McGrath J. T., Murphy B. F., Szot R. J., Black H. E. Subchronic toxicity studies of N-D-ornithyl amphotericin B methyl ester in dogs and rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1985 Aug;5(4):737–753. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(85)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medoff G., Brajtburg J., Kobayashi G. S., Bolard J. Antifungal agents useful in therapy of systemic fungal infections. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:303–330. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oblack D. L., Hewitt W. L., Martin W. J. Comparative in vitro susceptibility of yeasts to amphotericin B and three methyl ester derivatives. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):106–109. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perfect J. R., Durack D. T. Comparison of amphotericin B and N-D-ornithyl amphotericin B methyl ester in experimental cryptococcal meningitis and Candida albicans endocarditis with pyelonephritis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Dec;28(6):751–755. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.6.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saag M. S., Dismukes W. E. Azole antifungal agents: emphasis on new triazoles. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculier J. P., Coune A., Meunier F., Brassinne C., Laduron C., Hollaert C., Collette N., Heymans C., Klastersky J. Pilot study of amphotericin B entrapped in sonicated liposomes in cancer patients with fungal infections. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1988 Mar;24(3):527–538. doi: 10.1016/s0277-5379(98)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm A. M., Diasio R. B., Dismukes W. E., Shadomy S., Cloud G. A., Bowles C. A., Karam G. H., Espinel-Ingroff A. Toxicity of amphotericin B plus flucytosine in 194 patients with cryptococcal meningitis. Am J Med. 1987 Aug;83(2):236–242. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90691-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay C., Barza M., Fiore C., Szoka F. Efficacy of liposome-intercalated amphotericin B in the treatment of systemic candidiasis in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):170–173. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh T. J., Aoki S., Mechinaud F., Bacher J., Lee J., Rubin M., Pizzo P. A. Effects of preventive, early, and late antifungal chemotherapy with fluconazole in different granulocytopenic models of experimental disseminated candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):755–760. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wey S. B., Mori M., Pfaller M. A., Woolson R. F., Wenzel R. P. Hospital-acquired candidemia. The attributable mortality and excess length of stay. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Dec;148(12):2642–2645. doi: 10.1001/archinte.148.12.2642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



