Abstract
DNA topoisomerases, a class of enzymes that change the topological structure of DNA, have been shown to be the target of many therapeutic agents, including antibacterial agents (quinolones) and anticancer agents. These drugs inhibit the enzyme in a unique way so that the enzyme is converted into a cellular poison. Candida albicans and Aspergillus niger are two major opportunistic fungal pathogens. Our results show that these fungi have high levels of both type I and type II topoisomerases (with a minimum of 5 x 10(5) ATP-independent relaxation units and 2 x 10(5) P-4 unknotting units per liter of wild-type C. albicans). The ATP-dependent type II topoisomerase (termed C. albicans topoisomerase II) was purified by approximately 2,000-fold from C. albicans cells by using a simple isolation scheme that consists of three column procedures: hydroxylapatite, phosphocellulose, and heparin-agarose chromatographies. The responses of the Candida and the calf thymus topoisomerase II to some known topoisomerase II inhibitors were measured. Etoposide and 4'-(9-acridinylamino)methanesulfon-m-anisidide, compounds known to inhibit catalysis and to enhance DNA breakage by mammalian topoisomerase II, and A-80198, an etoposide derivative, enhanced cleavage by both enzymes at similar concentrations of these compounds, with the response of the calf thymus topoisomerase II from slightly to fourfold higher in magnitude than the response of the Candida enzyme in the same concentration range. In contrast, A-75272 (a cytotoxic tricyclic quinolone) shows a slightly stronger DNA cleavage enhancement effect with the Candida enzyme than with the mammalian counterpart. The abundance of the enzyme in cells and the different drug responses of the host enzyme and the fungal enzyme suggest that the fungal topoisomerase may serve as a target for the discovery of effective and safe antifungal agents.
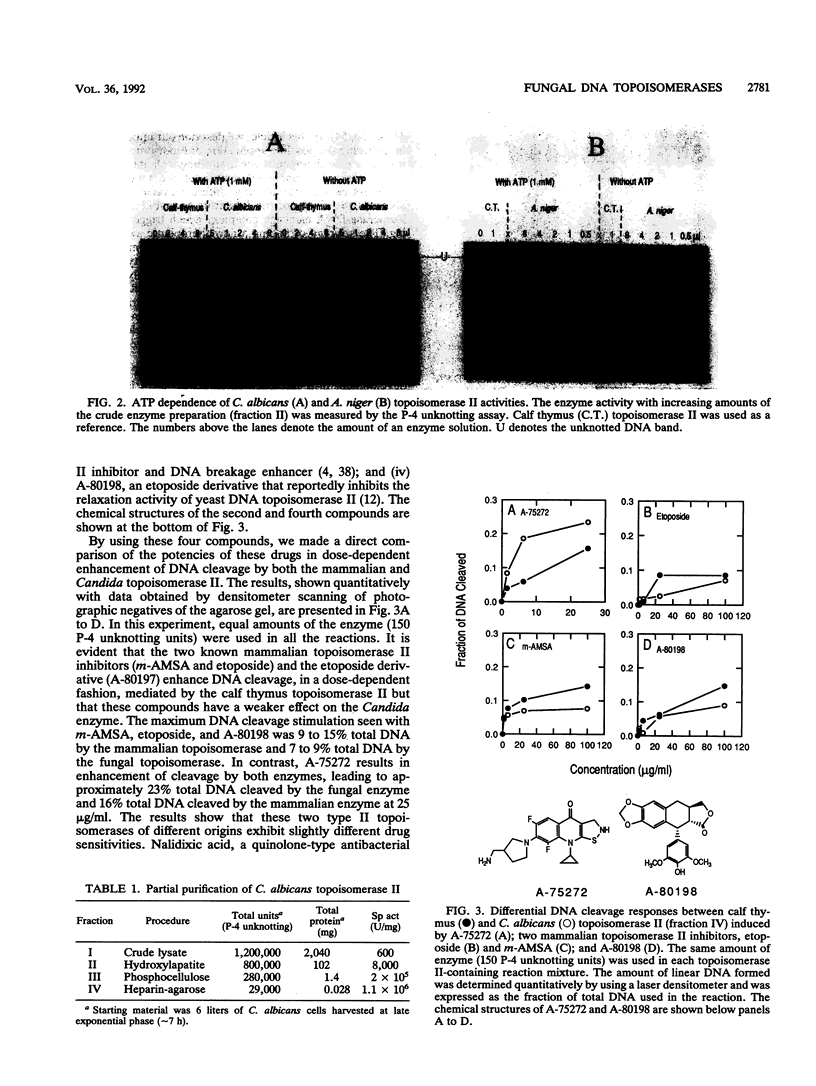
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown P. O., Cozzarelli N. R. A sign inversion mechanism for enzymatic supercoiling of DNA. Science. 1979 Nov 30;206(4422):1081–1083. doi: 10.1126/science.227059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G. L., Yang L., Rowe T. C., Halligan B. D., Tewey K. M., Liu L. F. Nonintercalative antitumor drugs interfere with the breakage-reunion reaction of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13560–13566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R. DNA gyrase and the supercoiling of DNA. Science. 1980 Feb 29;207(4434):953–960. doi: 10.1126/science.6243420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen M. E., Wyke A. W., Kuroda R., Fisher L. M. Cloning and characterization of a DNA gyrase A gene from Escherichia coli that confers clinical resistance to 4-quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jun;33(6):886–894. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.6.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K. Biology of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid topoisomerases. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):273–289. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.273-289.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Franco R. J. Inhibitors of DNA topoisomerases. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2253–2259. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein R. J. Topoisomerases in human disease. Lancet. 1988 Mar 5;1(8584):521–524. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91308-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes P. B. Mode of action, and in vitro and in vivo activities of the fluoroquinolones. J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;28(2):156–168. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1988.tb05967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figgitt D. P., Denyer S. P., Dewick P. M., Jackson D. E., Williams P. Topoisomerase II: a potential target for novel antifungal agents. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 14;160(1):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91649-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Nash H. A. DNA gyrase: an enzyme that introduces superhelical turns into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanella B. C., Stehlin J. S., Wall M. E., Wani M. C., Nicholas A. W., Liu L. F., Silber R., Potmesil M. DNA topoisomerase I--targeted chemotherapy of human colon cancer in xenografts. Science. 1989 Nov 24;246(4933):1046–1048. doi: 10.1126/science.2555920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto T., Laipis P., Wang J. C. The purification and characterization of DNA topoisomerases I and II of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10422–10429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck M. M., Earnshaw W. C. Topoisomerase II: A specific marker for cell proliferation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2569–2581. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg R. P., Caranfa M. J., Holden K. G., Jakas D. R., Gallagher G., Mattern M. R., Mong S. M., Bartus J. O., Johnson R. K., Kingsbury W. D. Modification of the hydroxy lactone ring of camptothecin: inhibition of mammalian topoisomerase I and biological activity. J Med Chem. 1989 Mar;32(3):715–720. doi: 10.1021/jm00123a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S. The fluoroquinolones: pharmacology, clinical uses, and toxicities in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):716–721. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Hertzberg R., Hecht S., Liu L. F. Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14873–14878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Liu L. F. Identification of mammalian DNA topoisomerase I as an intracellular target of the anticancer drug camptothecin. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1722–1726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Liu L. F., Wall M. E., Wani M. C., Nicholas A. W., Manikumar G., Kirschenbaum S., Silber R., Potmesil M. DNA topoisomerase I-mediated DNA cleavage and cytotoxicity of camptothecin analogues. Cancer Res. 1989 Aug 15;49(16):4385–4389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Wu H. Y., Liu L. F. Proliferation-dependent regulation of DNA topoisomerase II in cultured human cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 1;48(11):3230–3235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Wu H. Y., Liu L. F. Topoisomerases: novel therapeutic targets in cancer chemotherapy. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 May 1;37(9):1801–1802. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90453-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Escherichia coli mutants thermosensitive for deoxyribonucleic acid gyrase subunit A: effects on deoxyribonucleic acid replication, transcription, and bacteriophage growth. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):424–435. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.424-435.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerases--enzymes that catalyse the breaking and rejoining of DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1983;15(1):1–24. doi: 10.3109/10409238309102799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Davis J. L., Calendar R. Novel topologically knotted DNA from bacteriophage P4 capsids: studies with DNA topoisomerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):3979–3989. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.3979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Rowe T. C., Yang L., Tewey K. M., Chen G. L. Cleavage of DNA by mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15365–15370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattern M. R., Mong S. M., Bartus H. F., Mirabelli C. K., Crooke S. T., Johnson R. K. Relationship between the intracellular effects of camptothecin and the inhibition of DNA topoisomerase I in cultured L1210 cells. Cancer Res. 1987 Apr 1;47(7):1793–1798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson E. M., Tewey K. M., Liu L. F. Mechanism of antitumor drug action: poisoning of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II on DNA by 4'-(9-acridinylamino)-methanesulfon-m-anisidide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1361–1365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitiss J., Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerase-targeting antitumor drugs can be studied in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7501–7505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheroff N. Effect of antineoplastic agents on the DNA cleavage/religation reaction of eukaryotic topoisomerase II: inhibition of DNA religation by etoposide. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6157–6160. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss G. J., Drlica K. DNA supercoiling and prokaryotic transcription. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):521–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90574-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. J., Osheroff N. Stabilization of the topoisomerase II-DNA cleavage complex by antineoplastic drugs: inhibition of enzyme-mediated DNA religation by 4'-(9-acridinylamino)methanesulfon-m-anisidide. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 13;29(10):2511–2515. doi: 10.1021/bi00462a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. E. DNA topoisomerases as targets for cancer therapy. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Dec 15;34(24):4191–4195. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90273-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Rowe T., Glisson B., Yalowich J., Liu L. Role of topoisomerase II in mediating epipodophyllotoxin-induced DNA cleavage. Cancer Res. 1984 Dec;44(12 Pt 1):5857–5860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe T. C., Chen G. L., Hsiang Y. H., Liu L. F. DNA damage by antitumor acridines mediated by mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. Cancer Res. 1986 Apr;46(4 Pt 2):2021–2026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarachek A. Population changes induced in Candida albicans by nalidixic acid. Mycopathologia. 1979 Sep 17;68(2):105–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00441090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Baranowski J., Pernet A. G. Mechanism of inhibition of DNA gyrase by quinolone antibacterials: specificity and cooperativity of drug binding to DNA. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3879–3885. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Pernet A. G. Mechanism of inhibition of DNA gyrase by analogues of nalidixic acid: the target of the drugs is DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):307–311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausfeld U., Richter A. Simultaneous purification of DNA topoisomerase I and II from eukaryotic cells. Prep Biochem. 1989;19(1):37–48. doi: 10.1080/10826068908544895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewey K. M., Chen G. L., Nelson E. M., Liu L. F. Intercalative antitumor drugs interfere with the breakage-reunion reaction of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9182–9187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Sci Am. 1982 Jul;247(1):94-7, 100-9. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0782-94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases: nature's solution to the topological ramifications of the double-helix structure of DNA. Harvey Lect. 1985 1986;81:93–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Interaction between DNA and an Escherichia coli protein omega. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90334-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]