Abstract
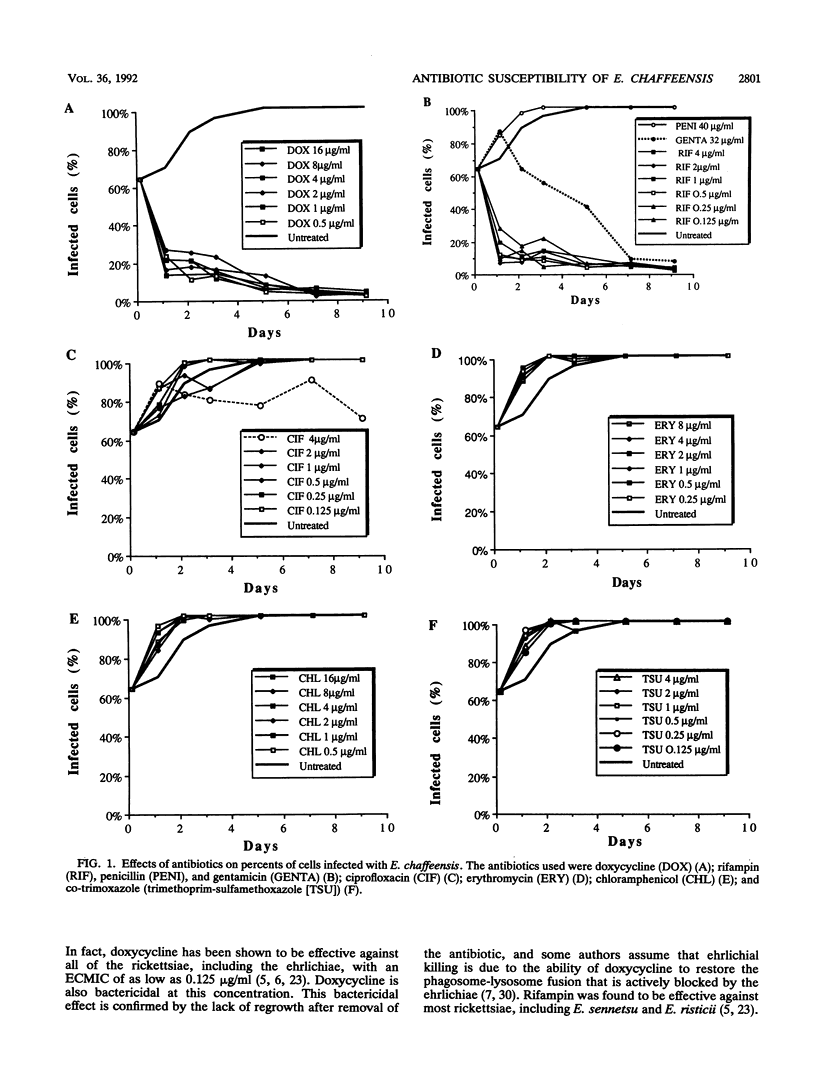
Ehrlichiosis in humans, a rickettsial disease recently discovered in the United States, is generally treated successfully with tetracyclines; however treatment with these agents is usually avoided with children and pregnant women. The in vitro susceptibility of Ehrlichia chaffeensis, the agent of human ehrlichiosis in the United States, was assessed by a quantitative evaluation of infected DH82 cells cultivated in 96-well microtiter plates in the presence of different concentrations of selected antibiotics. Extracellular MICs and MBCs were evaluated after 72 h of exposure to the antibiotics. Doxycycline and rifampin were found to exert rapidly bactericidal effects, with MBCs in the extracellular culture medium of less than 0.5 and 0.125 microgram/ml, respectively. E. chaffeensis was resistant to chloramphenicol, ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, co-trimoxazole, penicillin, and gentamicin, which had MICs greater than 16, 4, 8, 4, 40, and 32 micrograms/ml, respectively. These observations are consistent with the finding that human ehrlichiosis appears to respond to tetracycline therapy, which has been the therapy of first choice. Further clinical investigations are necessary to evaluate the role of rifampin in the treatment of human ehrlichiosis, especially in children.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton L. L., Foy T. M. Ehrlichia canis infection in a child. Pediatrics. 1989 Sep;84(3):580–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton L. L., Rathore M. H., Dawson J. E. Infection with Ehrlichia in childhood. J Pediatr. 1992 Jun;120(6):998–1001. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81978-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton L. L. Therapy of human ehrlichiosis reconsidered. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):398–398. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Imhoff J. G. Uptake of h-dihydrostreptomycin by macrophages in culture. Infect Immun. 1970 Jul;2(1):89–95. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.1.89-95.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouqui P., Raoult D. In vitro susceptibility of Ehrlichia sennetsu to antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Aug;34(8):1593–1596. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.8.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. E., Anderson B. E., Fishbein D. B., Sanchez J. L., Goldsmith C. S., Wilson K. H., Duntley C. W. Isolation and characterization of an Ehrlichia sp. from a patient diagnosed with human ehrlichiosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2741–2745. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2741-2745.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran T. I., Parmley R. T., Logas P. C., Chamblin S. Infection with Ehrlichia canis in a child. J Pediatr. 1989 May;114(5):809–812. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(89)80143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumler J. S., Brouqui P., Aronson J., Taylor J. P., Walker D. H. Identification of Ehrlichia in human tissue. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 10;325(15):1109–1110. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110103251517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng T. R., Harkess J. R., Fishbein D. B., Dawson J. E., Greene C. N., Redus M. A., Satalowich F. T. Epidemiologic, clinical, and laboratory findings of human ehrlichiosis in the United States, 1988. JAMA. 1990 Nov 7;264(17):2251–2258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishbein D. B., Kemp A., Dawson J. E., Greene N. R., Redus M. A., Fields D. H. Human ehrlichiosis: prospective active surveillance in febrile hospitalized patients. J Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;160(5):803–809. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.5.803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. J., Ristic M., Cole A. I., Johnson P., Baker G., Goetz T. Isolation, experimental transmission, and characterization of causative agent of Potomac horse fever. Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):522–524. doi: 10.1126/science.3880925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda K., Markowitz N., Hawley R. C., Ristic M., Cox D., McDade J. E. Human infection with Ehrlichia canis, a leukocytic rickettsia. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 2;316(14):853–856. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704023161406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Comparative biology of intracellular parasitism. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):298–337. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.298-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce C. J., Conrad M. E., Nolan P. E., Fishbein D. B., Dawson J. E. Ehrlichiosis: a cause of bone marrow hypoplasia in humans. Am J Hematol. 1988 May;28(1):53–55. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830280111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikihisa Y., Jiang B. M. In vitro susceptibilities of Ehrlichia risticii to eight antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jul;32(7):986–991. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.7.986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. P., Betz T. G., Fishbein D. B., Roberts M. A., Dawson J., Ristic M. Serological evidence of possible human infection with Ehrlichia in Texas. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):217–220. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellman M. L., Krakowka S., Jacobs R. M., Kociba G. J. A macrophage-monocyte cell line from a dog with malignant histiocytosis. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1988 Mar;24(3):223–229. doi: 10.1007/BF02623551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells M. Y., Rikihisa Y. Lack of lysosomal fusion with phagosomes containing Ehrlichia risticii in P388D1 cells: abrogation of inhibition with oxytetracycline. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3209–3215. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3209-3215.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



