Abstract
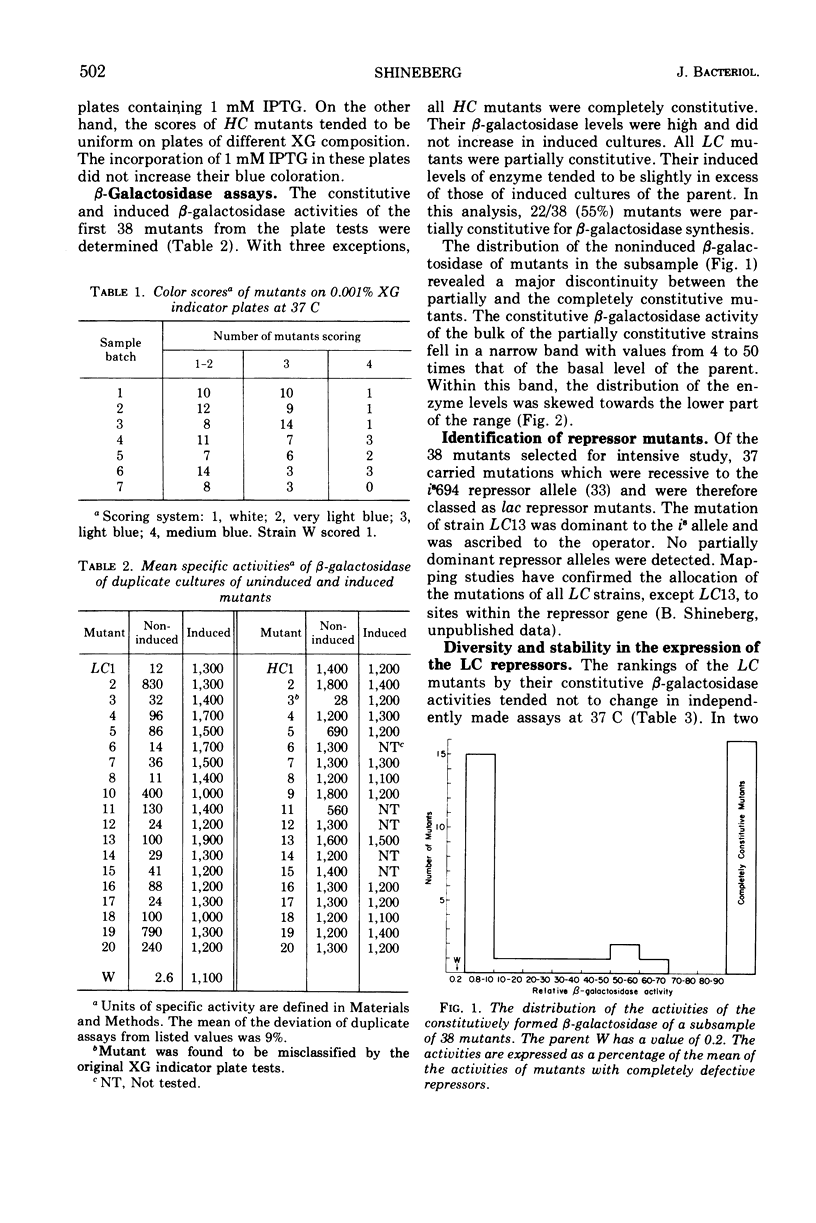
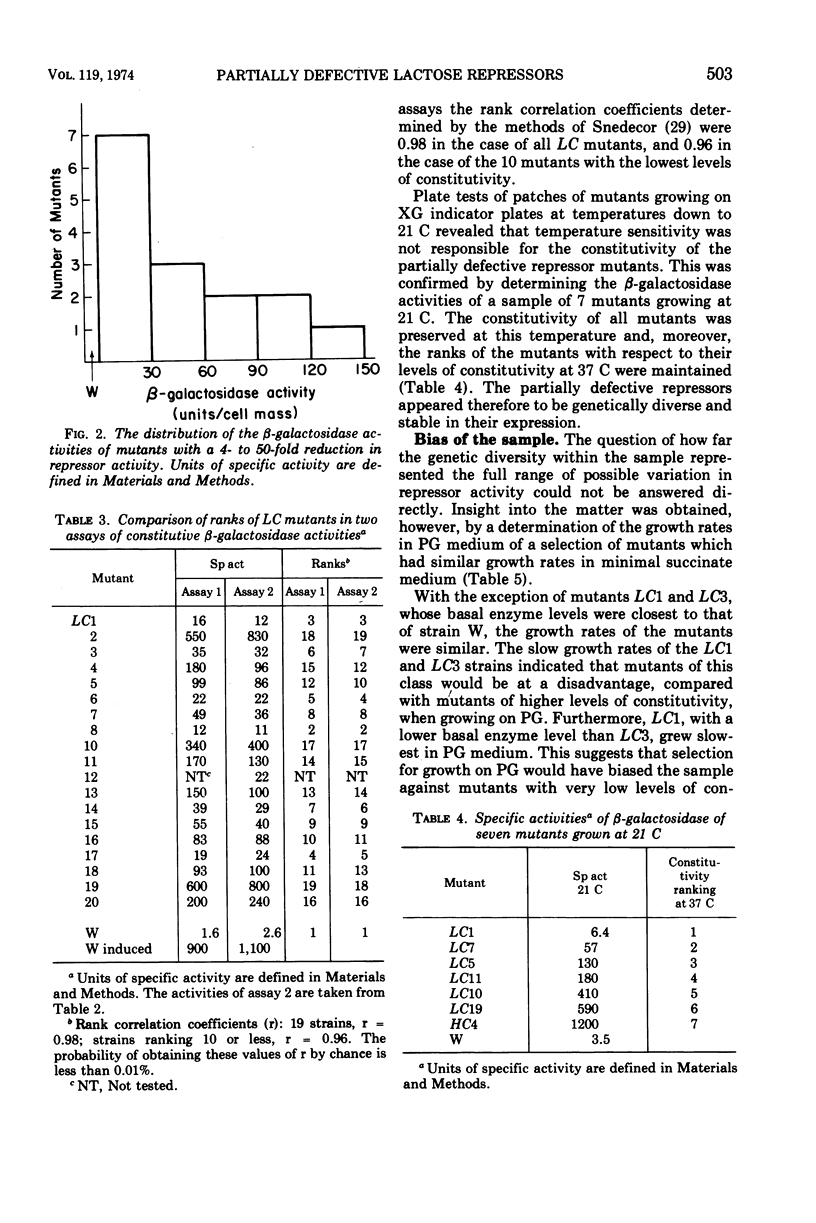
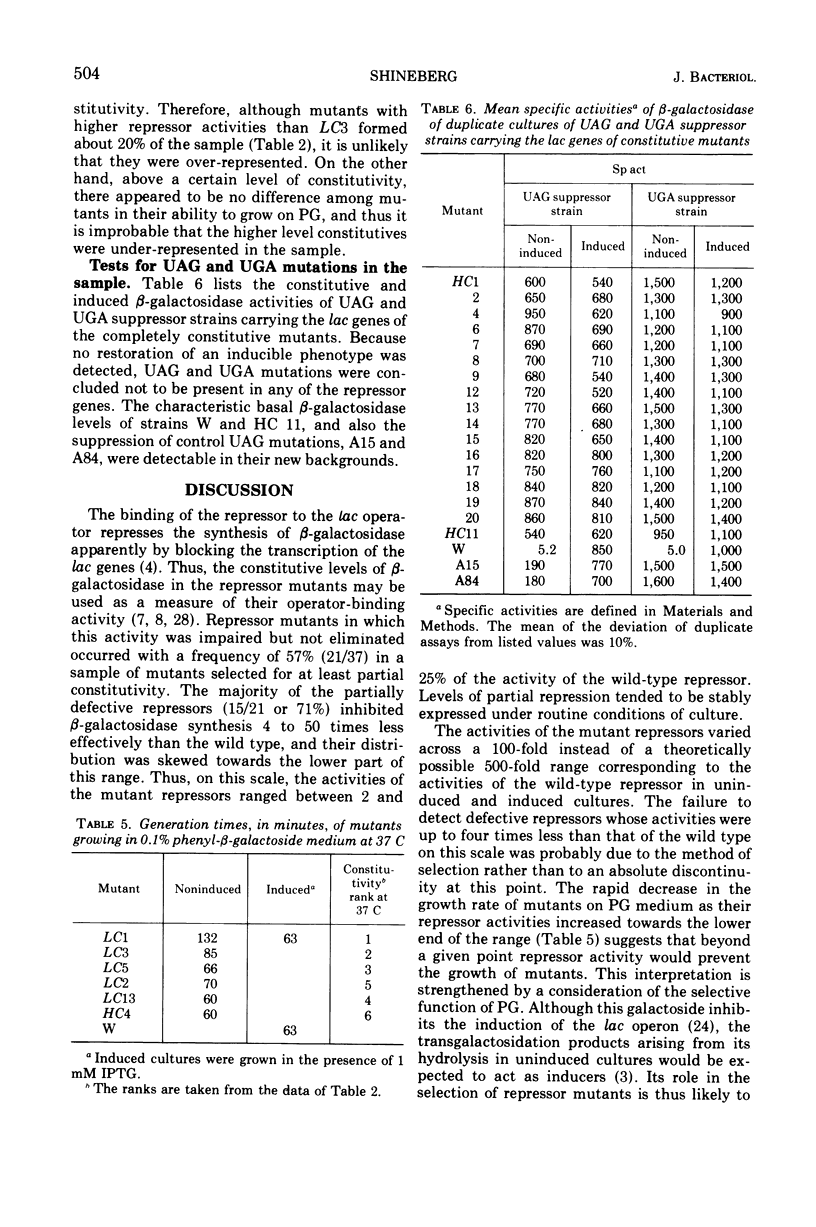
After treatment with N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine, 133 independent mutants of a haploid strain of Escherichia coli able to use phenyl-β-galactoside as a carbon source were obtained. The galactoside was specific in selecting for mutants with increases in their uninduced levels of β-galactosidase. Virtually all mutants (37 in a subsample of 38) carried mutations in the lac repressor gene. There were two classes of repressor mutants. As well as the commonly identified class of mutants with completely inactivated repressors, there was a frequent class of mutants (21/37) whose repressors were partially inactivated. Most of these (15/21) repressed β-galactosidase synthesis 4 to 50 times less than wild type, but were more numerous in the lower part of this range. Their β-galactosidase was inducible to levels characteristic of the parent strain. The repressor activities were diverse and stably expressed under routine growth conditions. The decreased activity did not result from the formation of temperature-sensitive repressors. None of the mutants with completely inactivated repressors appeared to carry UAG or UGA chain-terminating codons. On the assumption that the partially defective repressor mutants carried missense mutations, it is argued that missense mutations in the lac repressor gene modify the repressor's affinity for the operator with high probability. An explanation is proposed for the apparent sensitivity of this repressor function to partial inactivation as the result of amino acid substitutions.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURSTEIN C., COHN M., KEPES A., MONOD J. R OLE DU LACTOSE ET DE SES PRODUITS M'ETABOLIQUES DANS L'INDUCTION DE L'OP'ERON LACTOSE CHEZ ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Apr 19;95:634–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois S., Cohn M., Orgel L. E. Suppression of and complementation among mutants of the regulatory gene of the lactose operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):300–302. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80252-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN-BAZIRE G., JOLIT M. Isolement par sélection de mutants d'Escherichia coli synthétisant spontanément l'amylomaltase et la beta-galactosidase. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 May;84(5):937–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen B., de Crombrugghe B., Anderson W. B., Gottesman M. E., Pastan I., Perlman R. L. On the mechanism of action of lac repressor. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 15;233(37):67–70. doi: 10.1038/newbio233067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Jacob F. Genetic mapping of the regulator and operator genes of the lac operon. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 28;36(3):413–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W., Müller-Hill B. The lac operator is DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2415–2421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ippen K., Miller J. H., Scaife J., Beckwith J. New controlling element in the Lac operon of E. coli. Nature. 1968 Mar 2;217(5131):825–827. doi: 10.1038/217825a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman K., Müller-Hill B., Rickenberg H. V. Inhibition of the synthesis of beta-galactosidase in Escherichia coli by 2-nitrophenyl-beta-D-fucoside. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(2):339–343. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KESSLER D. P., RICKENBERG H. V. A NEW METHOD FOR THE SELECTION OF MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI FORMING BETA-GALACTOSIDASE CONSTITUTIVELY. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Sep 4;90:609–610. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90241-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langridge J., Campbell J. H. Classification and intragenic position of mutations in the beta-galactosidase gene of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1969;103(4):339–347. doi: 10.1007/BF00383484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langridge J. Mutations conferring quantitative and qualitative increases in beta-galactosidase activity in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1969;105(1):74–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00750315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Beckwith J., Muller-Hill B. Direction of transcription of a regulatory gene in E. coli. Nature. 1968 Dec 28;220(5174):1287–1290. doi: 10.1038/2201287a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Ippen K., Scaife J. G., Beckwith J. R. The promoter-operator region of the lac operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):413–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90395-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Hill B. Suppressible regulator constitutive mutants of the lactose system in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):374–376. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F., Lehmann H. Molecular pathology of human haemoglobin. Nature. 1968 Aug 31;219(5157):902–909. doi: 10.1038/219902a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Bourgeois S., Cohn M. The lac repressor-operator interaction. 3. Kinetic studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 14;53(3):401–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Newby R. F., Bourgeois S. lac repressor--operator interaction. II. Effect of galactosides and other ligands. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90144-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler J. R., Smith T. F. Mapping of the lactose operator. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 28;62(1):139–169. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J. F., Fan D. P., Brenner S. A strong suppressor specific for UGA. Nature. 1967 Apr 29;214(5087):452–453. doi: 10.1038/214452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L., Trotter C. D. Linkage map of Escherichia coli strain K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):504–524. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.504-524.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLSON C., PERRIN D., COHN M., JACOB F., MONOD J. NON-INDUCIBLE MUTANTS OF THE REGULATOR GENE IN THE "LACTOSE" SYSTEM OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:582–592. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Platt T., Ganem D., Miller J. H. Altered sequences changing the operator-binding properties of the Lac repressor: colinearity of the repressor protein with the i-gene map. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3624–3628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield H. J., Jr, Martin R. G., Ames B. N. Classification of aminotransferase (C gene) mutants in the histidine operon. J Mol Biol. 1966 Nov 14;21(2):335–355. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


