Abstract
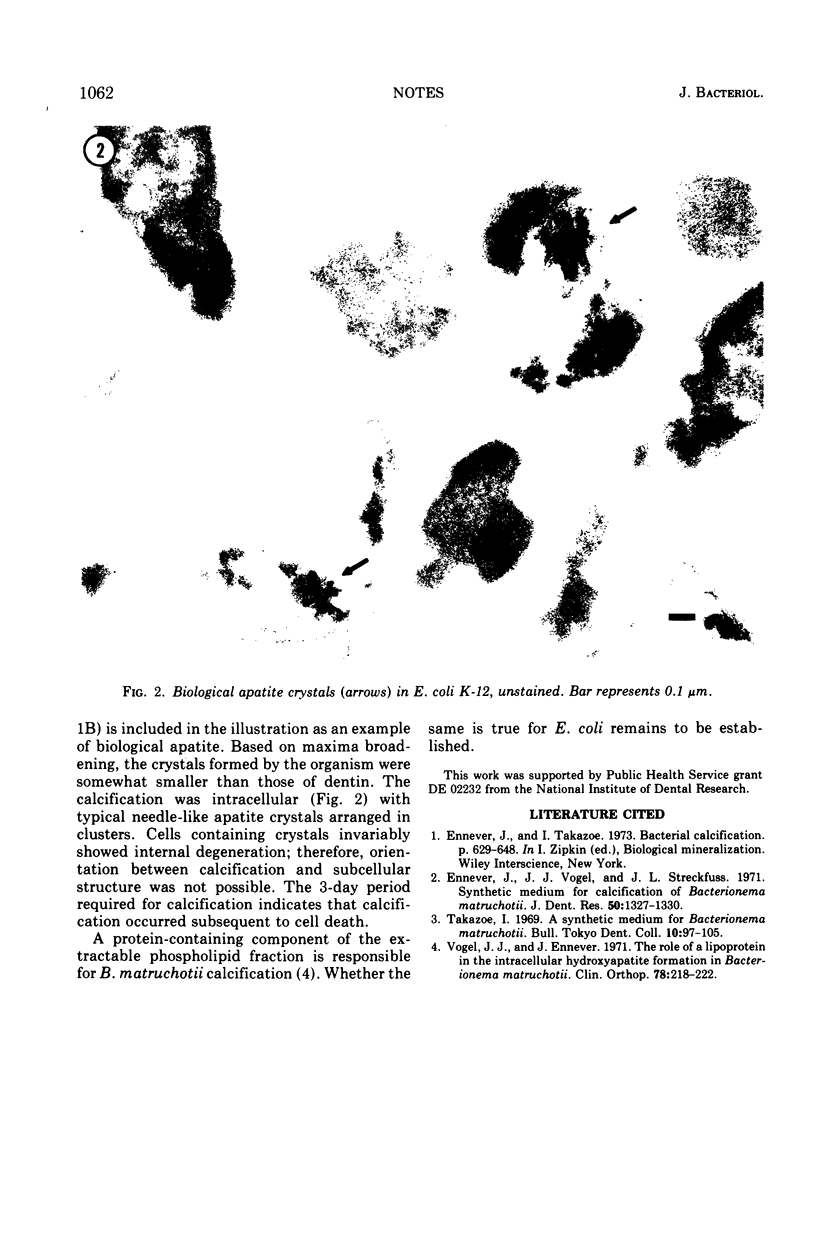
Escherichia coli K-12, grown in a synthetic medium containing metastable calcium phosphate, formed intracellular biological apatite crystals.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ennever J., Vogel J. J., Streckfuss J. L. Synthetic medium for calcification of Bacterionema matruchotii. J Dent Res. 1971 Sep-Oct;50(5):1327–1330. doi: 10.1177/00220345710500054101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takazoe I. A synthetic medium for Bacterionema matruchotii. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 1969 Aug;10(3):97–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel J. J., Ennever J. The role of a lipoprotein in the intracellular hydroxyapatite formation in Bacterionema matruchotii. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1971;78:218–222. doi: 10.1097/00003086-197107000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]