Abstract
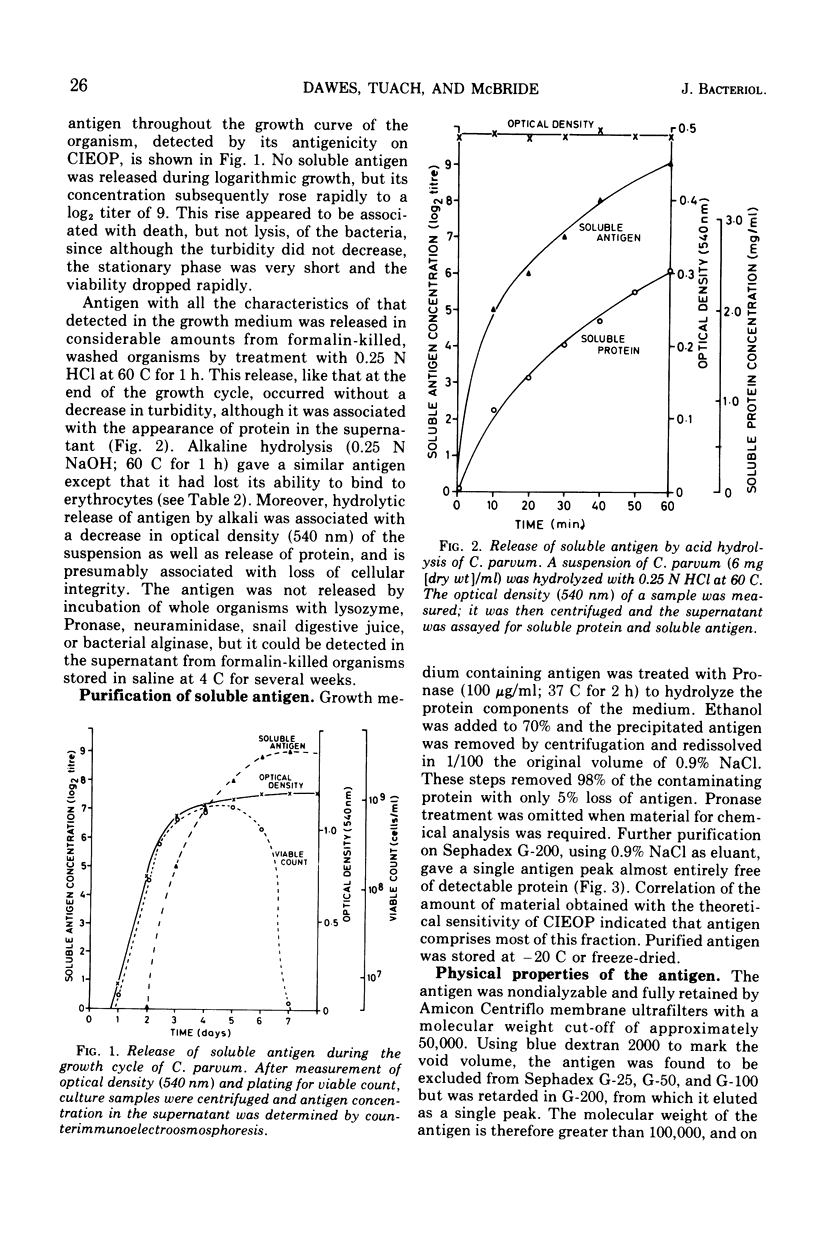
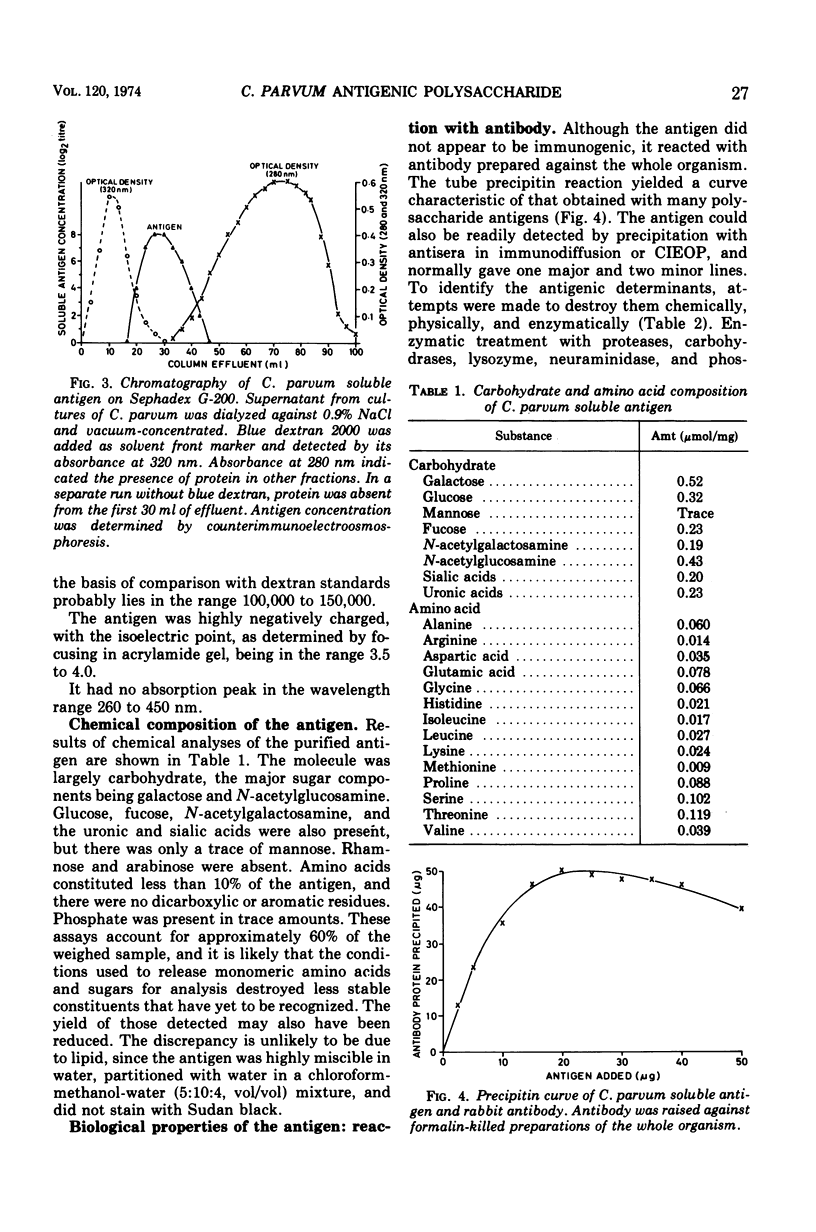
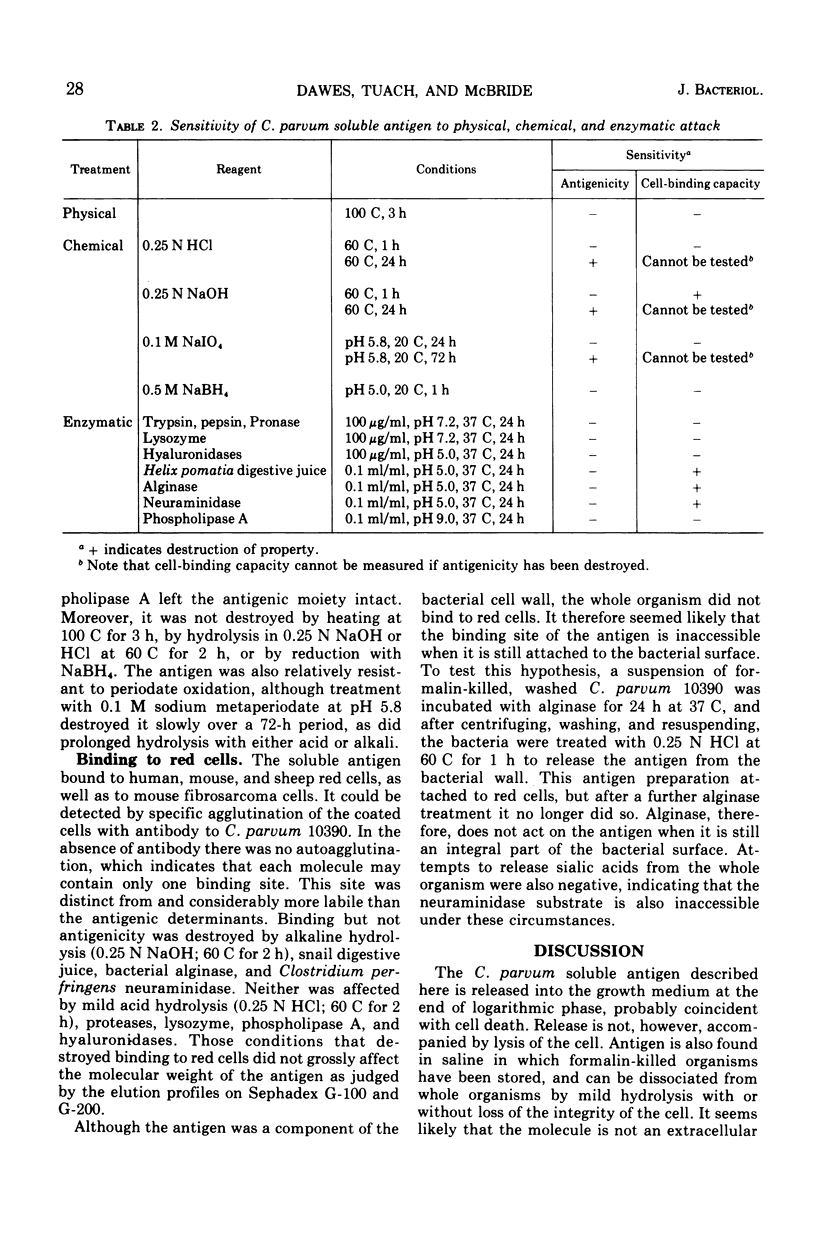
Corynebacterium parvum strain 10390 is an antitumor agent and stimulant of the reticuloendothelial system and produces a soluble antigen towards the end of its growth cycle. This material, which is a cell wall component and can also be released from the organism by acid or alkaline hydrolysis, has been purified. It is an acidic polysaccharide of molecular weight 100,000 to 150,000 and contains galactose, glucose, fucose, N-acetylgalactosamine, N-acetylglucosamine, uronic acids, sialic acids, and a small proportion of amino acids. The antigen gives a precipitin reaction with antisera raised against the whole organism and also binds to animal cells. The antigenic determinants are extremely resistant to oxidation, reduction, and enzymatic and chemical hydrolysis, but the single cell-binding site is destroyed by alkali and also by Helix pomatia digestive juice, alginase, and neuraminidase without substantially affecting the molecular weight. This site is inaccessible until the molecule is released from the cell surface. The possibility that the soluble antigen is the biologically active fraction of C. parvum is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINS C. S. Chemical composition and antigenic structure of cell walls of Corynebacterium, Mycobacterium, Nocardia, Actinomyces and Arthrobacter. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Apr;28:35–50. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-1-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINS C. S., HARRIS H. The chemical composition of the cell wall in some gram-positive bacteria and its possible value as a taxonomic character. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Jul;14(3):583–600. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-3-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Mauriño T., Perkins H. R. The presence of acidic polysaccharides and muramic acid phosphate in the walls of Corynebacterium poinsettiae and Corynebacterium betae. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Feb;80(2):533–539. doi: 10.1099/00221287-80-2-533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALPERN B. N., PREVOT A. R., BIOZZI G., STIFFEL C., MOUTON D., MORARD J. C., BOUTHILLIER Y., DECREUSEFOND C. STIMULATION DE L'ACTIVIT'E PHAGOCYTAIRE DU SYST'EME R'ETICULOENDOTH'ELIAL PROVOQU'EE PAR CORYNEBACTERIUM PARVUM. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1964 Jan;1:77–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris G., Fraser J. R. Behavior of serum in the borate modification of the carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1969 Mar;27(3):433–438. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Cummins C. S. Cell wall composition and deoxyribonucleic acid similarities among the anaerobic coryneforms, classical propionibacteria, and strains of Arachnia propionica. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1047–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1047-1066.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Likhosherstov L. M., Martynova M. D., Derevitskaia V. A. Izuchenie spetsifichnosti glikozidaz fermentnogo preparata iz Clostridium perfringens (tip A) Biokhimiia. 1968 Nov-Dec;33(6):1135–1139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride W. H., Jones J. T., Weir D. M. Increased phagocytic cell activity and anaemia in Corynebacterium parvum treated mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Feb;55(1):38–46. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Henderson D. C., White R. G. The role of anaerobic coryneforms on specific and non-specific immunological reactions. I. Effect on particle clearance and humoral and cell-mediated immunological responses. Immunology. 1973 Jun;24(6):977–995. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Burke K. Serum hepatitis antigen (SH): rapid detection by high voltage immunoelectroosmophoresis. Science. 1970 Aug 7;169(3945):593–595. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3945.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prévot A. R., Nguyen-Dang T., Thouvenot H. Influence des parois cellulaires du Corynebacterium parvum (souche 936 B) sur le système réticulo-endothélial de la souris. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1968 Sep 16;267(12):1061–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SRIVASTAVA H. C., BREUNINGER E., CREECH H. J., ADAMS G. A. Preparation and properties of polysaccharide-lipid complexes from Serratia marcescens. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1962 Jul;40:905–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrager J., Oates M. D. The carbohydrate components of hydrolysates of gastric secretion and extracts from mucous glands of the gastric body mucosa and antrum. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(2):523–529. doi: 10.1042/bj1060523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner H., Mann S. Chemische Analyse der Zellwand von Corynebacterium acnes und C. parvum. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1968 May;206(4):486–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C., O'Neill G. J., Wapshaw K. G. Role of anaerobic coryneforms in specific and non-specific immunological reactions. II. Production of a chemotactic factor specific for macrophages. Immunology. 1973 Jun;24(6):997–1006. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff M. F., Boak J. L. Inhibitory effect of injection of Corynebacterium parvum on the growth of tumour transplants in isogenic hosts. Br J Cancer. 1966 Jun;20(2):345–355. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1966.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


