Abstract
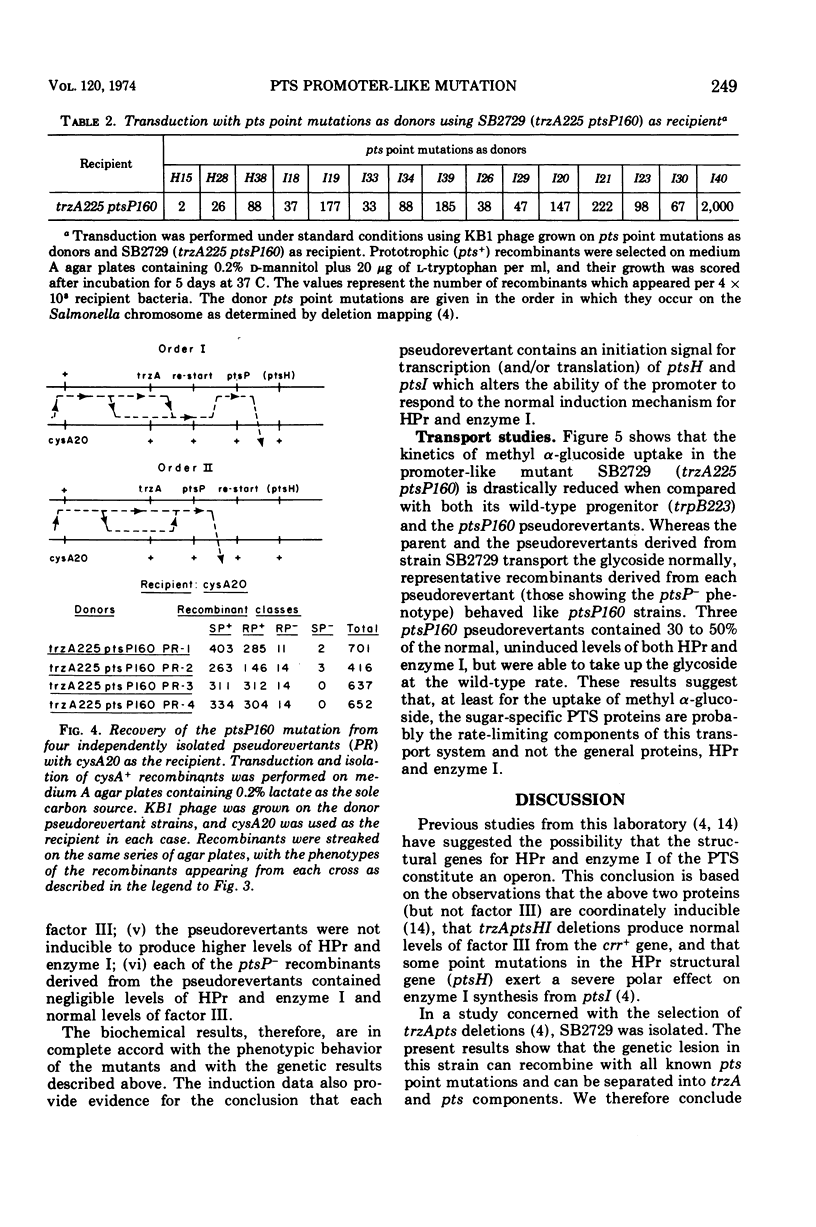
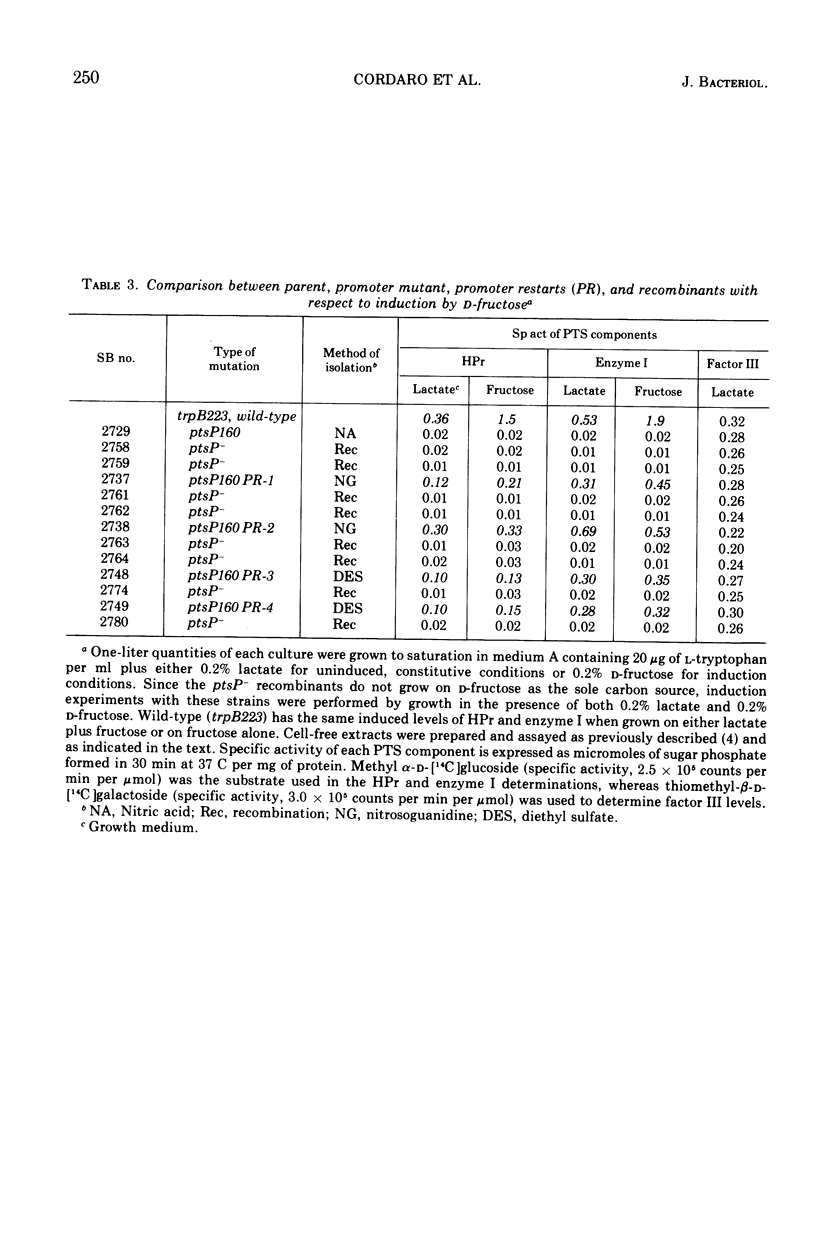
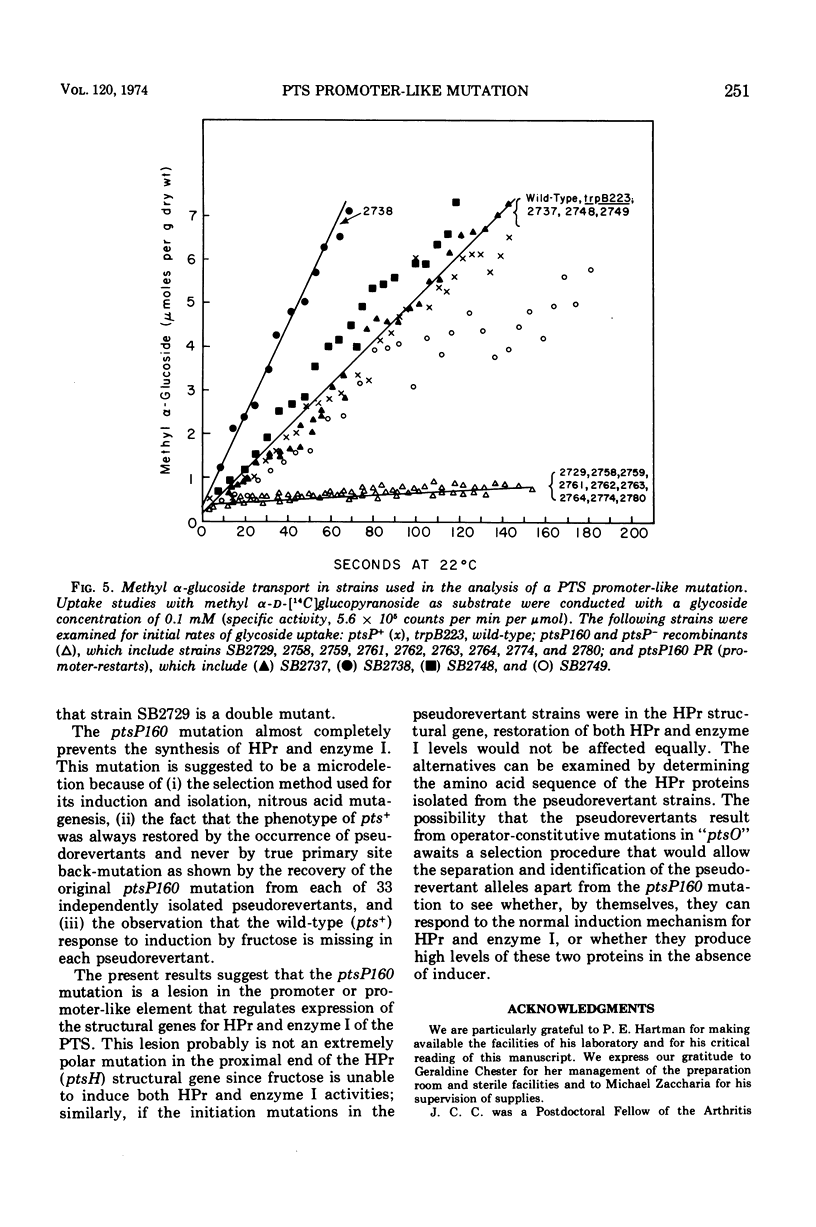
A promoter-like mutation, ptsP160, has been identified which drastically reduces expression of the genes specifying two proteins, HPr and enzyme I, of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system (PTS) in Salmonella typhimurium. This mutation lies between trzA, a gene specifying susceptibility to 1,2,4-triazole, and ptsH, the structural gene for HPr. It leads to a loss of active transport of those sugars that require the PTS for entry into the cell. Pseudorevertants of strains carrying this promoter-like mutation have additional lesions very closely linked to ptsP160 by transduction analysis and are noninducible for HPr and enzyme I above a basal level. Presumably, strains carrying ptsP160 are defective in the normal induction mechanism for HPr and enzyme I, and the pseudorevertants derived from them result from second-site initiation signals within or near this promoter-like element. The induction of HPr and enzyme I above their noninduced levels apparently is not required for transport of at least one PTS sugar, methyl α-d-glucopyranoside, since this sugar is taken up by the pseudorevertants at the same rate as by the wild type. The existence of a promoter-like element governing the coordinate inducibility of both HPr and enzyme I suggests that ptsH and ptsI constitute an operon. Wild-type levels of a sugar-specific PTS protein, factor III, are synthesized in response to the crr+ gene in both a ptsP160 strain and its pseudorevertants; this suggests that the crr+ gene has its own promoter distinct from ptsP.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B., Weigel N., Kundig W., Roseman S. Sugar transport. 3. Purification and properties of a phosphocarrier protein (HPr) of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):7023–7033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boro H., Brenchley J. E. A new generalized transducing phage for Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):835–836. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90208-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordaro J. C., Balbinder E. Evidence for the separability of the operator from the first structural gene in the tryptophan operon of Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1971 Feb;67(2):151–169. doi: 10.1093/genetics/67.2.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordaro J. C., Roseman S. Deletion mapping of the genes coding for HPr and enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):17–29. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.17-29.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNDIG W., GHOSH S., ROSEMAN S. PHOSPHATE BOUND TO HISTIDINE IN A PROTEIN AS AN INTERMEDIATE IN A NOVEL PHOSPHO-TRANSFERASE SYSTEM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1067–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundig W., Roseman S. Sugar transport. I. Isolation of a phosphotransferase system from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1393–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundig W., Roseman S. Sugar transport. II. Characterization of constitutive membrane-bound enzymes II of the Escherichia coli phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1407–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota N., Galsworthy P. R., Pardee A. B. Genetics of sulfate transport by Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1053-1062.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Simoni R. D., Roseman S. The physiological behavior of enzyme I and heat-stable protein mutants of a bacterial phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5870–5873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Roseman S. Inducer exclusion and repression of enzyme synthesis in mutants of Salmonella typhimurium defective in enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):972–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. O., Beckwith J. R. Mutagens which cause deletions in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1969 Feb;61(2):371–376. doi: 10.1093/genetics/61.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Levinthal M., Kundig F. D., Kundig W., Anderson B., Hartman P. E., Roseman S. Genetic evidence for the role of a bacterial phosphotransferase system in sugar transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1963–1970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Levine M. A phage P22 gene controlling integration of prophage. Virology. 1967 Feb;31(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J., Roseman S. A sodium-dependent sugar co-transport system in bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):132–138. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80168-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



