Abstract
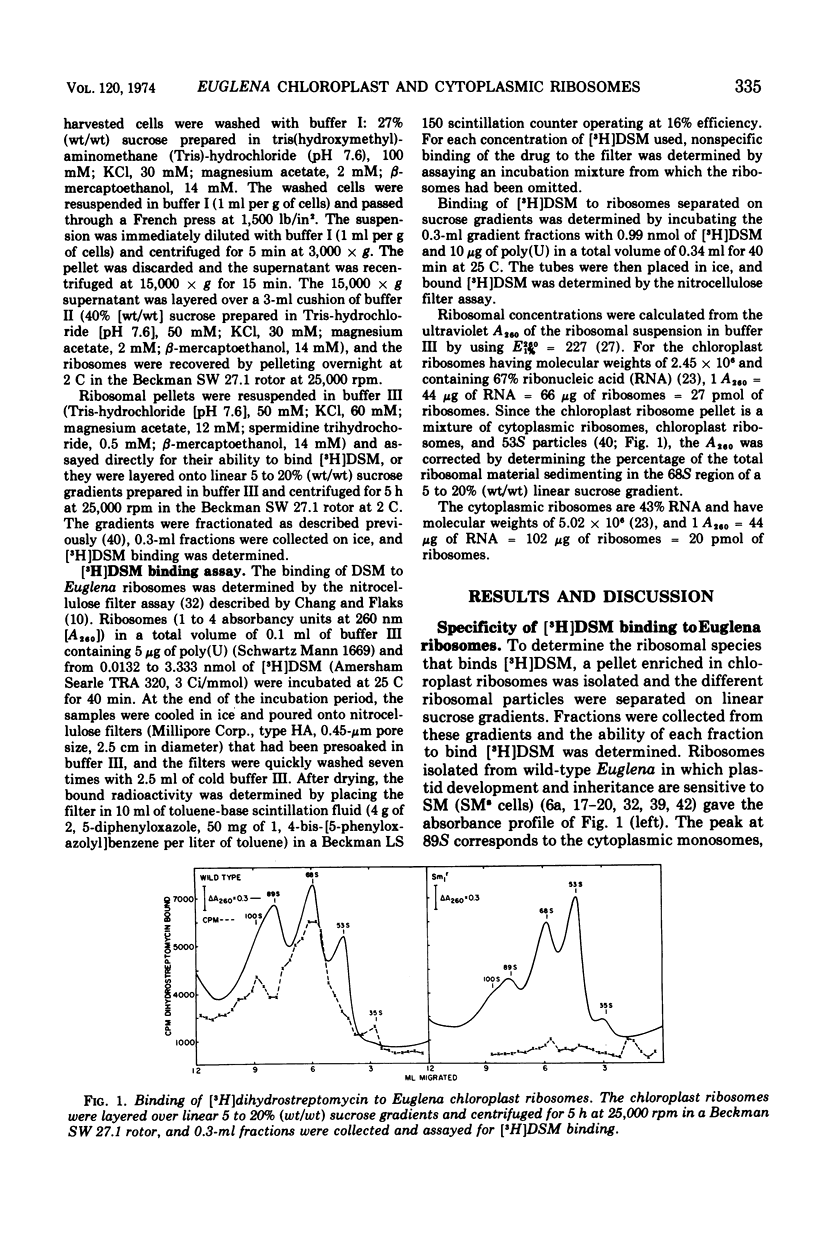
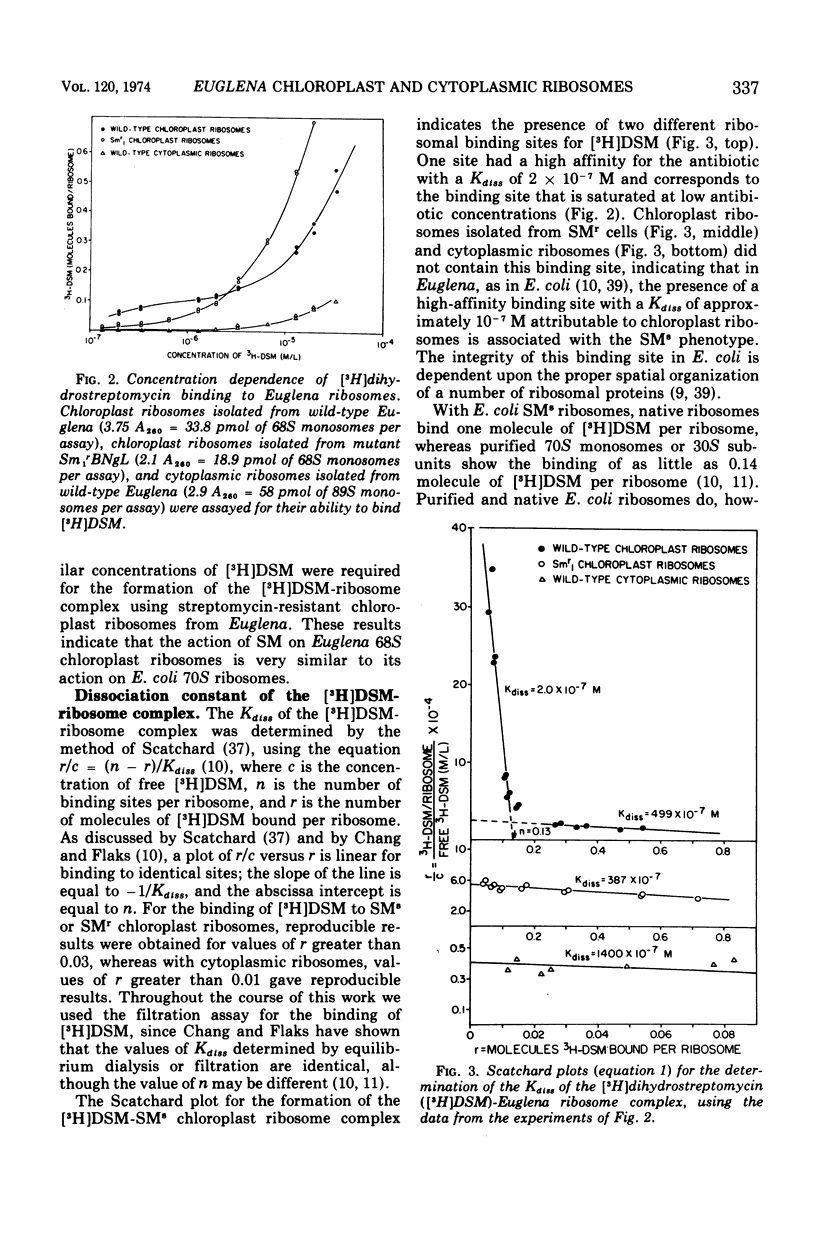
Dihydrostreptomycin binds preferentially to chloroplast ribosomes of wild-type Euglena gracilis Klebs var. bacillaris Pringsheim. The Kdiss for the wild-type chloroplast ribosome-dihydrostreptomycin complex is 2 × 10−7 M, a value comparable with that found for the Escherichia coli ribosome-dihydrostreptomycin complex. Chloroplast ribosomes isolated from the streptomycin-resistant mutant Sm1rBNgL and cytoplasmic ribosomes from wild-type have a much lower affinity for the antibiotic. The Kdiss for the chloroplast ribosome-dihydrostreptomycin complex of Sm1r is 387 × 10−7 M, and the value for the cytoplasmic ribosome-dihydrostreptomycin complex of the wild type is 1,400 × 10−7 M. Streptomycin competes with dihydrostreptomycin for the chloroplast ribosome binding site, and preincubation of streptomycin with hydroxylamine prevents the binding of streptomycin to the chloroplast ribosome. These results indicate that the inhibition of chloroplast development and replication in Euglena by streptomycin and dihydrostreptomycin is related to the specific inhibition of protein synthesis on the chloroplast ribosomes of Euglena.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARONSON J., MEYER W. L., BROCK T. D. A MOLECULAR MODEL FOR CHEMICAL AND BIOLOGICAL DIFFERENCES BETWEEN STREPTOMYCIN AND DIHYDROSTREPTOMYCIN. Nature. 1964 May 9;202:555–557. doi: 10.1038/202555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avadhani N. G., Buetow D. E. Isolation of active polyribosomes from the cytoplasm, mitochondria and chloroplasts of Euglena gracilis. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(2):353–365. doi: 10.1042/bj1280353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avadhani N. G., Buetow D. E. Protein synthesis with isolated mitochondrial polysomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):773–778. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80207-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas D. K., Gorini L. The attachment site of streptomycin to the 30S ribosomal subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2141–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschetti A., Bogdanov S. Binding of dihydrostreptomycin to ribosomes and ribosomal subunits from streptomycin-resistant mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 15;38(1):19–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80502-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovarnick J. G., Chang S. W., Schiff J. A., Schwartzbach S. D. Events surrounding the early development of Euglena chloroplasts: experiments with streptomycin in non-dividing cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jul;83(0):51–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-1-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink N. G., Kuehl F. A., Jr, Folkers K. STREPTOMYCES ANTIBIOTICS. III. DEGRADATION OF STREPTOMYCIN TO STREPTOBIOSAMINE DERIVATIVES. Science. 1945 Nov 16;102(2655):506–507. doi: 10.1126/science.102.2655.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. S., LICHTENSTEIN J. The isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from bacterial extracts by precipitation with streptomycin. J Biol Chem. 1960 Nov;235:PC55–PC56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX E. C., WHITE J. R., FLAKS J. G. STREPTOMYCIN ACTION AND THE RIBOSOME. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Apr;51:703–709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.4.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Flaks J. G. Binding of dihydrostreptomycin to Escherichia coli ribosomes: characteristics and equilibrium of the reaction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Oct;2(4):294–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.4.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Flaks J. G. Binding of dihydrostreptomycin to Escherichia coli ribosomes: kinetics of the reaction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Oct;2(4):308–319. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.4.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Flaks J. G. Topography of the Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunit and streptomycin binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1321–1328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Wang Y. J., Fetterolf C. J., Flaks J. G. Letter: Unequal contribution to ribosomal assembly of both str alleles in Escherichia coli merodiploids and its relationship to the dominance phenomenon. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 15;82(2):273–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90345-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. S., Carr C. W. Competitive binding of streptomycin and magnesium with Escherichia coli ribosomes. Nature. 1968 Feb 10;217(5128):556–557. doi: 10.1038/217556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES J. E. STUDIES ON THE RIBOSOMES OF STREPTOMYCIN-SENSITIVE AND RESISTANT STRAINS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Apr;51:659–664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.4.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebringer L. Are plastids derived from prokaryotic micro-organisms? Action of antibiotics on chloroplasts of Euglena gracilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jun;71(1):35–52. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-1-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebringer L., Mego J. L., Jurásek A., Kada R. The action of streptomycins on the chloroplast system of Euglena gracilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Dec;59(2):203–209. doi: 10.1099/00221287-59-2-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebringer L., Nemec P., Santová H., Foltínová P. Changes of the plastid system of Euglena gracilis induced with streptomycin and dihydrostreptomycin. Arch Mikrobiol. 1970;73(3):268–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00410628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman M., Cowan C. A., Epstein H. T., Schiff J. A. STUDIES OF CHLOROPLAST DEVELOPMENT IN EUGLENA, VIII. CHLOROPLAST-ASSOCIATED DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Nov;52(5):1214–1219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.5.1214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLAKS J. G., COX E. C., WHITE J. R. Inhibition of polypeptide synthesis by streptomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 11;7:385–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90320-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLAKS J. G., COX E. C., WITTING M. L., WHITE J. R. Polypeptide synthesis with ribosomes from streptomycin-resistant and dependent E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 11;7:390–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90321-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji H., Tanaka Y. Binding of dihydrostreptomycin to ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroon A. M., de Vries H. Antibiotics: a tool in the search for the degree of autonomy of mitochondria in higher animals. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1970;24:181–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. Streptomycin resistance; a genetically recessive mutation. J Bacteriol. 1951 May;61(5):549–550. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.5.549-550.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mets L. J., Bogorad L. Mendelian and uniparental alterations in erythromycin binding by plastid ribosomes. Science. 1971 Nov 12;174(4010):707–709. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4010.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mets L., Bogorad L. Altered chlorplast ribosomal proteins associated with erythromycin-resistant mutants in two genetic systems of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3779–3783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M., LEDER P. RNA CODEWORDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. THE EFFECT OF TRINUCLEOTIDES UPON THE BINDING OF SRNA TO RIBOSOMES. Science. 1964 Sep 25;145(3639):1399–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3639.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki M., Mizushima S., Nomura M. Identification and functional characterization of the protein controlled by the streptomycin-resistant locus in E. coli. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):333–339. doi: 10.1038/222333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petitpas-Dewandre A., Barbason H., Verly W. G. Affinité pour la streptomycine des ribosomes d'Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jan;7(3):307–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPEYER J. F., LENGYEL P., BASILIO C. Ribosomal localization of streptomycin sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Apr 15;48:684–686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.4.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R., Ramanis Z. A genetic map of non-Mandelian genes in Chlamydomonas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):593–600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff J. A. The development, inheritance, and origin of the plastid in Euglena. Adv Morphog. 1973;10:265–312. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-028610-2.50010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G., Nierhaus K. H. Protein involved in the binding of dihydrostreptomycin to ribosomes of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 25;81(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90248-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzbach S. D., Freyssinet G., Schiff J. A. The chloroplast and cytoplasmic ribosomes of euglena: I. Stability of chloroplast ribosomes prepared by an improved procedure. Plant Physiol. 1974 Apr;53(4):533–542. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.4.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzbach S. D., Freyssinet G., Schiff J. A. The chloroplast and cytoplasmic ribosomes of euglena: I. Stability of chloroplast ribosomes prepared by an improved procedure. Plant Physiol. 1974 Apr;53(4):533–542. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.4.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Vogel T., Elson D., Zamir A. Ribosome activation and the binding of dihydrostreptomycin: effect of polynucleotides and temperature on activation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):379–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90436-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. J., Davis B. D. Cyclic blockade of initiation sites by streptomycin-damaged ribosomes in Escherichia coli: an explanation for dominance of sensitivity. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):377–390. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Davies J. A genetic and biochemical study of streptomycin- and spectinomycin-resistance in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;110(3):197–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00337833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


