Abstract
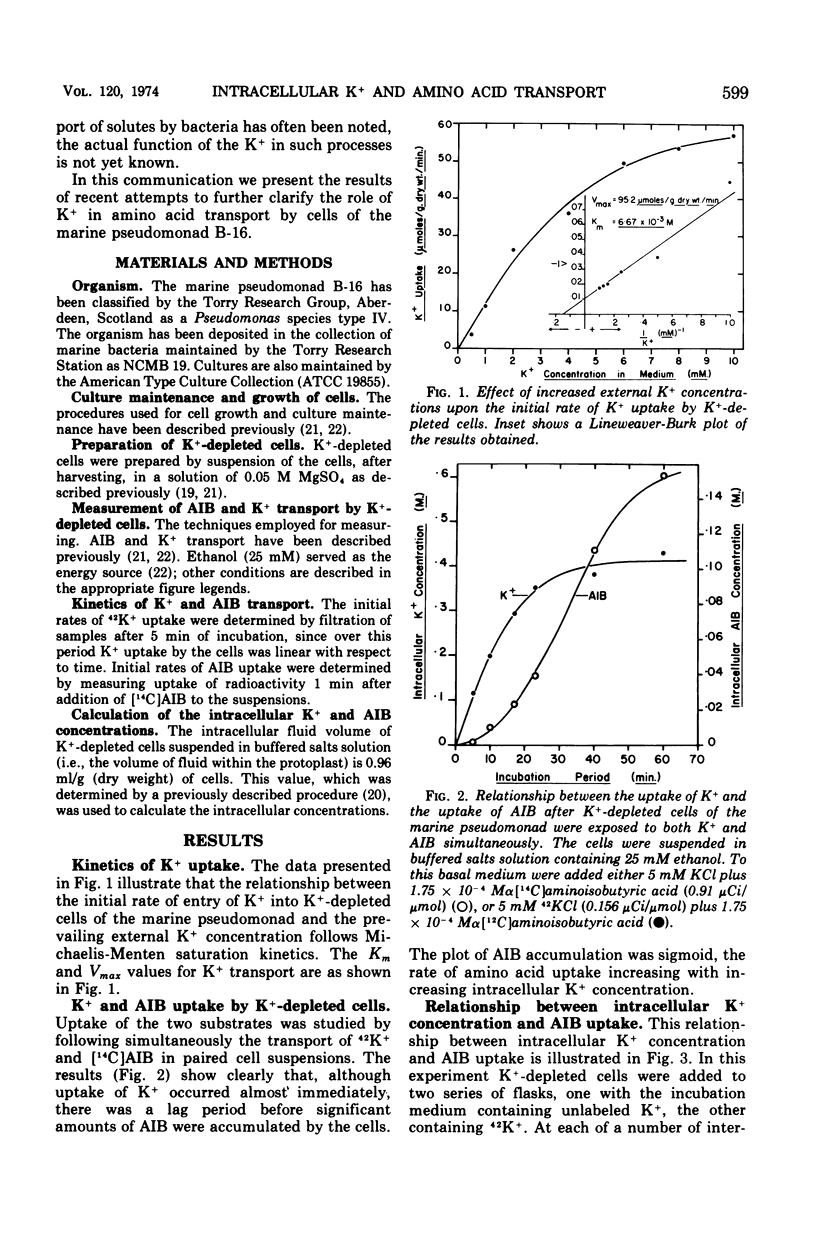
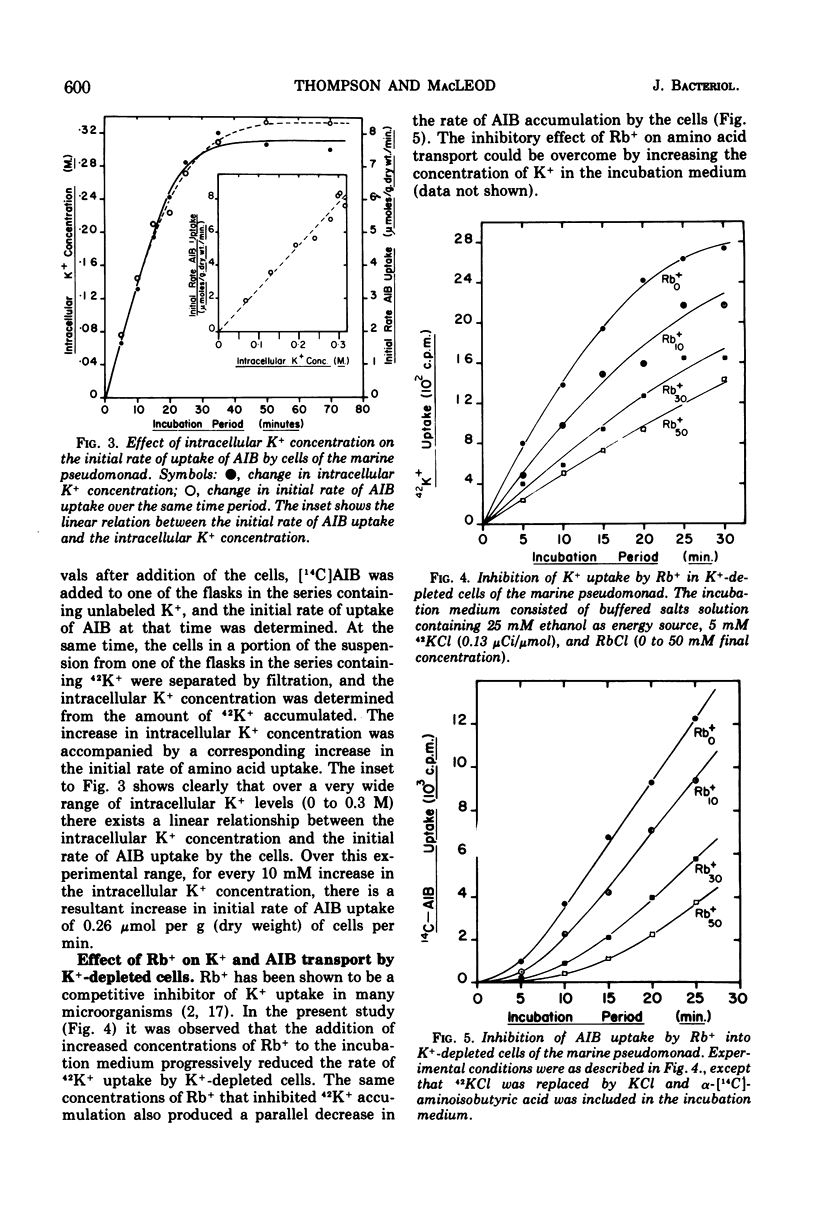
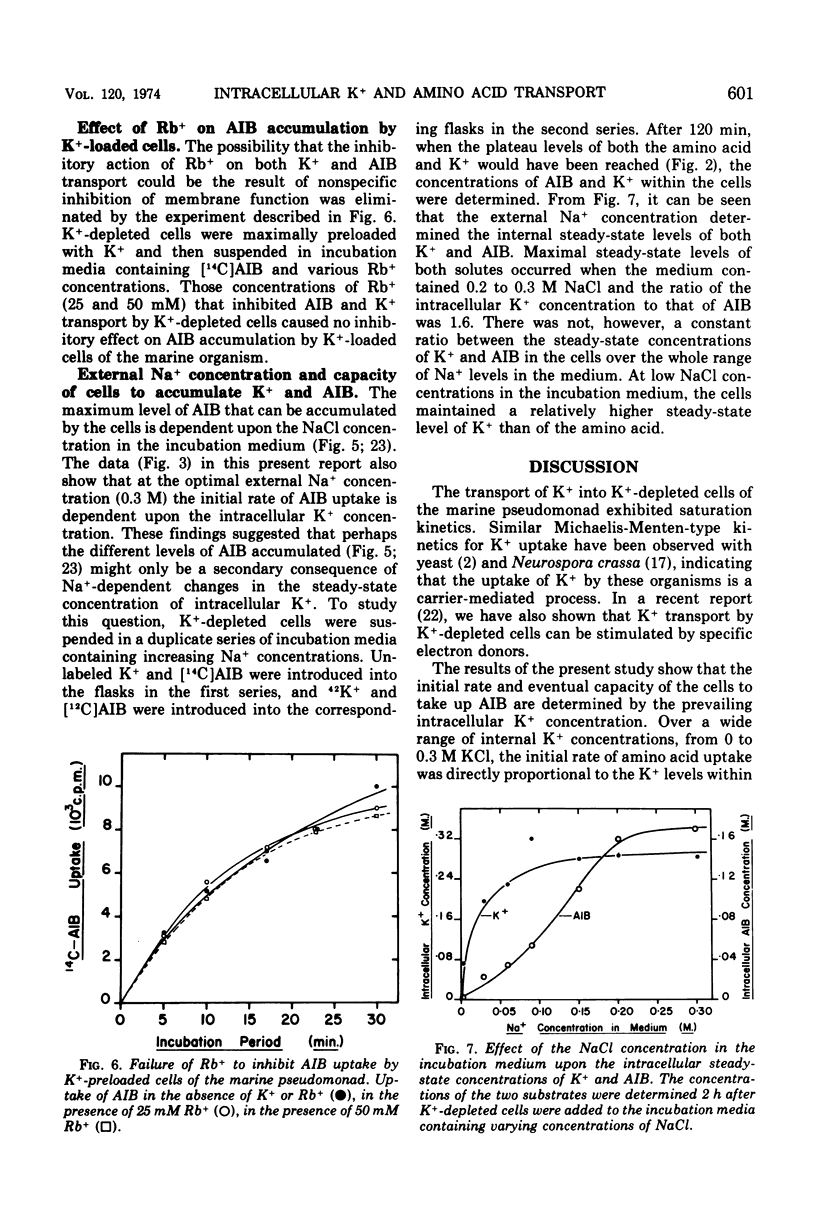
Transport of K+ by K+-depleted cells of marine pseudomonad B-16 (ATCC 19855) exhibited saturation kinetics. Rb+ inhibited both K+ transport and the K+-dependent transport of α-aminoisobutyric acid (AIB) into K+-depleted cells of the organism in proportion to the concentration of Rb+ in the suspending medium. Inhibition of the K+-dependent uptake of AIB into K+-depleted cells by Rb+ could be overcome by increasing the concentration of K+ in the medium. When AIB and K+ were added simultaneously to a suspension of K+-depleted cells, the uptake of K+ occurred immediately and rapidly, whereas the accumulation of AIB occurred only after a lag. The initial uptake rate of AIB was directly proportional to the intracellular K+ concentration. The intracellular concentration of K+ and AIB at their steady-state levels increased to a maximum as the Na+ concentration in the suspending medium was increased. At Na+ concentrations between 0.2 and 0.3 M, the molar ratio of K+ to AIB at their intracellular steady-state concentrations was constant at 1.6. At external Na+ concentrations less than 0.2 M, the cells maintained a relatively higher K+ intracellular steady-state level than AIB.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMS A. Metabolically dependent penetration of oligosaccharides into bacterial cells and protoplasts. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1281–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong W. M., Rothstein A. Discrimination between alkali metal cations by yeast. II. Cation interactions in transport. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Mar;50(4):967–988. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.4.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. Solute concentrations within cells of halophilic and non-halophilic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 17;65:506–508. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charalampous F. C. Metabolic functions of myo-inositol. IX. Role of intracellular K+ and of Na plus- and K plus-activated adenosine triphosphatase in the transport of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 25;246(2):461–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane R. K. Na+ -dependent transport in the intestine and other animal tissues. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):1000–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES R., FOLKES J. P., GALE E. F., BIGGER L. C. The assimilation of amino-acids by micro-organisms. XVI. Changes in sodium and potassium accompanying the accumulation of glutamic acid or lysine by bacteria and yeast. Biochem J. 1953 Jun;54(3):430–437. doi: 10.1042/bj0540430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G. R., Matula T. I., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XV. Relation of Na+-activated transport to the Na+ requirement of a marine pseudomonad for growth. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):63–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.63-71.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagon R. G., Wilkerson L. S. A potassium-dependent citric acid transport system in Aerobacter aerogenes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 10;46(5):1944–1950. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern Y. S., Barash H., Dover S., Druck K. Sodium and potassium requirements for active transport of glutamate by Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):53–58. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.53-58.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Barnes E. M., Jr Mechanisms of active transport in isolated membrane vesicles. II. The mechanism of energy coupling between D-lactic dehydrogenase and beta-galactoside transport in membrane preparations from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5523–5531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A. THE QUESTION OF THE EXISTENCE OF SPECIFIC MARINE BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:9–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough G. A., Rumley M. K., Kennedy E. P. The function of adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the lactose transport system of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):951–958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Curran P. F. Coupled transport of sodium and organic solutes. Physiol Rev. 1970 Oct;50(4):637–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprott G. D., MacLeod R. A. Nature of the specificity of alcohol coupling to L-alanine transport into isolated membrane vesicles of a marine pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1043–1054. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1043-1054.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Costerton J. W., MacLeon R. A. K plus-dependent deplasmolysis of a marine pseudomonad plasmolyzed in a hypotonic solution. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):843–854. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.843-854.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Functions of Na+ and K+ in the active transport of -aminoisobutyric acid in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):4066–4074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Na+ and K+ gradients and alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7106–7111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Specific electron donor-energized transport of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid and K+ into intact cells of a marine pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1055–1064. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1055-1064.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. T., Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XVII. Ion-dependent retention of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid and its relation to Na+ dependent transport in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):1016–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


