Abstract
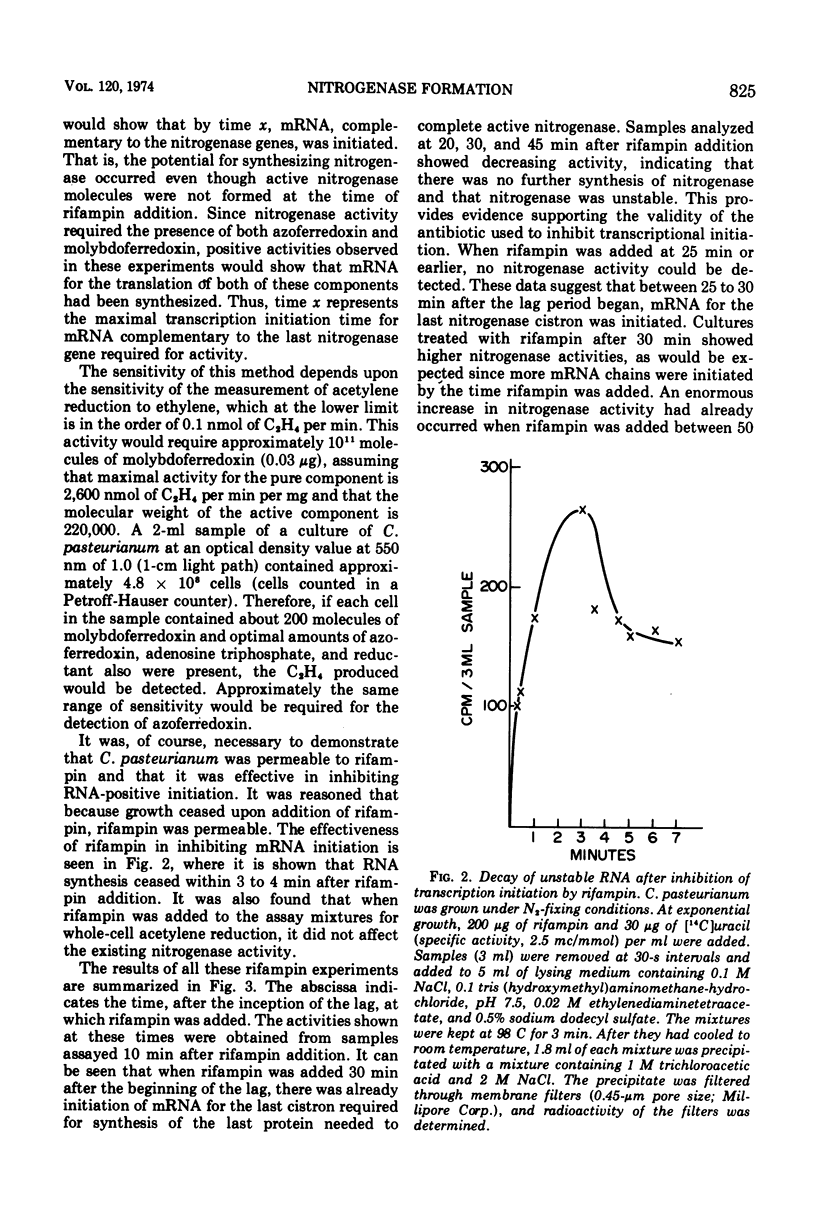
Clostridium pasteurianum exhibits diauxic growth when grown in the presence of both NH3 and N2; no nitrogenase activity or formation was detected either serologically or by activity during growth on NH3. During the 60-min lag that ensued after NH3 was consumed and before growth resumed, molybdoferredoxin and azoferredoxin were first detected by activity measurements and serologically at 25 and 40 min, respectively. With the use of rifampin and dactinomycin, it was found that azoferredoxin messenger ribonucleic acid was initiated between 25 and 30 min after the inception of the lag and was completed by 38 min. An explanation of these results and their relation to possible models for the regulation of nitrogenase is given.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BYRNE R., LEVIN J. G., BLADEN H. A., NIRENBERG M. W. THE IN VITRO FORMATION OF A DNA-RIBOSOME COMPLEX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:140–148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremer H., Yuan D. RNA chain growth-rate in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec 14;38(2):163–180. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90404-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daesch G., Mortenson L. E. Effect of ammonia on the synthesis and function of the N 2 -fixing enzyme system in Clostridium pasteurianum. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):103–109. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.103-109.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale B. A., Greenberg G. R. Effect of the folic acid analogue, trimethoprim, on growth, macromolecular synthesis, and incorporation of exogenous thymine in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):905–916. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.905-916.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das H. K., Goldstein A., Lowney L. I. Attachment of ribosomes to nascent messenger RNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 Mar 14;24(2):231–245. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90329-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstadt J., Lengyel P. Formylmethionyl-tRNA dependence of amino acid incorporation in extracts of trimethoprim-treated Escherichia coli. Science. 1966 Oct 28;154(3748):524–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEPES A., BEGUIN S. HYDROXYLAMINE, AN INHIBITOR OF PEPTIDE CHAIN INITIATION. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Feb 3;18:377–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90717-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kepes A., Beguin S. Peptide chain initiation and growth in the induced synthesis of beta-galactosidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Sep;123(3):546–560. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein A., Eisenstadt A., Eisenstadt J., Lengyel P. Inhibition of peptide-chain initiation in Escherichia coli by hydroxylamine and effects on ribonucleic acid synthesis. Biochemistry. 1970 Nov 10;9(23):4542–4549. doi: 10.1021/bi00825a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAAS W. K. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF REPRESSION OF ARGININE BIOSYNTHESIS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. II. DOMINANCE OF REPRESSIBILITY IN DIPLOIDS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Mar;8:365–370. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENGRA R. M., WILSON P. W. Physiology of nitrogen fixation by Aerobacter aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1958 Jan;75(1):21–25. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.1.21-25.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Davis L. C., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase. I. Repression and derepression of the iron-molybdenum and iron proteins of nitrogenase in Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;256(2):498–511. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90078-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubb R. S., Postgate J. R. Control of nitrogenase synthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Nov;79(1):103–117. doi: 10.1099/00221287-79-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Pengra R. M. Effect of amino acids on the nitrogenase system of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):618–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.618-622.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelitch I. Simultaneous Use of Molecular Nitrogen and Ammonia by Clostridium Pasteurianum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1951 Sep;37(9):559–565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.37.9.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G., Mortensson L. E. Evidence for a catalytic-centre heterogeneity of molybdoferredoxin from Clostridium pasteurianum. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jun 15;35(3):401–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



