Abstract
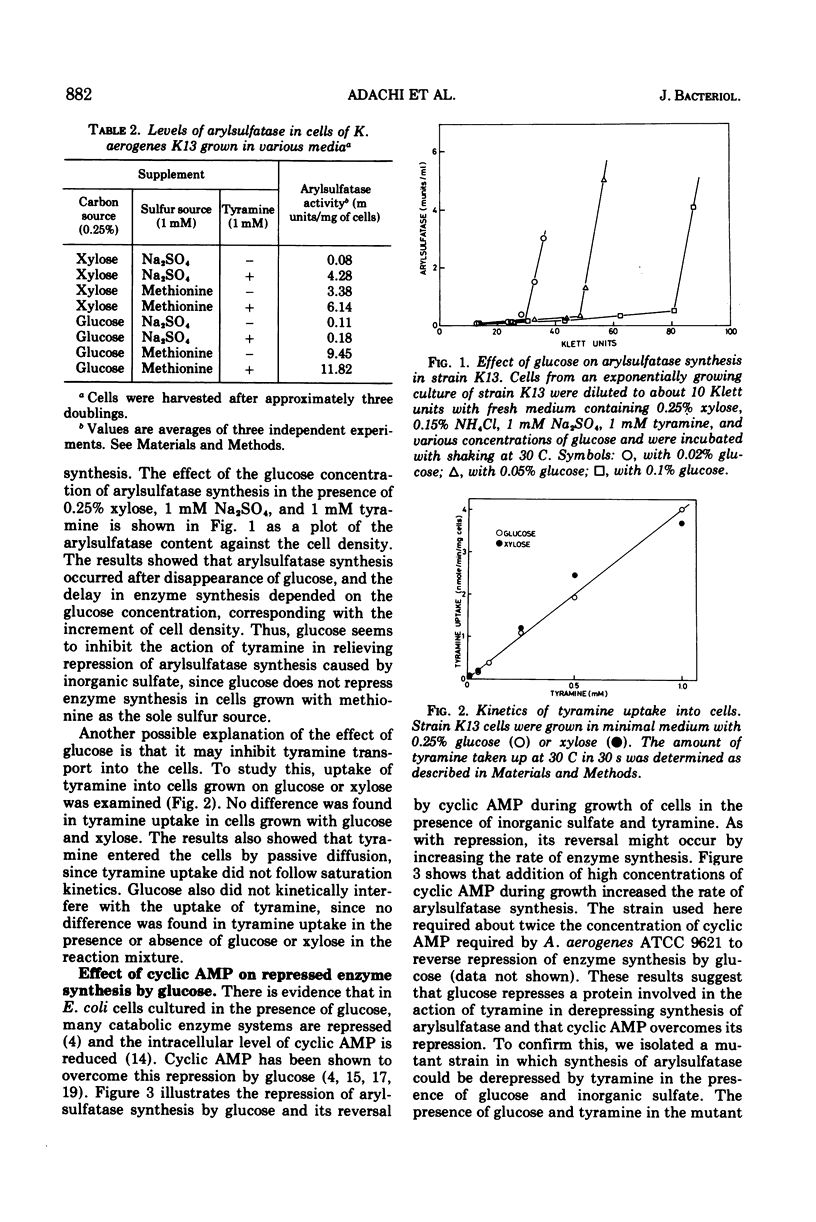
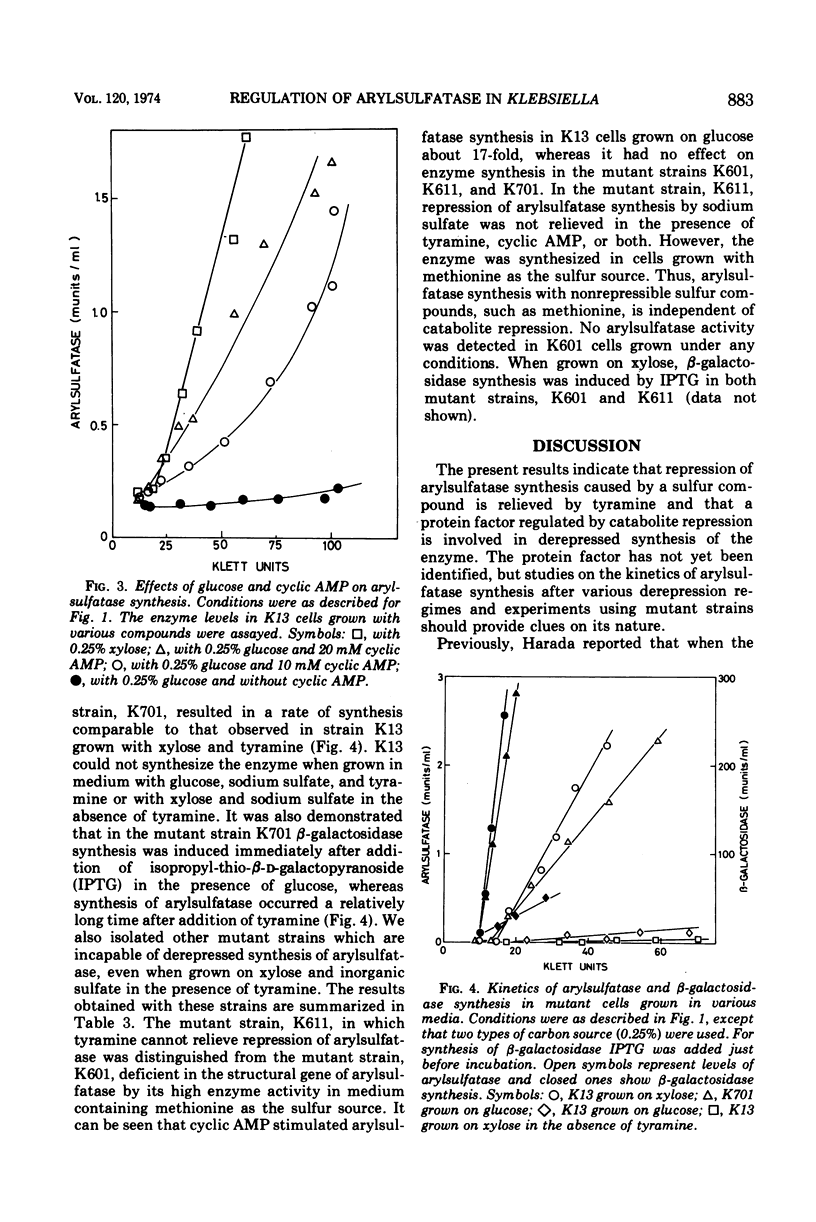
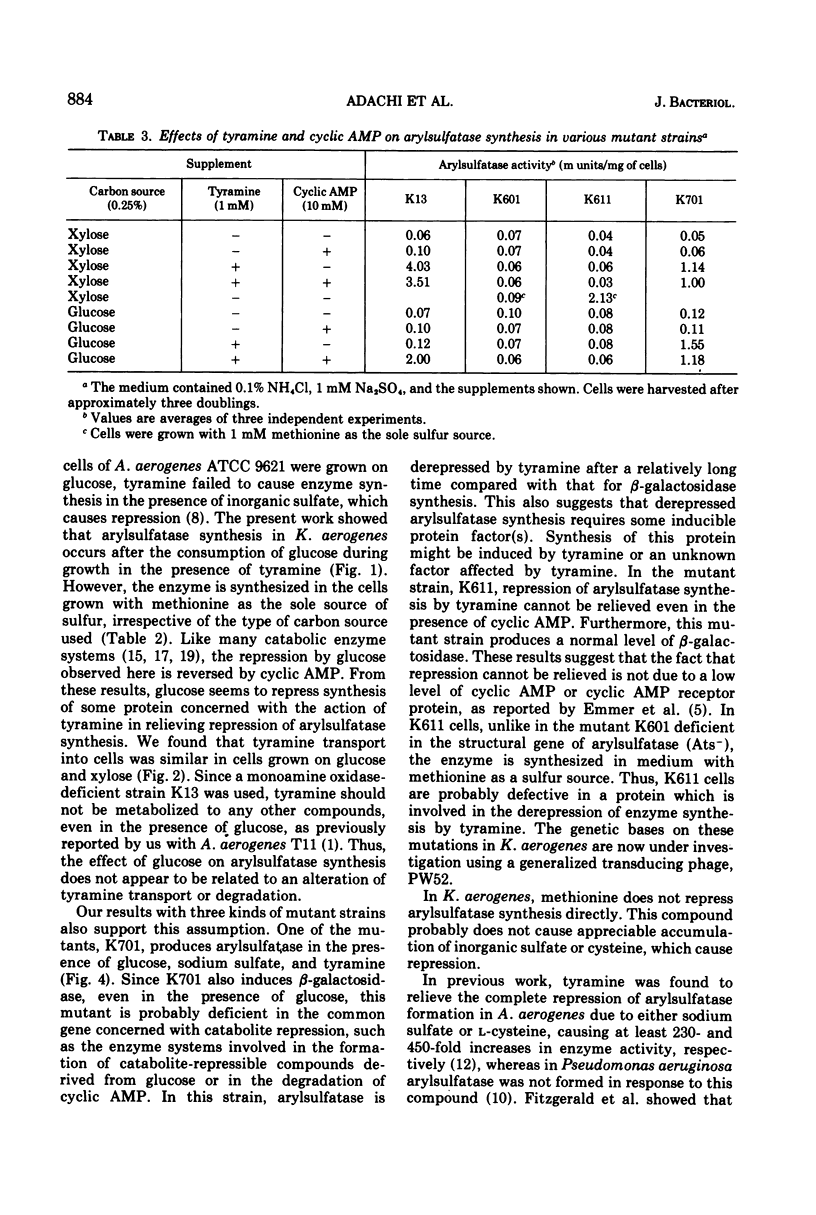
When a mutant (Mao−) of Klebsiella aerogenes lacking an enzyme for tyramine degradation (monoamine oxidase) was grown with d-xylose as a carbon source, arylsulfatase was repressed by inorganic sulfate and repression was relieved by tyramine. When the cells were grown on glucose, tyramine failed to derepress the arylsulfatase synthesis. When grown with methionine as the sole sulfur source, the enzyme was synthesized irrespective of the carbon source used. Addition of cyclic adenosine monophosphate overcame the catabolite repression of synthesis of the derepressed enzyme caused by tyramine. Uptake of tyramine was not affected by the carbon source. We isolated a mutant strain in which derepression of arylsulfatase synthesis by tyramine occurred even in the presence of glucose and inorganic sulfate. This strain also produced β-galactosidase in the presence of an inducer and glucose. These results, and those on other mutant strains in which tyramine cannot derepress enzyme synthesis, strongly suggest that a protein factor regulated by catabolite repression is involved in the derepression of arylsulfatase synthesis by tyramine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi T., Murooka Y., Harada T. Derepression of arylsulfatase synthesis in Aerobacter aerogenes by tyramine. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):19–24. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.19-24.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Crombrugghe B., Perlman R. L., Varmus H. E., Pastan I. Regulation of inducible enzyme synthesis in Escherichia coli by cyclic adenosine 3', 5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5828–5835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmer M., deCrombrugghe B., Pastan I., Perlman R. Cyclic AMP receptor protein of E. coli: its role in the synthesis of inducible enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):480–487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald J. W., Payne W. J. The regulation of arylsulphatase formation in Pseudomonas C 12 B. Microbios. 1972 Sep-Oct;6(22):147–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada T., Spencer B. Repression and induction of arylsulphatase synthesis in Aerobacter aerogenes. Biochem J. 1964 Nov;93(2):373–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0930373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKMAN R. S., SUTHERLAND E. W. ADENOSINE 3',5'-PHOSPHATE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1309–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee D. G., Sutherland I. W., Wilkinson J. F. Transduction in Klebsiella. Nature. 1969 Feb 1;221(5179):475–476. doi: 10.1038/221475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa T., Yokota T. Requirement of adenosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphate for L-arabinose isomerase synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1412–1418. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1412-1418.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman R. L., Pastan I. Regulation of beta-galactosidase synthesis in Escherichia coli by cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5420–5427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMMLER D. H., GRADO C., FOWLER L. R. SULFUR METABOLISM OF AEROBACTER AEROGENES. I. A REPRESSIBLE SULFATASE. Biochemistry. 1964 Feb;3:224–230. doi: 10.1021/bi00890a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao M., Schweiger M. Stimulation of galactokinase synthesis in Escherichia coli by adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):138–141. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.138-141.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



