Abstract
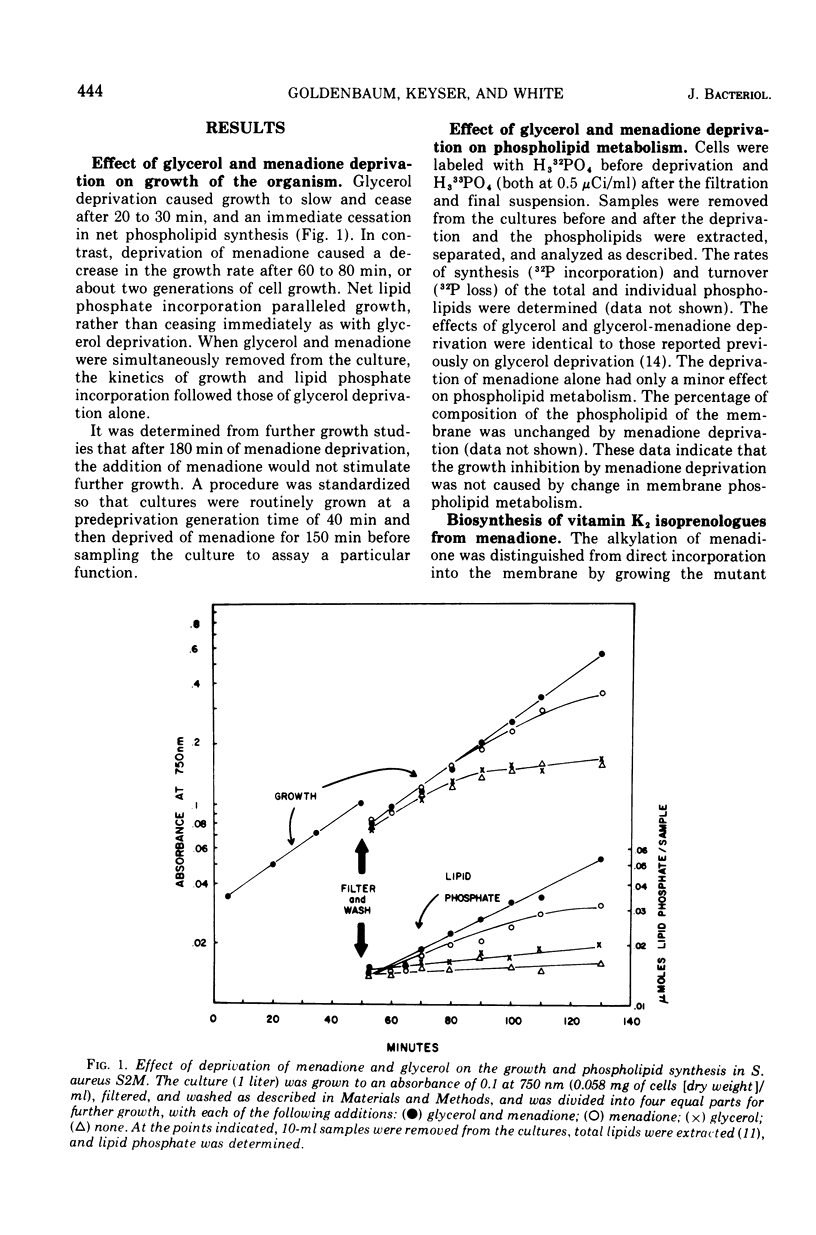
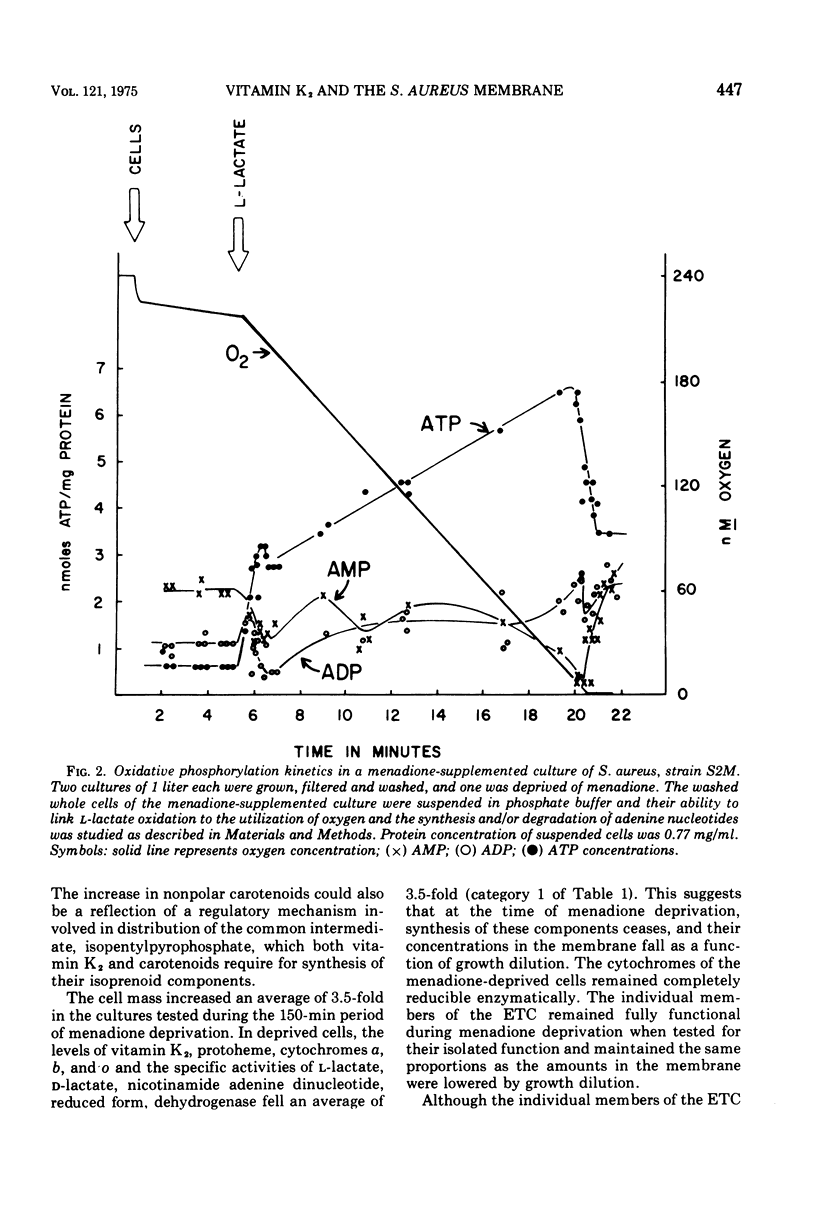
A mutant of Staphylococcus aureus auxotrophic for menadione (a vitamin K2 precursor) was used to study the effects of menadione deprivation on the structure and function of the cell membrane. The phospholipid composition and metabolism was essentially unaltered by menadione deprivation. Removal of this percursor caused cellular levels of the cytochromes, protoheme, vitamin K2, and several membrane-bound flavoprotein dehydrogenase activities to decrease as a function of growth dilution. The cytochromes were enzymatically reducible and maintained in the same proportions as menadione-supplemented cells. Oxidative phosphorylation, however, was reduced more than 10-fold and membrane vesicles obtained from menadione-deprived cells were unable to couple glycine transport to L-lactate oxidation. Succinic dehydrogenase and adenosine 5' triphosphate hydrolysis appeared unaffected by menadione deprivation. These data suggest that menadione deprivation in the mutant stops the synthesis of vitamin K2 and other electron transport chain components and prosthetic groups. Although individual electron transport chain members remained fully functional during menadione deprivation, the overall efficiency of the chain, measured in terms of its function in electron transport, oxidative phosphorylation, and electron transport chain-linked transport, dropped greatly. This suggests that the synthesis of vitamin K2 is modulated to the synthesis of other components of the electron transport system, and that their organization into a functional system requires a specific concentration of vitamin K2 with respect to total membrane lipid.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLS H. A. A colorimetric method for the assay of soluble succinic dehydrogenase and pyridinenucleotide-linked dehydrogenases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Dec;85:561–562. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frerman F. E., White D. C. Membrane lipid changes during formation of a functional electron transport system in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1868–1874. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1868-1874.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Carotenoid formation by Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):191–198. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.191-198.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Formation of vitamin K2 isoprenologues by Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):573–578. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.573-578.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Inhibition of carotenoid hydroxylation in Staphylococcus aureus by mixed-function oxidase inhibitors. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):607–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.607-610.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Inhibition of vitamin K2 and carotenoid synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus by diphenylamine. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):611–615. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.611-615.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Separation of vitamin K2 isoprenologues by reversed-phase thin-layer chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1969 Dec 23;45(3):446–452. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)86242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillich T. T., White D. C. Phospholipid metabolism in the absence of net phospholipid synthesis in a glycerol-requiring mutant of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):790–797. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.790-797.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. H., Lillich T. T., White D. C. Consequences of glycerol deprivation on the synthesis of membrane components in a glycerol auxotroph of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):413–420. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.413-420.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. H., White D. C. Effect of glycerol deprivation on the phospholipid metabolism of a glycerol auxotroph of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):668–677. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.668-677.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short S. A., White D. C., Kaback H. R. Active transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. V. The transport of amino acids by membrane vesicles prepared from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):298–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short S. A., White D. C. Metabolism of the glycosyl diglycerides and phosphatidylglucose of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):126–132. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.126-132.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silbert D. F., Cronan J. E., Jr, Beacham I. R., Harder M. E. Proceedings: Genetic engineering of membrane lipid. Fed Proc. 1974 Jun;33(6):1725–1732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien W., White D. C. Linear sequential arrangement of genes for the biosynthetic pathway of protoheme in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1392–1398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Frerman F. E. Extraction, characterization, and cellular localization of the lipids of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1854–1867. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1854-1867.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



