Abstract
The first enzyme of histidine biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium, adenosine triphosphate phosphoribosyltransferase (EC 2.4.2.17), has been purified from two bacterial strains containing histidine operator deletions and compared to the eenzyme from a strain that has a normal operator. The enzymes isolated in different ways also are compared. Evidence as to the separateness of the operator and first structural gene or covalent modification of the first enzyme was sought. Specific activity, histidine feedback inhibition, amino acid analysis, discontinuous-gel electrophoresis, and gel filtration of the native enzyme, and Ouchterlony double-immunodiffusion tests were carried out. The purified enzyme contains little phosphorous and has five cysteine residues per subunit, which all are readily titratable. No evidence for differences in the enzyme preparations was obtained. Thus, no evidence for overlap of the histidine operator with the first structural gene was obtained.
Full text
PDF


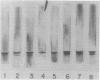
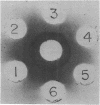
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell R. M., Parsons S. M., Dubravac S. A., Redfield A. G., Koshland D. E., Jr Characterization of slowly interconvertible states of phosphoribosyladenosine triphosphate synthetase dependent on temperature, substrates, and histidine. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4110–4118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi F., Aloj S. M., Goldberger R. F. Effect of histidine on the enzyme which catalyzes the first step of histidine biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 13;10(8):1409–1417. doi: 10.1021/bi00784a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi F., Bruni C. B., Avitabile A., Deeley R. G., Goldberger R. F., Meyers M. M. Inhibition of transcription of the histidine operon in vitro by the first enzyme of the histidine pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2692–2696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink G. R., Klopotowski T., Ames B. N. Histidine regulatory mutants in Salmonella typhimurium. IV. A positive selection for polar histidine-requiring mutants from histidine operator constitutive mutants. J Mol Biol. 1967 Nov 28;30(1):81–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90245-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger R. F., Kovach J. S. Regulation of histidine biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1972;5:285–308. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152805-8.50014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai T. Regulation of the expression of the histidine operon in Salmonella typhimurium. Nature. 1974 Jun 7;249(457):523–527. doi: 10.1038/249523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovach J. S., Ballesteros A. O., Meyers M., Soria M., Goldberger R. F. A cis-trans test of the effect of the first enzyme for histidine biosynthesis on regulation of the histidine operon. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):351–356. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.351-356.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. M., Koshland D. E., Jr A rapid isolation of phosphoribosyladenosine triphosphate synthetase and comparison to native enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4104–4109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. M., Koshland D. E., Jr Multiple aggregation states of phosphoribosyladenosine triphosphate synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4119–4126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfahl M., Stockter C., Gronenborn B. Genetic analysis of the active sites of lac repressor. Genetics. 1974 Apr;76(4):669–679. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.4.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T., Files J. G., Weber K. Lac repressor. Specific proteolytic destruction of the NH 2 -terminal region and loss of the deoxyribonucleic acid-binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):110–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Chrambach A. Estimation of molecular radius, free mobility, and valence using polyacylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Mar;40(1):95–134. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. R., Antón D. N., Hartman P. E. Histidine regulatory mutants in Salmonella typhimurium. I. Isolation and general properties. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):305–323. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. S., Wyche J. H. Histidine regulation in Salmonella typhimurium. XV. Procedure for the selection of mutants unable to derepress the histidine operon. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):116–125. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.116-125.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner J. B. A METHOD FOR THE COLORIMETRIC DETERMINATION OF PHOSPHORUS. Science. 1944 Nov 3;100(2601):413–414. doi: 10.1126/science.100.2601.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voll M. J., Appella E., Martin R. G. Purification and composition studies of phosphoribosyladenosine triphosphate:pyrophosphate phosphoribosyltransferase, the first enzyme of histidine biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1760–1767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]