Abstract
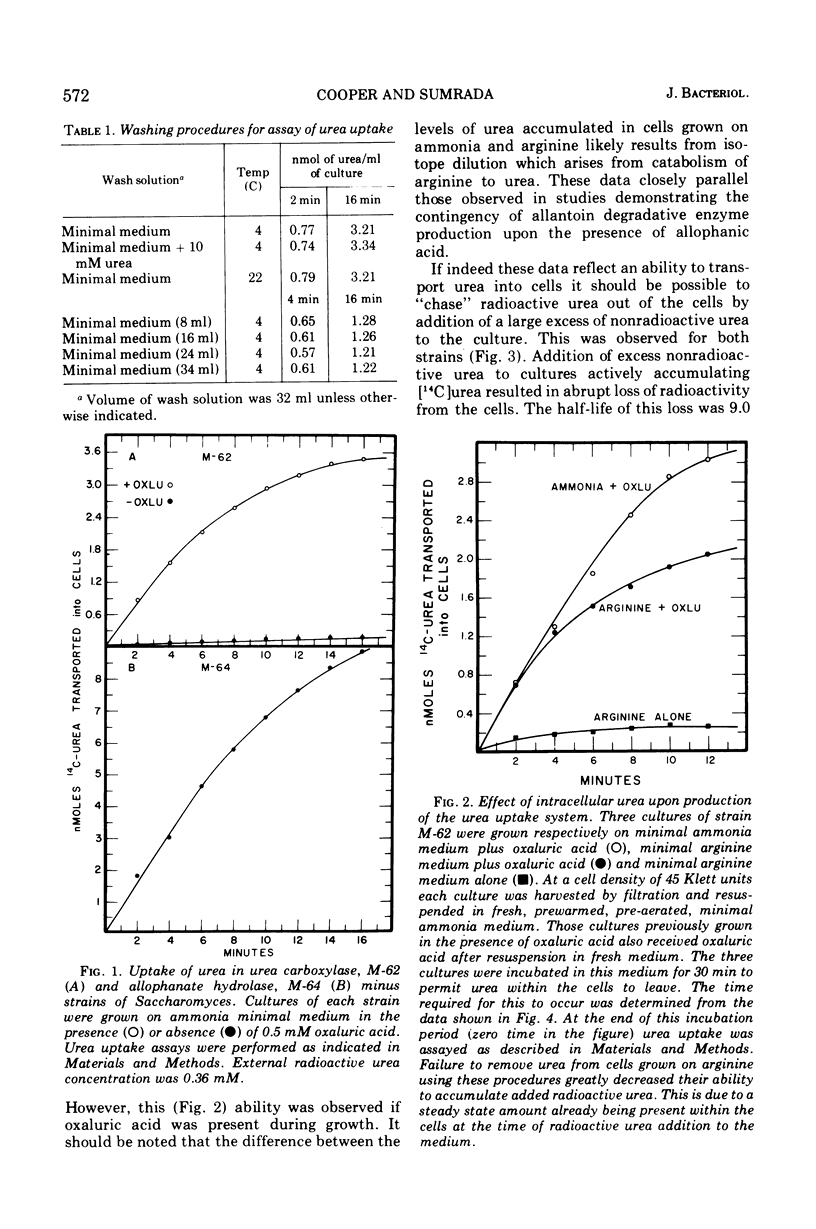
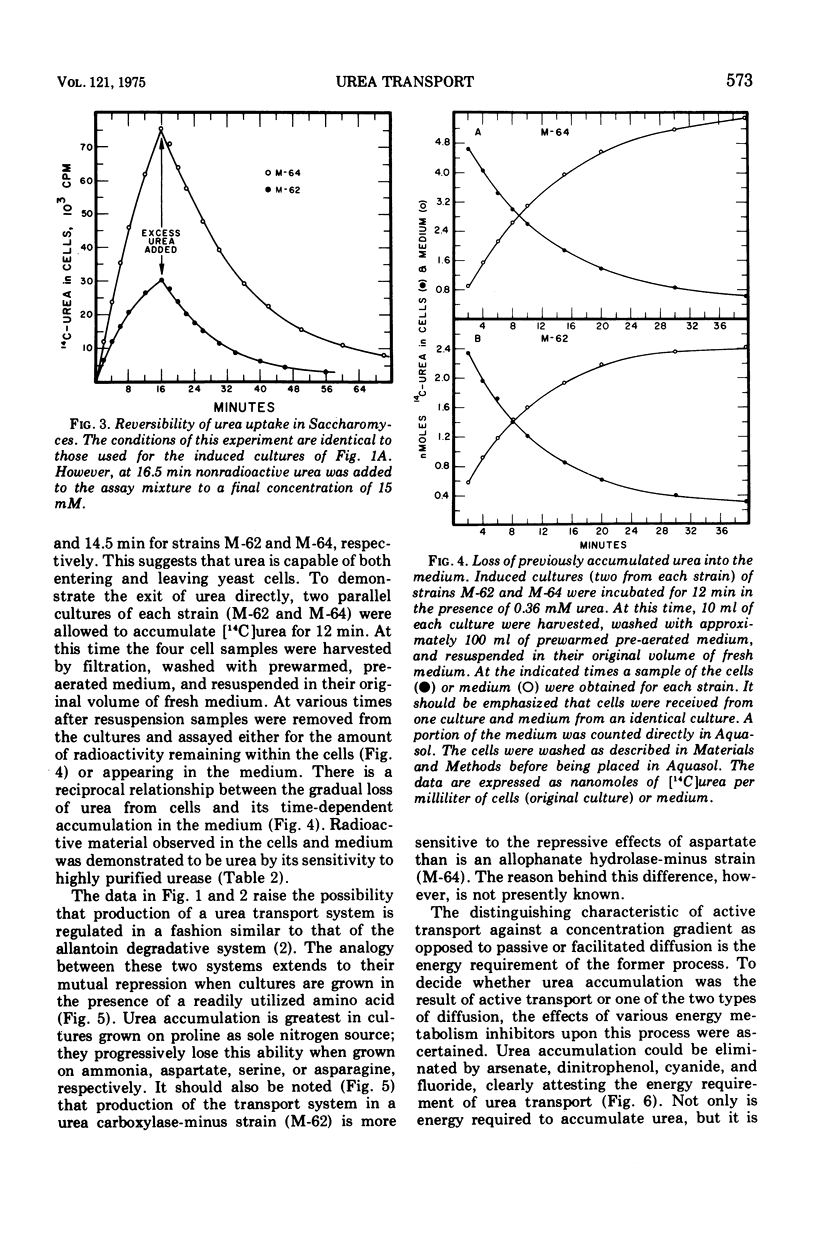
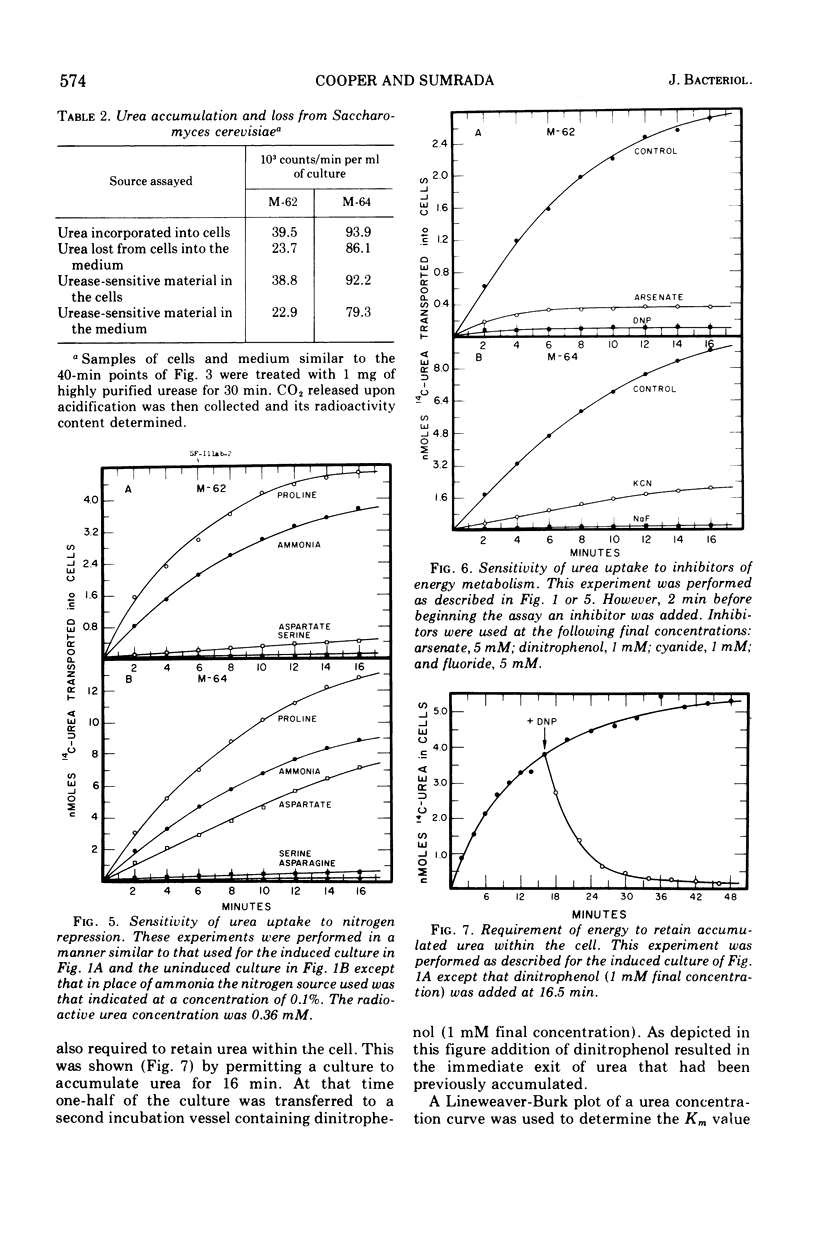
Urea transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae occurs by two pathways. The first mode of uptake is via an active transport system which: (i) has an apparent Km value of 14 muM, (ii) is absolutely dependent upon energy metabolism, (iii) requires pre-growth of the cultures in the presence of oxaluric acid, gratuitous inducer of the allantoin degradative enzymes, and (iv) is sensitive to nitrogen repression. The second mode of uptake which occurs at external urea concentrations in excess of 0.5 mM is via either passive or facilitated diffusion.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bossinger J., Lawther R. P., Cooper T. G. Nitrogen repression of the allantoin degradative enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):821–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.821-829.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Lawther R. P. Induction of the allantoin degradative enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by the last intermediate of the pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2340–2344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOMNAS A. Amide metabolism in yeasts. II. The uptake of amide and amide like compounds by yeast. J Biochem. 1962 Sep;52:149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Luria S. E. Effects of colicins E1 and K on transport systems. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.57-63.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy E. P., Scarborough G. A. Mechanism of hydrolysis of O-nitrophenyl-beta-galactoside in Staphylococcus aureus and its significance for theories of sugar transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):225–228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klo S. C., Cano F. R., Lampen J. O. Lomofungin, an inhibitor of ribonucleic acid synthesis in yeast protoplasts: its effect on enzyme formation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jun;3(6):716–722. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.6.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawther R. P., Cooper T. G. Effects of inducer addition and removal upon the level of allophanate hydrolase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 19;55(4):1100–1104. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumrada R., Cooper T. G. Oxaluric acid: a non-metabolizable inducer of the allantoin degradative enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1240–1247. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1240-1247.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P. A., Cooper T. G., Magasanik B. The induction of urea carboxylase and allophanate hydrolase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6203–6209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P. A., Cooper T. G. Requirement for HCO3- by ATP: urea amido-lyase in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Aug 24;40(4):814–819. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90975-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P. A., Cooper T. G. Urea carboxylase and allophanate hydrolase. Two components of adenosine triphosphate:urea amido-lyase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1349–1353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P. A., Cooper T. G. Urea carboxylase and allophanate hydrolase: two components of a multienzyme complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 6;49(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


