Abstract
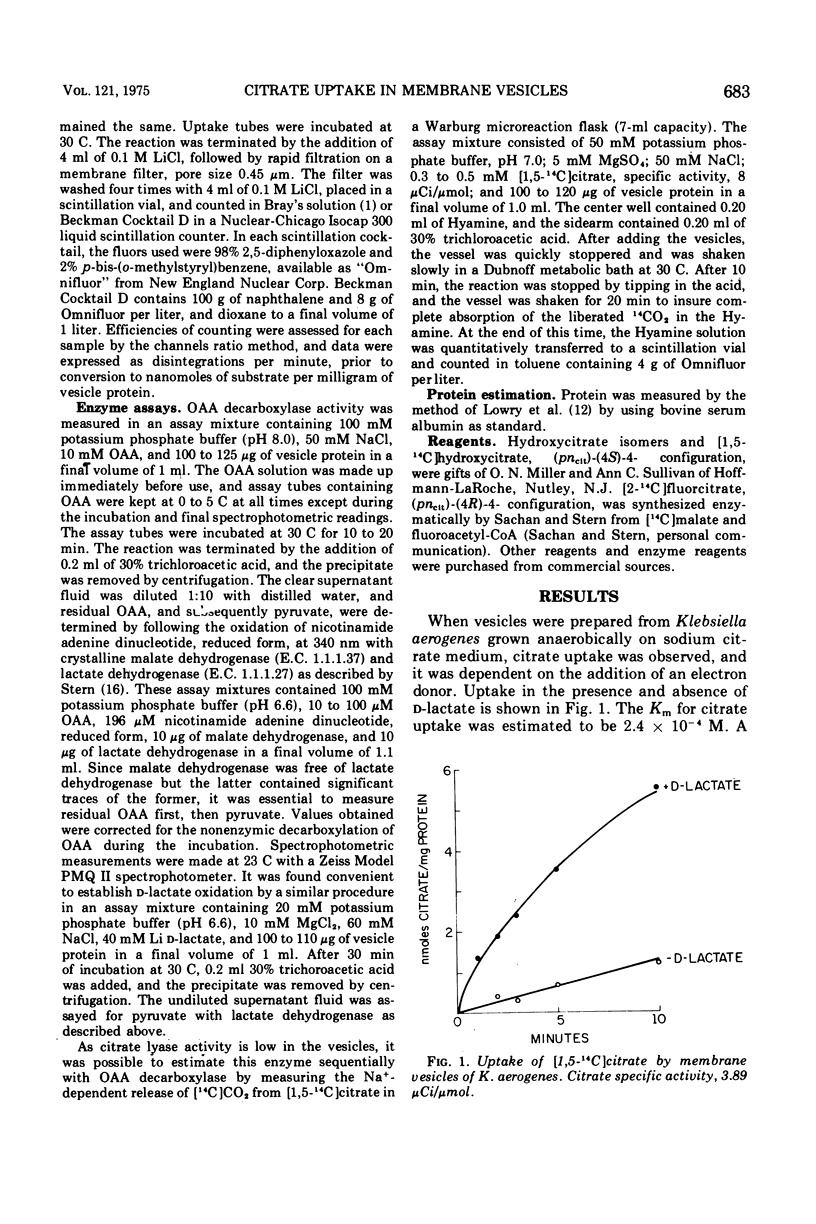
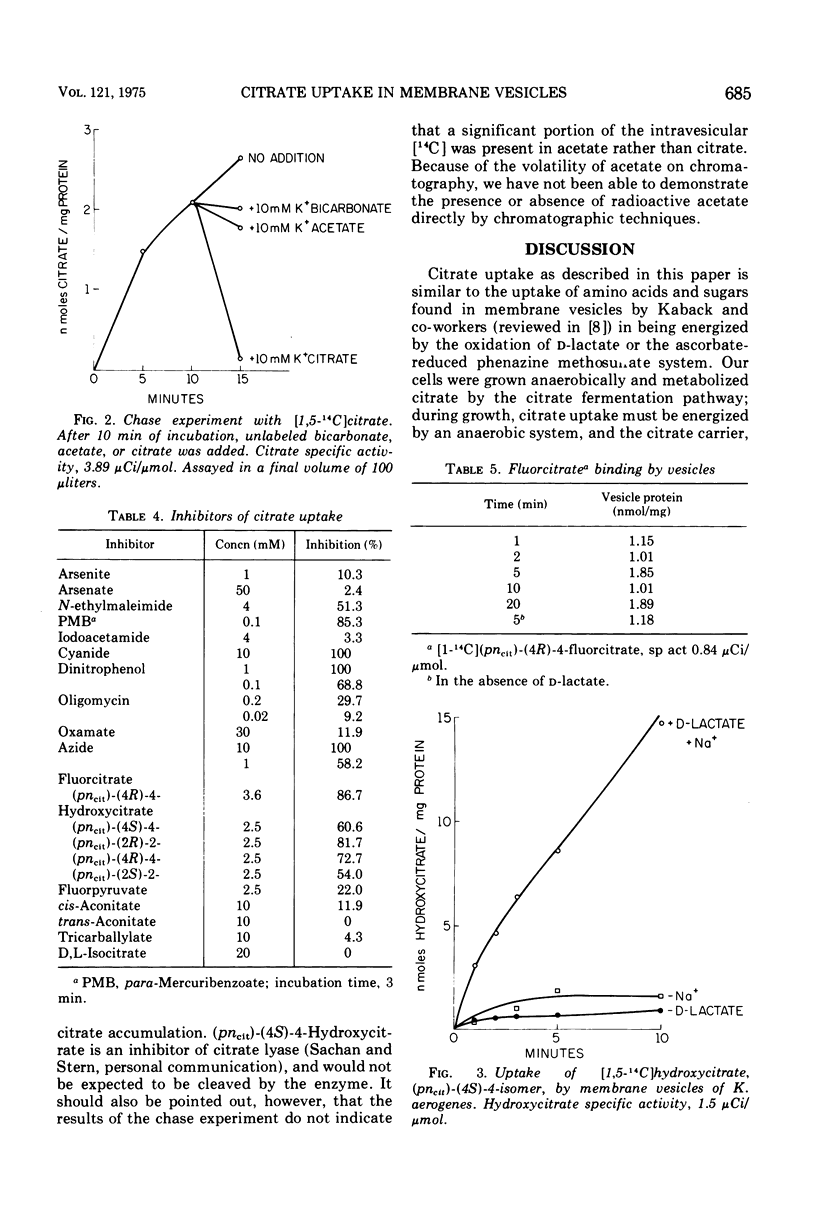
In whole cells of Klebsiella aerogenes grown anaerobically on citrate as sole carbon source, citrate uptake is followed by rapid catabolism of the substrate via the inducible citrate fermentation pathway. Membrane vesicles prepared from such cells take up citrate but do not catabolize it. Vesicles process d-lactate dehydrogenase and the Na+-requiring oxalacetate decarboxylase. Citrate is taken up in the presence of Na+, and other monovalent cations, such as NH4+, Rb+, Cs+, or K+, do not substitute for Na+. Li+ appears to act synergistically with Na+. Citrate uptake is inhibited by N-2, cyanide, azide, sulfhydryl reagents, dinitrophenol, fluorcitrate, and hydroxycitrate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAGLEY S., DAWES E. A. Dissimilation of citric acid by bacterial extracts. Nature. 1953 Aug 15;172(4372):345–346. doi: 10.1038/172345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagon R. G., Wilkerson L. S. A potassium-dependent citric acid transport system in Aerobacter aerogenes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 10;46(5):1944–1950. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings W. N., Kaback H. R. Anaerobic transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3376–3381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawford H. G., Williams G. R. The transport of citrate and other tricarboxylic acids in two species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(4):571–577. doi: 10.1042/bj1230571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi F. J., Kaback H. R. Mechanisms of active transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. 8. The transport of amino acids by membranes prepared from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):7844–7857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. W., Stern J. R. Requirement for sodium in the anaerobic growth of Aerobacter aerogenes on citrate. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):388–393. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.388-393.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehr P., Willecke K. Citrate-Mg2+ transport in Bacillus subtilis. Studies with 2-fluoro-L-erythro-citrate as a substrate. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2037–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachan D. S., Stern J. R. Studies of citrate transport in Aerobacter aerogenes: binding of citrate by a membrane bound oxalacetate decarboxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Oct 15;45(2):402–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90833-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. R. Oxalacetate decarboxylase of Aerobacter aerogenes. I. Inhibition by avidin and requirement for sodium ion. Biochemistry. 1967 Nov;6(11):3545–3551. doi: 10.1021/bi00863a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson L. S., Eagon R. G. Effect of sodium on the transport and utilization of citric acid by Aerobacter (Enterobacter) aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):121–124. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.121-124.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson L. S., Eagon R. G. Transport of citric acid by Aerobacter aerogenes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Mar;149(1):209–221. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willecke K., Gries E. M., Oehr P. Coupled transport of citrate and magnesium in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):807–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willecke K., Pardee A. B. Inducible transport of citrate in a Gram-positive bacterium, Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):1032–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


