Abstract
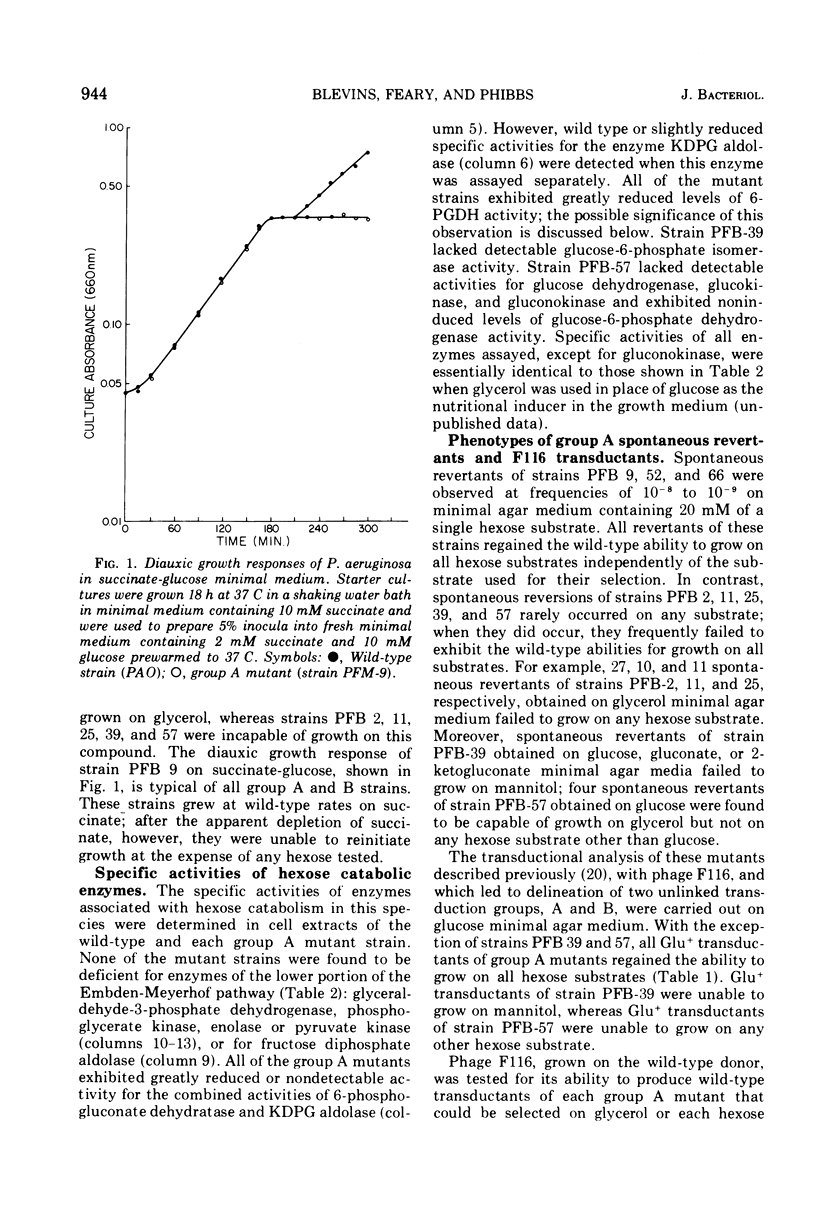
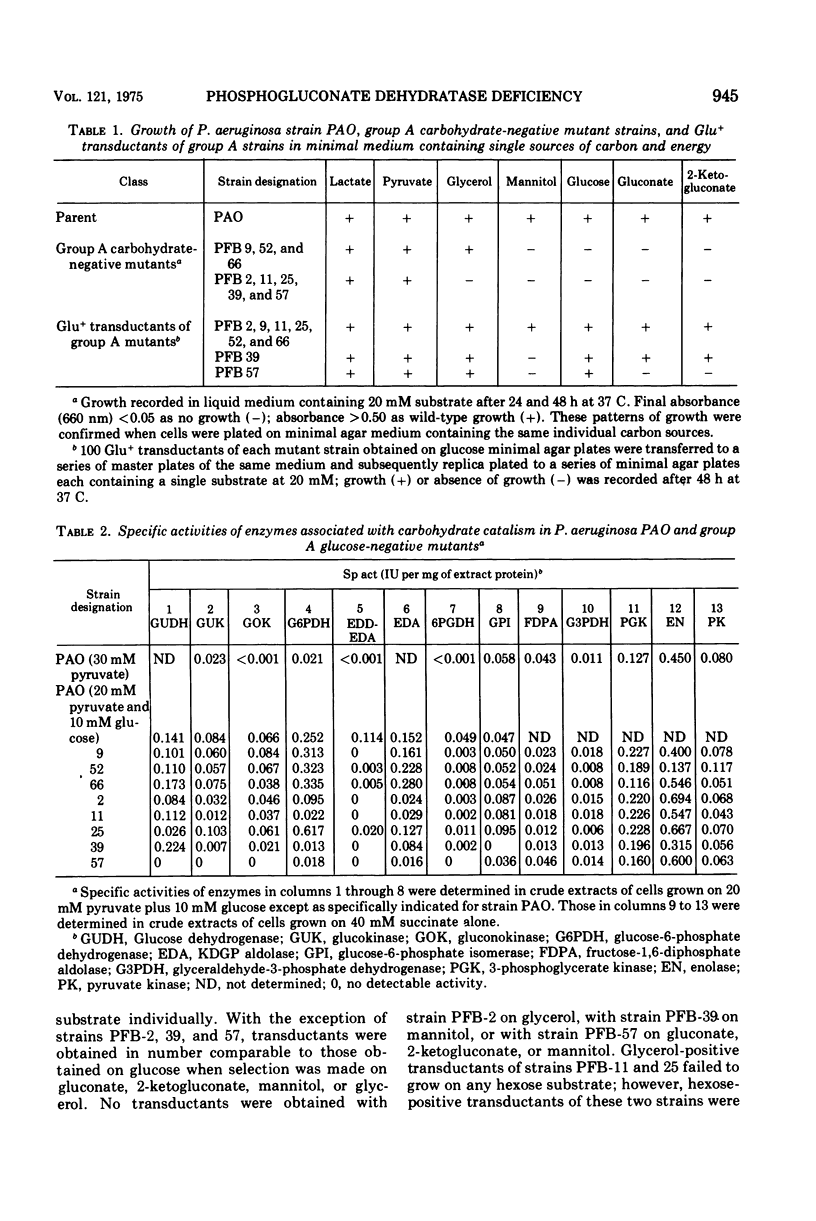
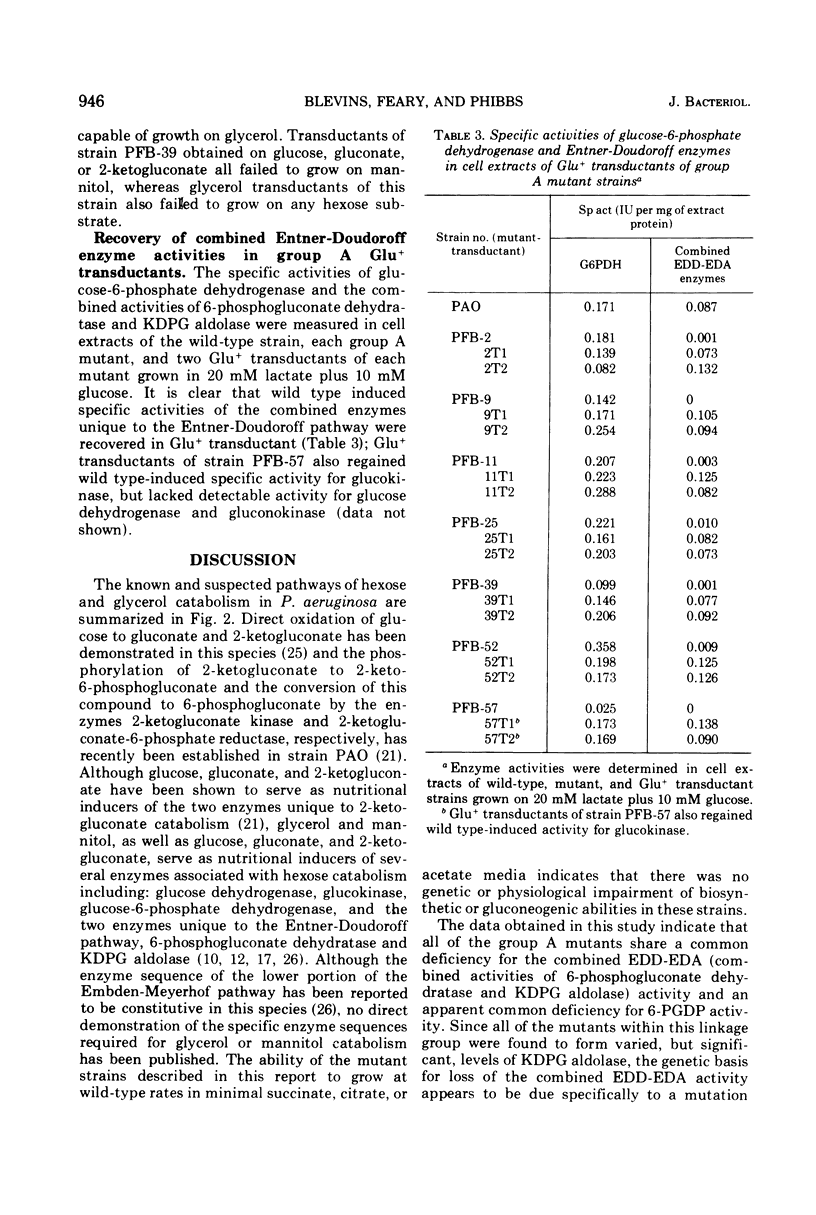
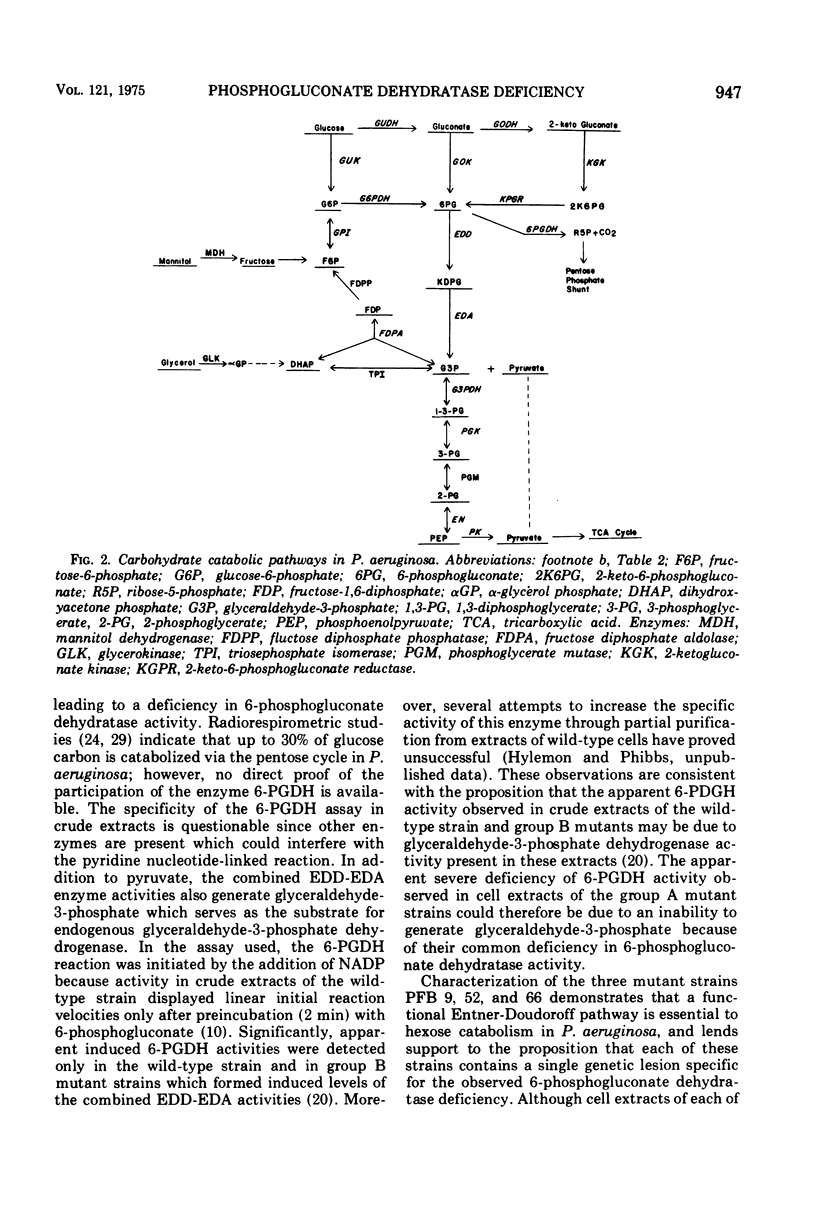
Mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, strain PAO, have been isolated that are unable to grow on mannitol, glucose, gluconate, or 2-ketogluconate, cut that exhibit wild-type growth on pyruvate, lactate, citrate, succinate, or acetate. Although some of these mutants were also unable to grow on glycerol, the mutations formed a single linkage group by quantitative transductional analysis with phage F116 on glucose minimal agar medium. Cell extracts of all mutant strains were either lacking or severely deficient in 6-phosphogluconate dehydratase activity. Glu+ transductants derived from mutant strains that retained the wild-type ability for growth at the expense of glycerol also regained the ability to grow on all C-6 compounds. Although a role for the pentose phosphate pathway in the catabolism of C6 substrates was not found, a functional Entner-Doudoroff pathway appears to be essential for the catabolism of mannitol, glucose, gluconate, and 2-ketogluconate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. L., Wood W. A. Carbohydrate metabolism in microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:539–578. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.002543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio M. L., Ruiz-Amil M., Vicente M., Cánovas J. L. The role of phosphoglycerate kinase in the metabolism of Pseudomonas putida. FEBS Lett. 1971 May 20;14(5):326–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerdá-Olmedo E., Hanawalt P. C. The replication of the Escherichia coli chromosome studied by sequential nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:599–607. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagon R. G., Phibbs P. V., Jr Kinetics of transport of glucose, fructose, and mannitol by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Biochem. 1971 Sep;49(9):1031–1041. doi: 10.1139/o71-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerola N., Ingraham J. L., Cerdá-Olmedo E. Induction of closely linked multiple mutations by nitrosoguanidine. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 24;230(12):122–125. doi: 10.1038/newbio230122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guymon L. F., Eagon R. G. Transport of glucose, gluconate, and methyl alpha-D-glucoside by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1261–1269. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1261-1269.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W. Genetics of Pseudomonas. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Sep;33(3):419–443. doi: 10.1128/br.33.3.419-443.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Rossiter H., Burgess D., Dodge J. Aeruginocin tolerant mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1973 Dec;22(3):239–253. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300013069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Krieg N. R., Phibbs P. V., Jr Transport and catabolism of D-fructose by Spirillum itersomii. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):144–150. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.144-150.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Phibbs P. V., Jr Independent regulation of hexose catabolizing enzymes and glucose transport activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1041–1048. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90813-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. The role of the phosphoenolpyruvate-phosphotransferase system in the transport of sugars by isolated membrane preparations of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3711–3724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessie T., Neidhardt F. C. Adenosine triphosphate-linked control of Pseudomonas aeruginosa glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1337–1345. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1337-1345.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Schuster E. 3-phosphoglycerate kinase from Hydrogenomonas facilis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):751–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.751-756.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley M., Dawes E. A. The regulation of transport of glucose and methyl alpha-glucoside in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):141–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1320141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukkada A. J., Long G. L., Romano A. H. The uptake of 2-deoxy-D-glucose by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its regulation. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):155–162. doi: 10.1042/bj1320155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng F. M., Dawes E. A. Chemostat studies on the regulation of glucose metabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by citrate. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):129–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1320129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. Regulation of catabolic pathways in Pseudomonas. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Jun;35(2):87–116. doi: 10.1128/br.35.2.87-116.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs P. V., Jr, Eagon R. G. Transport and phosphorylation of glucose, fructose, and mannitol by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jun;138(2):470–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90371-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs P. V., Jr, Feary T. W., Blevins W. T. Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency in pleiotropic carbohydrate-negative mutant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):999–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.999-1009.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. K., Midgley M., Dawes E. A. The metabolism of 2-oxogluconate by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Oct;78(2):319–329. doi: 10.1099/00221287-78-2-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Eberhard S. J., Dingle S. L., McDowell T. D. Distribution of the phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):808–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.808-813.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN I. J., WANG C. H., GILMOUR C. M. Comparative catabolism of carbohydrates in Pseudomonas species. J Bacteriol. 1960 Apr;79:601–611. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.4.601-611.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOKES F. N., CAMPBELL J. J. R. The oxidation of glucose and gluconic acid by dried cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Biochem. 1951 Jan;30(1):121–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari N. P., Campbell J. J. Enzymatic control of the metabolic activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown in glucose or succinate media. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 30;192(3):395–401. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90388-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicente M., Cánovas J. L. Glucolysis in Pseudomonas putida: physiological role of alternative routes from the analysis of defective mutants. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):908–914. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.908-914.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANG C. H., STERN I., GILMOUR C. M., KLUNGSOYR S., REED D. J., BIALY J. J., CHRISTENSEN B. E., CHELDELIN V. H. Comparative study of glucose catabolism by the radiorespirometric method. J Bacteriol. 1958 Aug;76(2):207–216. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.2.207-216.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


