Abstract
Multiple forms of 7-alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase were detected in six of nine strains of Bacteroides fragilis. The enzymes differed with respect to pyridine nucleotide specificity, thermal stability, divalent metal cation requirement, and elution profilies from Sephadex G-200 columns. The nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP)-dependent enzyme required divalent metal cations, preferentially Mn-2+ (Km, 57 muM), for maximum catalytic activity. The NADP-dependent enzyme was labile at 65 C for 10 min, whereas the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)-dependent enzyme was stable at 65 C for 10 min. The specific activity of both the NAD- and NADP-dependent enzymes in crude extracts increased markedly (15- and 7.5-fold, respectively) during the transition from exponential- to stationary-phase growth in glucose medium containing 0.5 mM sodium cholate. The time course of apparent enzyme induction correlated temporally with the transformation of the 7-alpha-hydroxy group of cholate in the culture supernatant fluid. Both NAD- and NADP-dependent 7-alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activities were found to be widely, but not universally, distributed in different strains and subspecies of B. fragilis. No NAD- or NADP-dependent 7-alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity could be detected in B. fragilis subsp. vulgatus Virginia Polytechnic Institute (VPI) no. 4245, subsp. thetaiotaomicron VPI 0061-1, or subsp. distasonis VPI 4243.
Full text
PDF

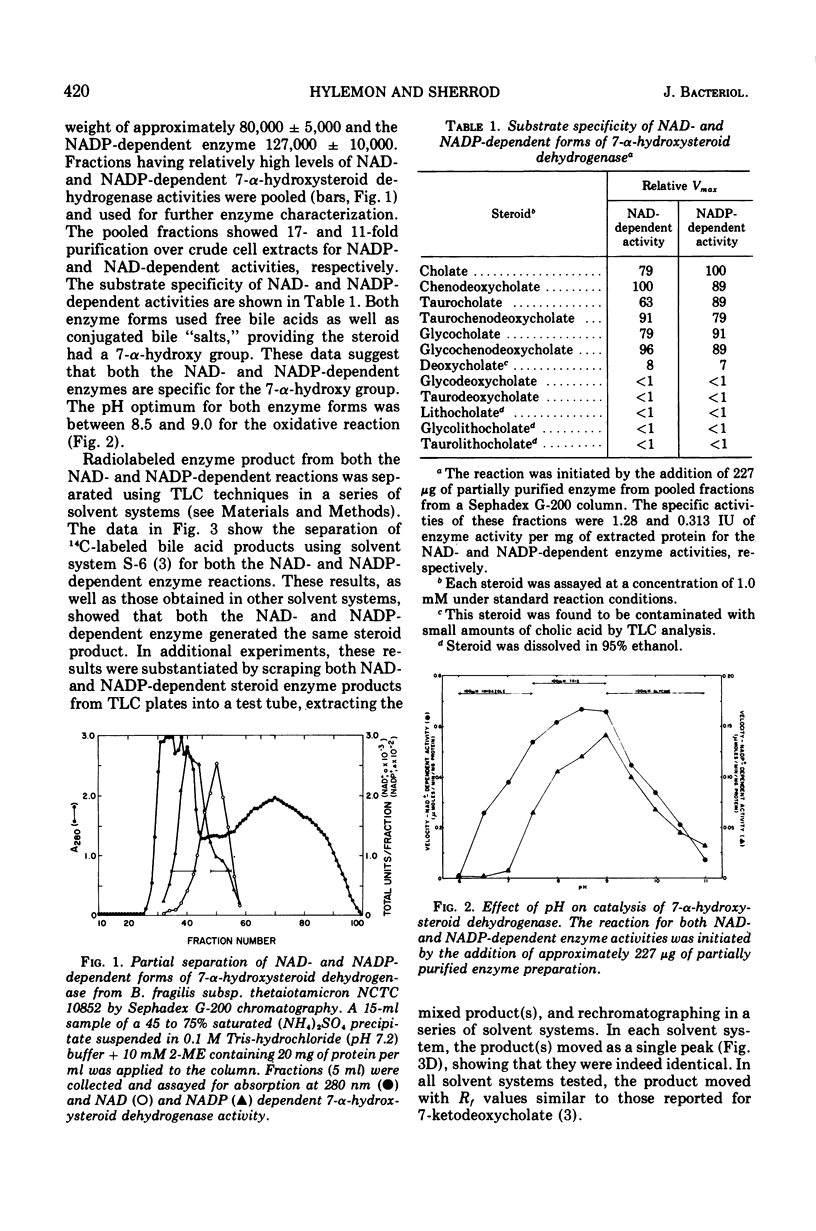
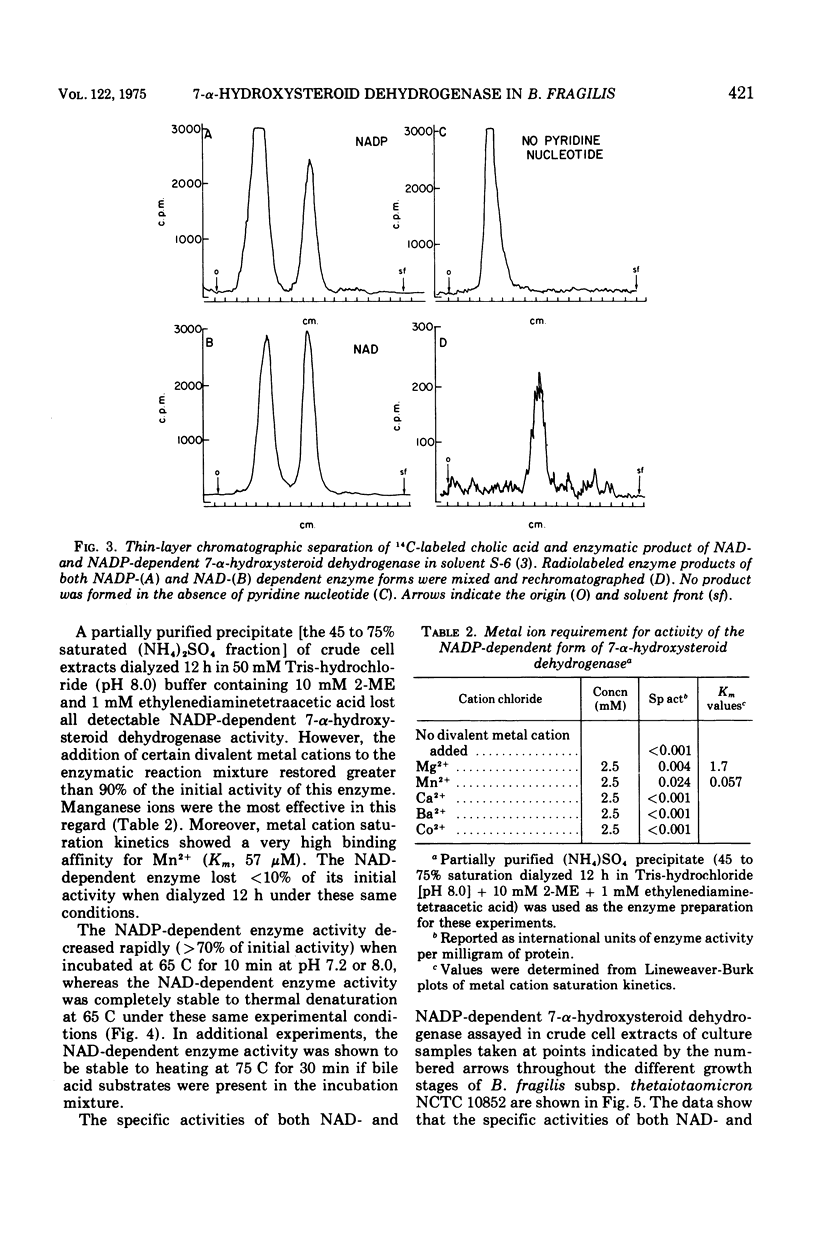
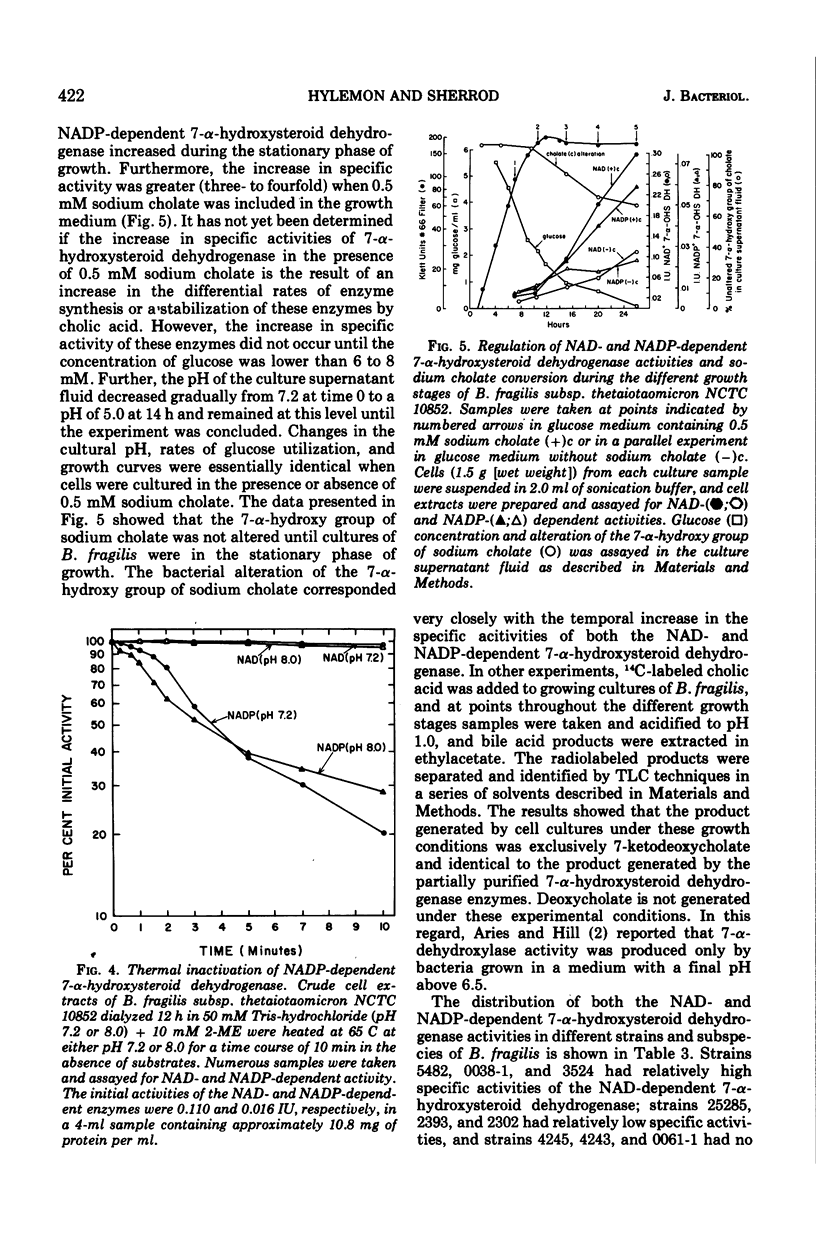


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aries V., Crowther J. S., Drasar B. S., Hill M. J. Degradation of bile salts by human intestinal bacteria. Gut. 1969 Jul;10(7):575–576. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.7.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aries V., Hill M. J. Degradation of steroids by intestinal bacteria. II. Enzymes catalysing the oxidoreduction of the 3 alpha-, 7 alpha- and 12 alpha-hydroxyl groups in cholic acid, and the dehydroxylation of the 7-hydroxyl group. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 5;202(3):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENEROTH P. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF BILE ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1963 Jan;4:11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eneroth P., Gordon B., Ryhage R., Sjövall J. Identification of mono- and dihydroxy bile acids in human feces by gas-liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jul;7(4):511–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Phibbs P. V., Jr Evidence against the presence of cyclic AMP and related enzymes in selected strains of Bacteroides fragilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 9;60(1):88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald I. A., Williams C. N., Mahony D. E. 7Alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli B: preliminary studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 6;309(2):243–253. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midtvedt T., Norman A. Bile acid transformations by microbial strains belonging to genera found in intestinal contents. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;71(4):629–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1967.tb05183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V. Human fecal flora: the normal flora of 20 Japanese-Hawaiians. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):961–979. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.961-979.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN A., SJOVALL J. On the transformation and enterohepatic circulation of cholic acid in the rat: bile acids and steroids 68. J Biol Chem. 1958 Oct;233(4):872–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


