Abstract
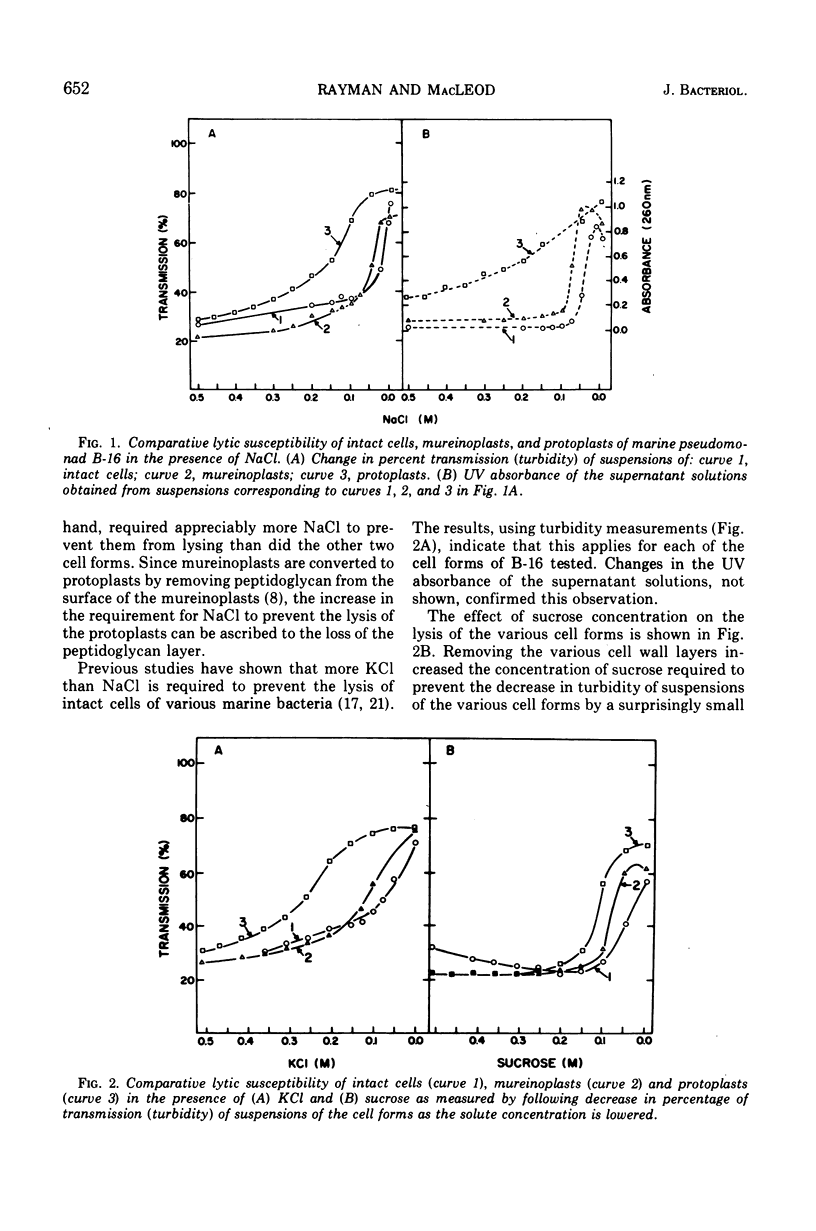
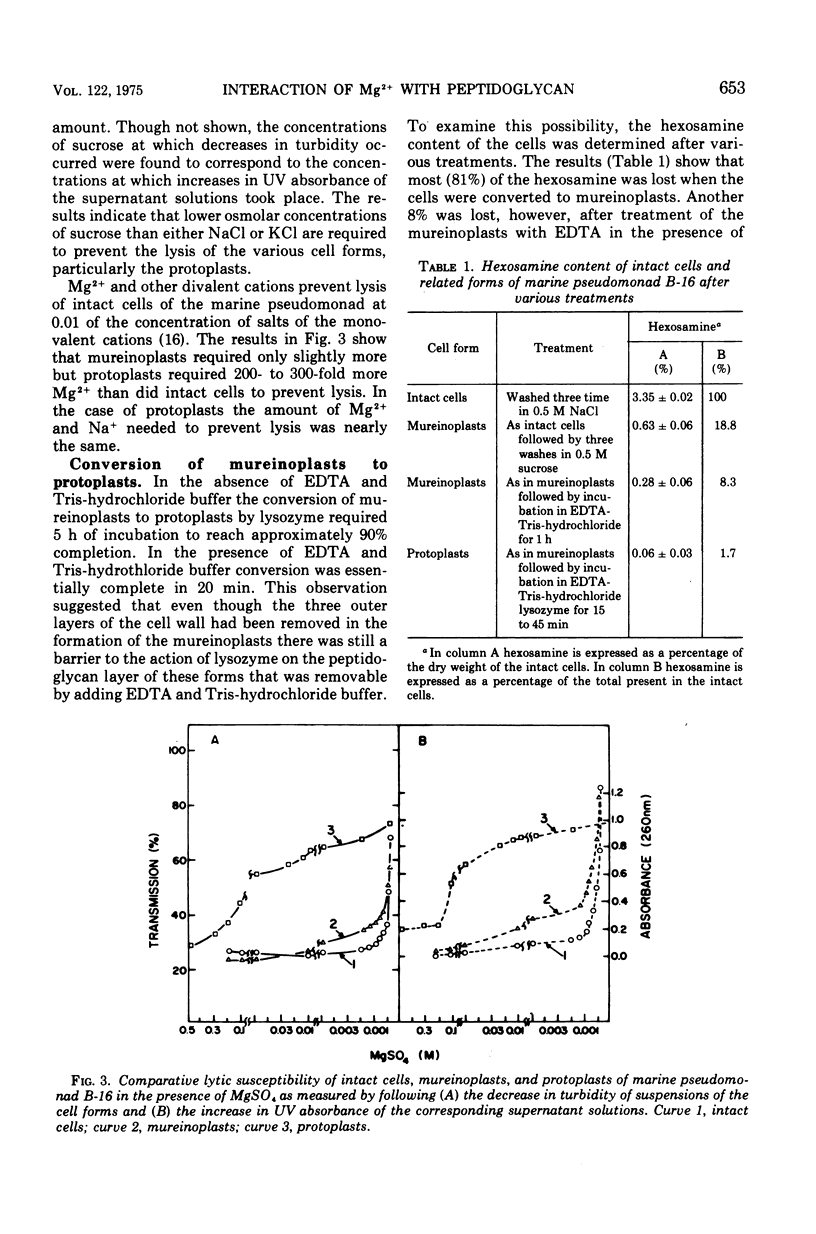
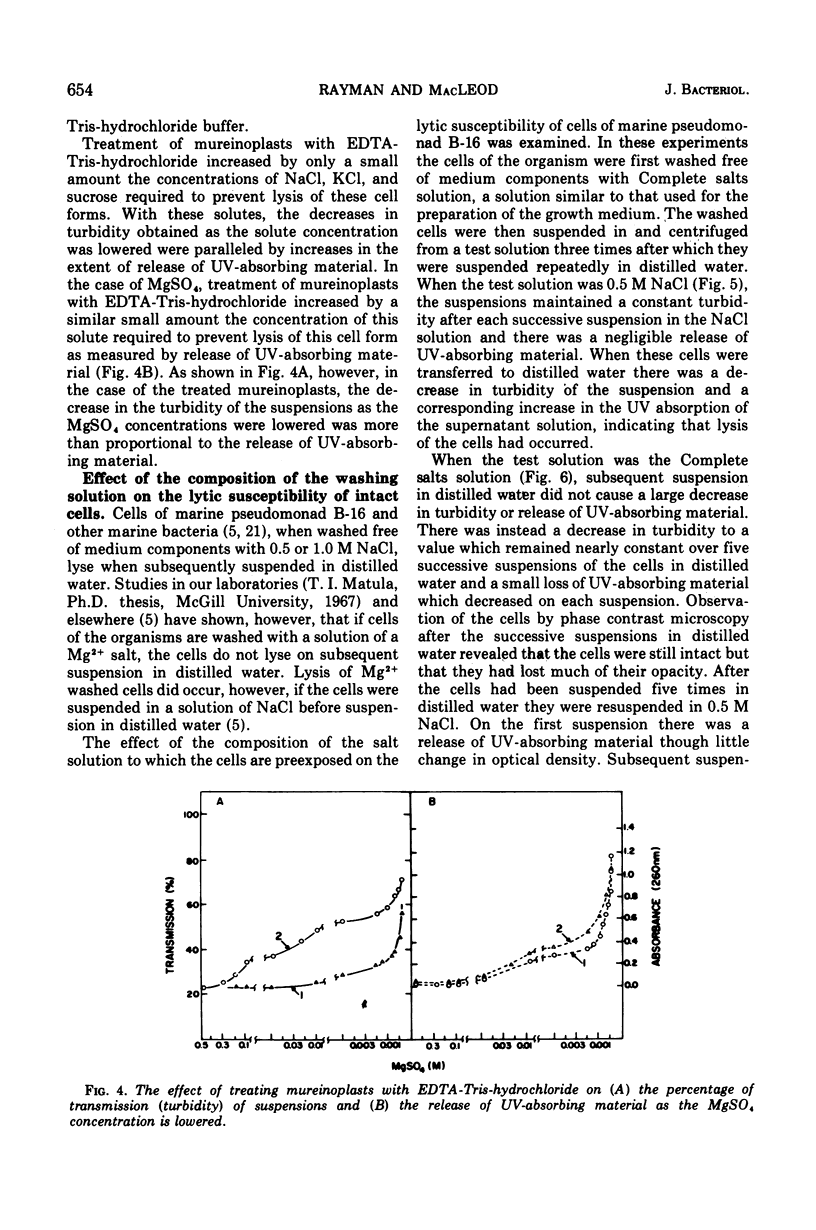
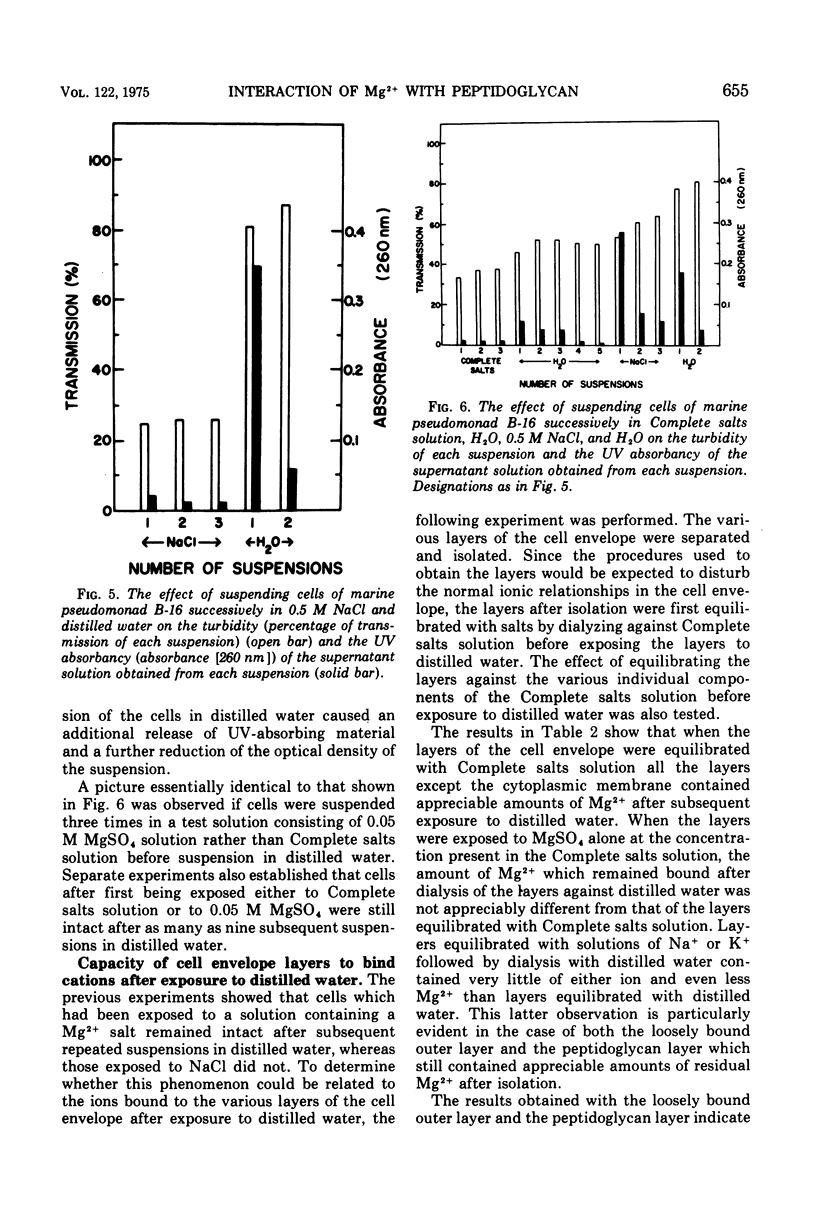
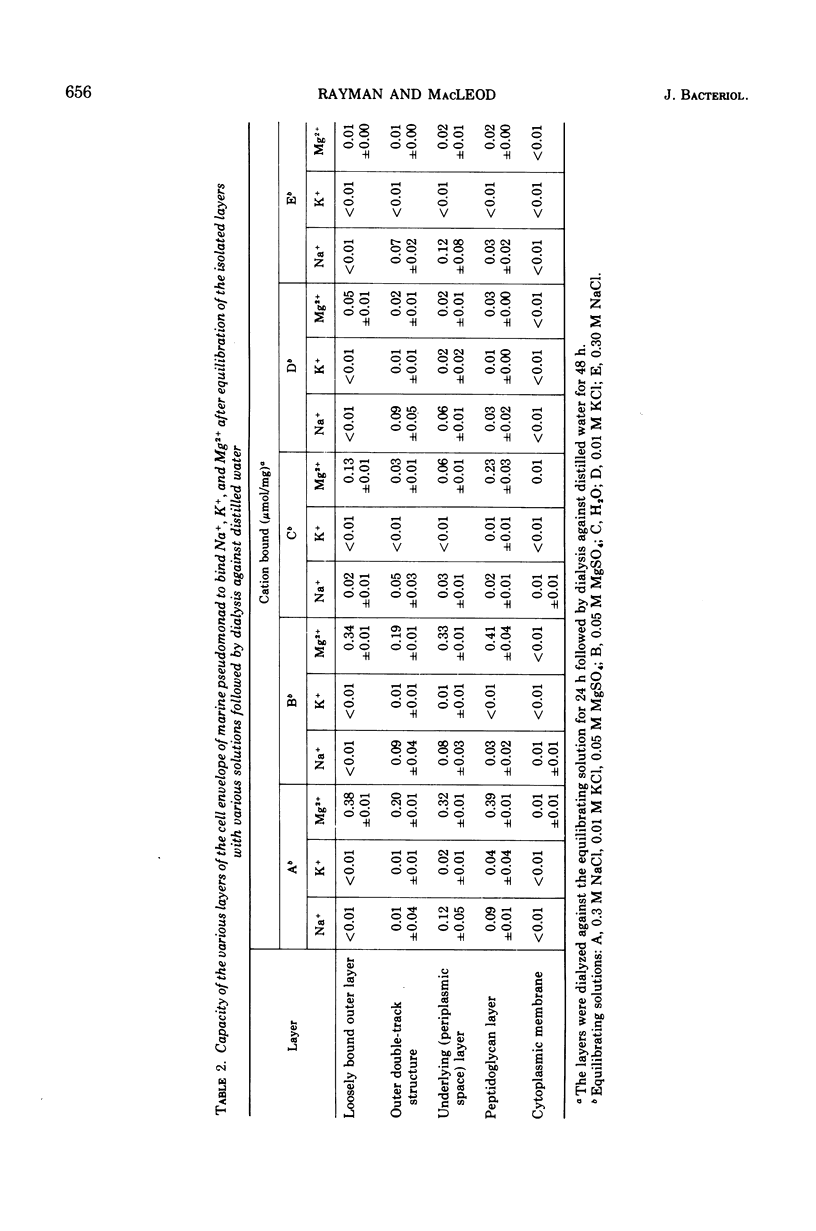
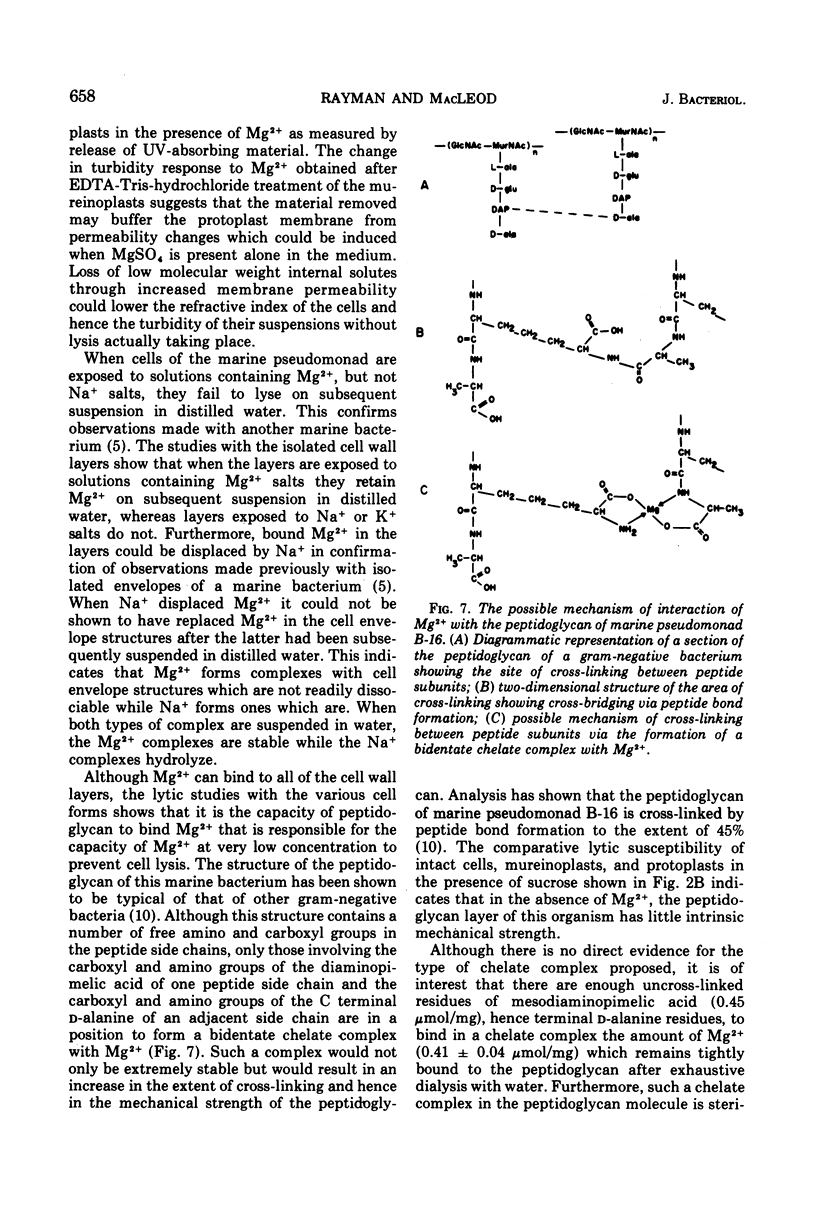
Intact cells of marine pseudomonad B-16 (ATCC 19855) which have been washed with a solution of NaCl require only 0.001 M MgSO4 and 100 to 300 times this concentration of NaCl or KCl to prevent lysis. Conversion of intact cells to mureinoplasts, a process involving removal of the outer double-track layer (outer membrane) and the periplasmic space layer of the cell wall, approximately doubled the requirement for the three salts to prevent lysis. The formation of protoplasts from mureinoplasts by removing the peptidoglycan layer again doubled the requirement for Na+ and K+ salts but increased the requirement for the Mg-2+ salt 200- to 300-fold. Cells of the marine pseudomonad suspended in solutions containing Mg-2+ salts failed to lyse on subsequent repeated suspension in distilled water, whereas cells presuspended in NaCl lysed immediately. Isolated envelope layers including the peptidoglycan layer, when dialyzed against solutiions containing Mg-2+ salts, retained Mg-2+ after subsequent suspension in distilled water. Envelope layers exposed to solutions of Na+ or K+ salts failed to retain these ions after exposure to distilled water. Na+ displaced Mg-2+ from the cell envelope layers. The results obtained indicate that the capacity of Mg-2+ salts at very low concentration to prevent lysis of intact cells and mureinoplasts of this organism is due primarily to the interaction of Mg-2+ with the peptidoglycan layer of the cell wall. Ion interaction with the layers lying outside of the peptidoglycan layer contributes only a small amount to the mechanical strength of the wall.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN A. D. The peripheral structures of gram-negative bacteria. III. Effects of cations of proteolytic degradation of the cell envelope of a marine pseudomonad. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 30;62:132–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90498-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckmire F. L., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XIV. On the mechanism of lysis of a marine bacterium. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Aug;11(4):677–691. doi: 10.1139/m65-091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Forsberg C., Matula T. I., Buckmire F. L., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XVI. Formation of protoplasts, spheroplasts, and related forms from a gram-negative marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1764–1777. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1764-1777.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Voe I. W., Oginsky E. L. Antagonistic effect of monovalent cations in maintenance of cellular integrity of a marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1355–1367. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1355-1367.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Voe I. W., Oginsky E. L. Cation interactions and biochemical composition of the cell envelope of a marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1368–1377. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1368-1377.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Voe I. W., Thompson J., Costerton J. W., MacLeod R. A. Stability and comparative transport capacity of cells, mureinoplasts, and true protoplasts of a gram-negative bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):1014–1026. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.1014-1026.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Costerton J. W., Macleod R. A. Quantitation, chemical characteristics, and ultrastructure of the three outer cell wall layers of a gram-negative bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1354–1368. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1354-1368.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Costerton J. W., Macleod R. A. Separation and localization of cell wall layers of a gram-negative bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1338–1353. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1338-1353.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Rayman M. K., Costerton J. W., MacLeod R. A. Isolation, characterization, and ultrastructure of the peptidoglycan layer of a marine pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):895–905. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.895-905.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gow J. A., DeVoe U. W., MacLeod R. A. Dissociation in a marine pseudomonad. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jun;19(6):695–701. doi: 10.1139/m73-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A. THE QUESTION OF THE EXISTENCE OF SPECIFIC MARINE BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:9–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E. L., MacLeod R. A. Isolation and chemical composition of the cytoplasmic membrane of a gram-negative bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1160–1167. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1160-1167.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANUI H., PACE N. Sodium and potassium binding by rat liver cell microsomes. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Jul 20;42(6):1325–1345. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.6.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unemoto T., Tsuruoka T., Hayashi M. Role of Na + and K + in preventing lysis of a slightly halophilic Vibrio alginolyticus. Can J Microbiol. 1973 May;19(5):563–571. doi: 10.1139/m73-093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



