Abstract
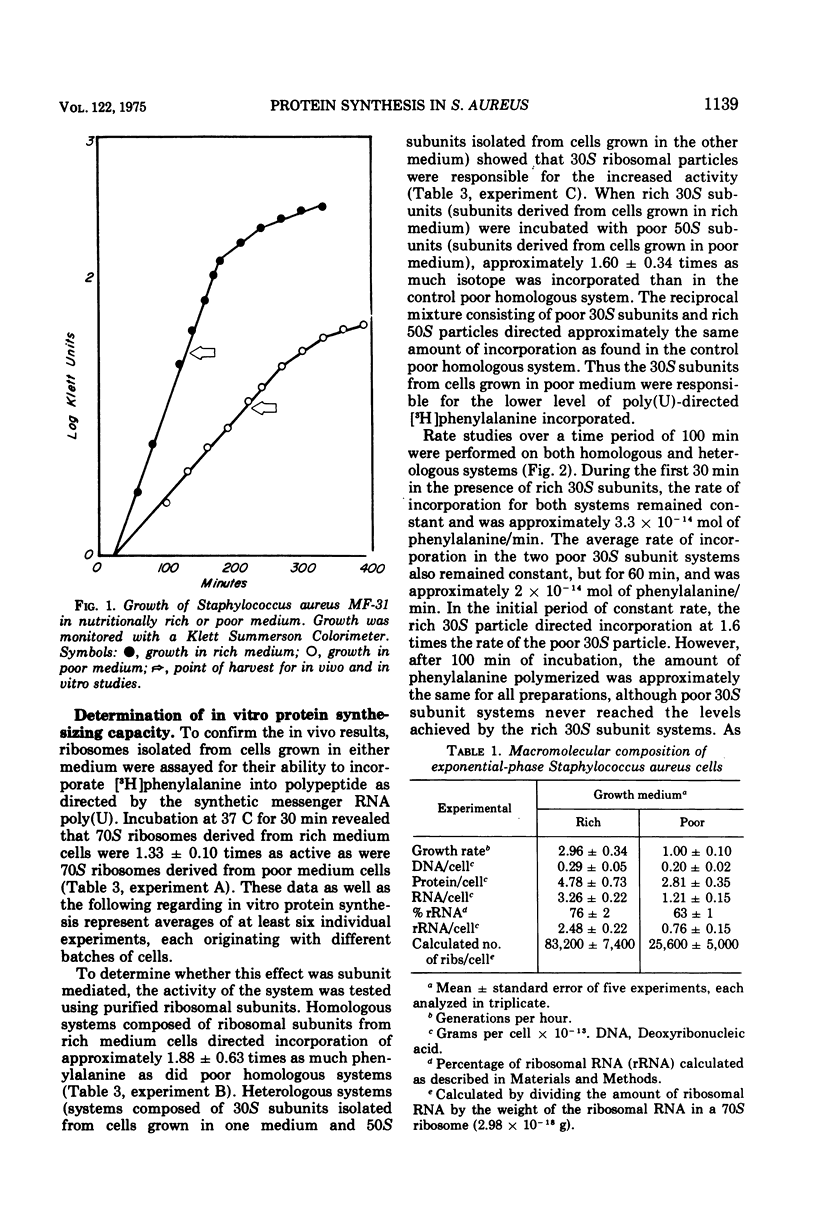
The calculated in vivo polypeptide chain growth rate for Staphylococcus auteus MF-31 grown in nutritionally rich medium assuming all the ribosomes were functional was found to be approximately 16 amino acids/s/ribosome, but decreased to 10.2 amino acids/s/ribosome for cells grown in poor medium. An in vitro analysis revealed that 70S ribosomes isolated from rich medium cells were more active than similar 70S ribosomes derived from cells grown in poor medium. The 30S subunit was found responsible for the increased activity of the rich monosomes, whereas the 50S subunit appeared to be capable of either high or low activity.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunschede H., Bremer H. Synthesis and breakdown of proteins in Escherichia coli during amino-acid starvation. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 14;57(1):35–57. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven G. R., Voynow P., Hardy S. J., Kurland C. G. The ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli. II. Chemical and physical characterization of the 30S ribosomal proteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2906–2915. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deusser E. Heterogeneity of ribosomal populations in Escherichia coli cells grown in different media. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(3):249–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00333862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstadt J., Lengyel P. Formylmethionyl-tRNA dependence of amino acid incorporation in extracts of trimethoprim-treated Escherichia coli. Science. 1966 Oct 28;154(3748):524–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engbaek F., Kjeldgaard N. O., Maaloe O. Chain growth rate of -galactosidase during exponential growth and amino acid starvation. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 25;75(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90532-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchhammer J., Lindahl L. Growth rate of polypeptide chains as a function of the cell growth rate in a mutant of Escherichia coli 15. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):563–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90337-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman E., Lodish H. F. Specificity of protein synthesis by bacterial ribosomes and initiation factors: absence of change after phage T4 infection. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 14;67(1):35–47. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante A. A., Baierlein R. Pressure-induced dissociation of sedimenting ribosomes: effect on sedimentation patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1780–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M., Hedgcoth C. Levels of 5,6-dihydrouridine in relaxed and chloramphenicol transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1970 Jun 9;9(12):2513–2519. doi: 10.1021/bi00814a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G. Structure and function of the bacterial ribosome. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41(10):377–408. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.002113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G., Voynow P., Hardy S. J., Randall L., Lutter L. Physical and functional heterogeneity of E. coli ribosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:17–24. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J., Lipmann F. Separation of three microbial amino acid polymerization factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1562–1566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C. Protein synthesis in a cell-free extract from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):80–86. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.80-86.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M. W., MATTHAEI J. H. The dependence of cell-free protein synthesis in E. coli upon naturally occurring or synthetic polyribonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1588–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. A., Hotham-Iglewski B., Franklin R. M. Polyribosomes of Escherichia coli. I. Effects of monovalent cations on the distribution of polysomes, ribosomes and ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1969 Mar 14;40(2):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90475-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traut R. R., Delius H., Ahmad-Zadeh C., Bickle T. A., Pearson P., Tissières A. Ribosomal proteins of E. Coli: stoichiometry and implications for ribosome structure. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:25–38. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EHRENSTEIN G., LIPMANN F. Experiments on hemoglobin biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Jul 15;47:941–950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.7.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Duin J., Kurland C. G. Functional heterogeneity of the 30S ribosomal subunit of E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;109(2):169–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00269653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk-Salkinoja M. S., Planta R. J. Rate of ribosome production in Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):20–27. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.20-27.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin J., van Knippenberg P. H., Dieben M. Functional heterogeneity of the 30S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. II. Effect of S21 on initiation. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;116(2):181–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00582227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin J., van Knippenberg P. H. Functional heterogeneity of the 30 S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. 3. Requirement of protein S1 for translation. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 25;84(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



