Abstract
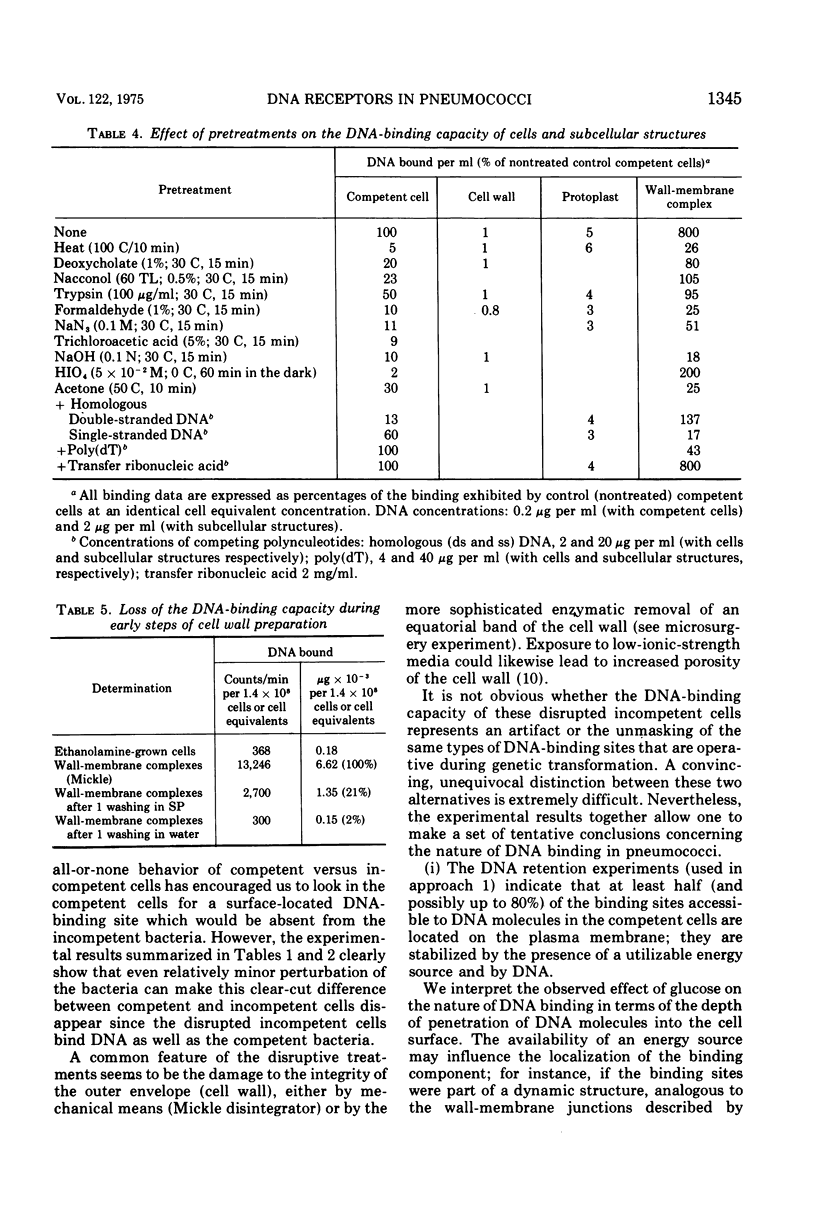
We studied deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) binding in transformable pneumococci. The relevant findings are as follows. (i) At least half of the DNA Molecules adsorbed to competent cells in the growth medium are attached to sites on the protoplast membrane. (ii) Most of the DNA bound to live competent cells in the presence of glucose is not released by moderate shear or by autolysin treatment. In contrast, most of the DNA adsorbed to competent cells in the absence of glucose is shear and autolysin sensitive. (iii) The presence of binding sites resembling in properties the sites in live competent cells can be demonstrated in wall-membrane complexes. Most of these sites are lost during preparation of cell walls and protoplasts. It is suggested that the DNA-binding site is a membrane component (protein?) Stabilized by polysaccharide (cell Wall) material. (IV) Mechanical or enzymatic damage to the cell wall or change in the ionic conditions can induce DNA binding (and surface-nuclease activity) in the incompetent pneumococci. However, such cells still show neither genetic transformation nor extensive nuclease-resistant binding of DNA. It is suggested that both competent and incompetent cells contain a large number of sequestered DNA-binding sites that can be unmasked by several experimental conditions. Induction of the competent state by the competence activator protein may involve an endogenous unmasking process.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akrigg A., Ayad S. R. Studies on the competence-inducing factor of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(2):397–403. doi: 10.1042/bj1170397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E. Areas of adhesion between wall and membrane of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Oct;53(3):395–404. doi: 10.1099/00221287-53-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deddish P., Slade H. D. Binding of deoxyribonucleic acid by cell walls of transformable and nontransformable streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):779–786. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.779-786.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi-Taylor H., Freed B. A. Incorporation of thymidine and amino acids into deoxyribonucleic acid and acid-insoluble cell structures in pneumococcal cultures synchronized for competence to transform. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1211–1215. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1211-1215.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson R. J., Young F. E., Braun W. Binding of rabbit gamma globulin by competent Bacillus subtilis cultures. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):125–131. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.125-131.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine F. P., Fox M. S. Bacterial inactivation of transforming deoxyribonucleate. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):889–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.889-899.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joenje H., Konings W. N., Venema G. Interactions between exogenous deoxyribonucleic acid and membrane vesicles isolated from Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):784–794. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.784-794.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelemen M. V., Rogers H. J. Three-dimensional molecular models of bacterial cell wall mucopeptides (peptidoglycans). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):992–996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACKS S. Molecular fate of DNA in genetic transformation of Pneumococcus. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:119–131. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B. Competence for deoxyribonucleic acid uptake and deoxyribonuclease action external to cells in the genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):152–163. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.152-163.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser J. L., Tomasz A. Choline-containing teichoic acid as a structural component of pneumococcal cell wall and its role in sensitivity to lysis by an autolytic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 25;245(2):287–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piechowska M., Fox M. S. Fate of transforming deoxyribonucleate in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):680–689. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.680-689.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., LANDMAN O. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MESOSOME LOSS AND THE STABLE L STATE (OR PROTOPLAST STATE) IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:457–467. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.457-467.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranhand J. M., Leonard C. G., Cole R. M. Autolytic activity associated with competent group H streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):257–268. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.257-268.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto H., Tomasz A. Early stages in DNA binding and uptake during genetic transformation of pneumococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1493–1498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto H., Tomasz A. Protoplast formation and leakage of intramembrane cell components: induction by the competence activator substance of pneumococci. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):344–353. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.344-353.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon L. D., Anderson T. F. The infection of Escherichia coli by T2 and T4 bacteriophages as seen in the electron microscope. I. Attachment and penetration. Virology. 1967 Jun;32(2):279–297. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS R. Recherches sur la cinétique des transformations bactériennes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Dec;18(4):467–481. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMASZ A., JAMIESON J. D., OTTOLENGHI E. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF DIPLOCOCCUS PNEUMONIAE. J Cell Biol. 1964 Aug;22:453–467. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.2.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Cellular metabolism in genetic transformation of pneumococci: requirement for protein synthesis during induction of competence. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):860–871. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.860-871.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Mosser J. L. On the nature of the pneumococcal activator substance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):58–66. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Zanati E., Ziegler R. DNA uptake during genetic transformation and the growing zone of the cell envelope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1848–1852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




