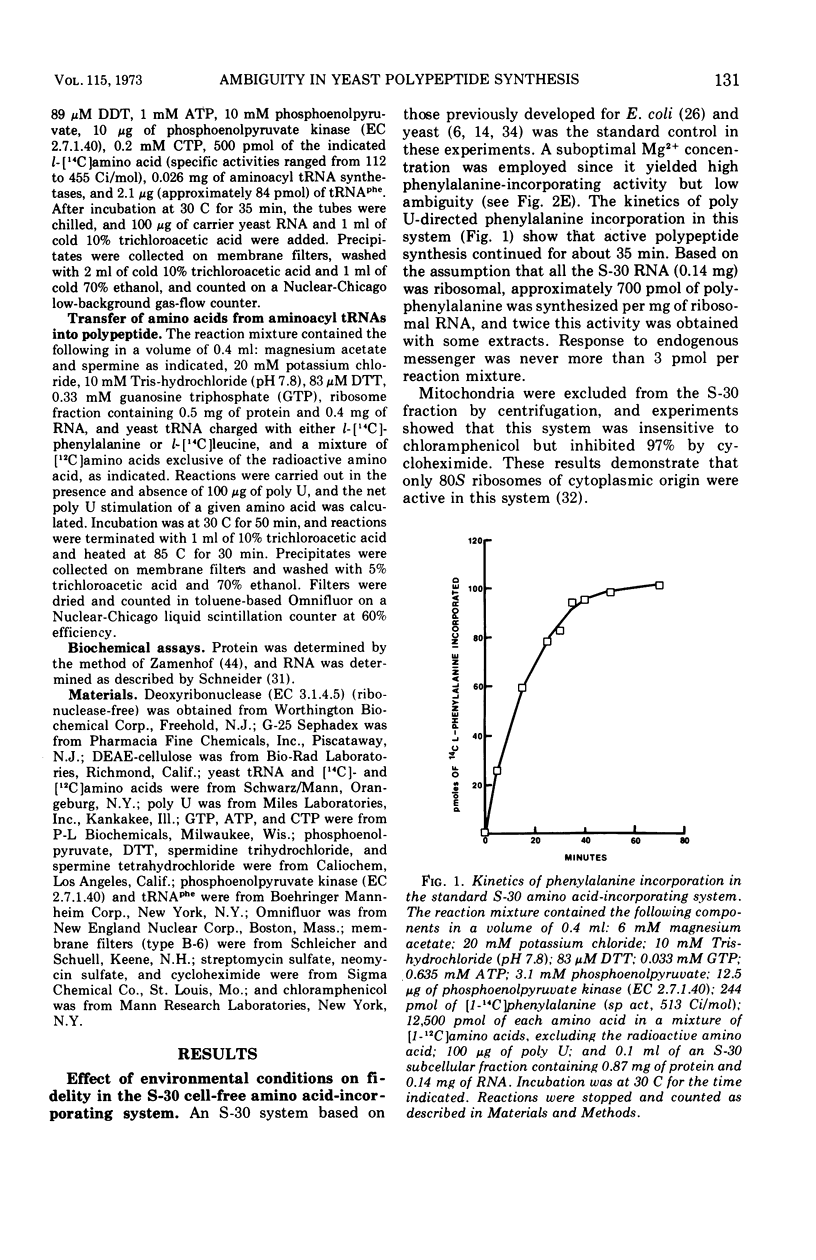
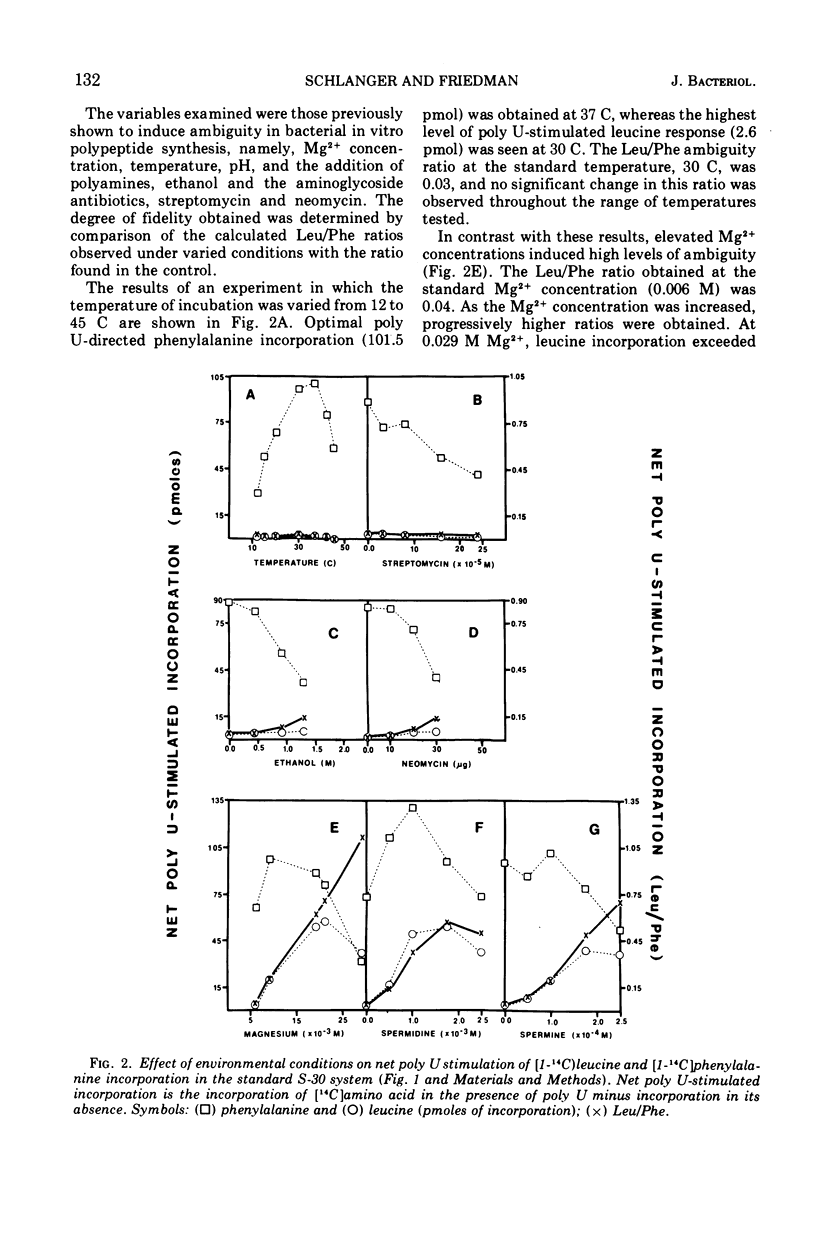
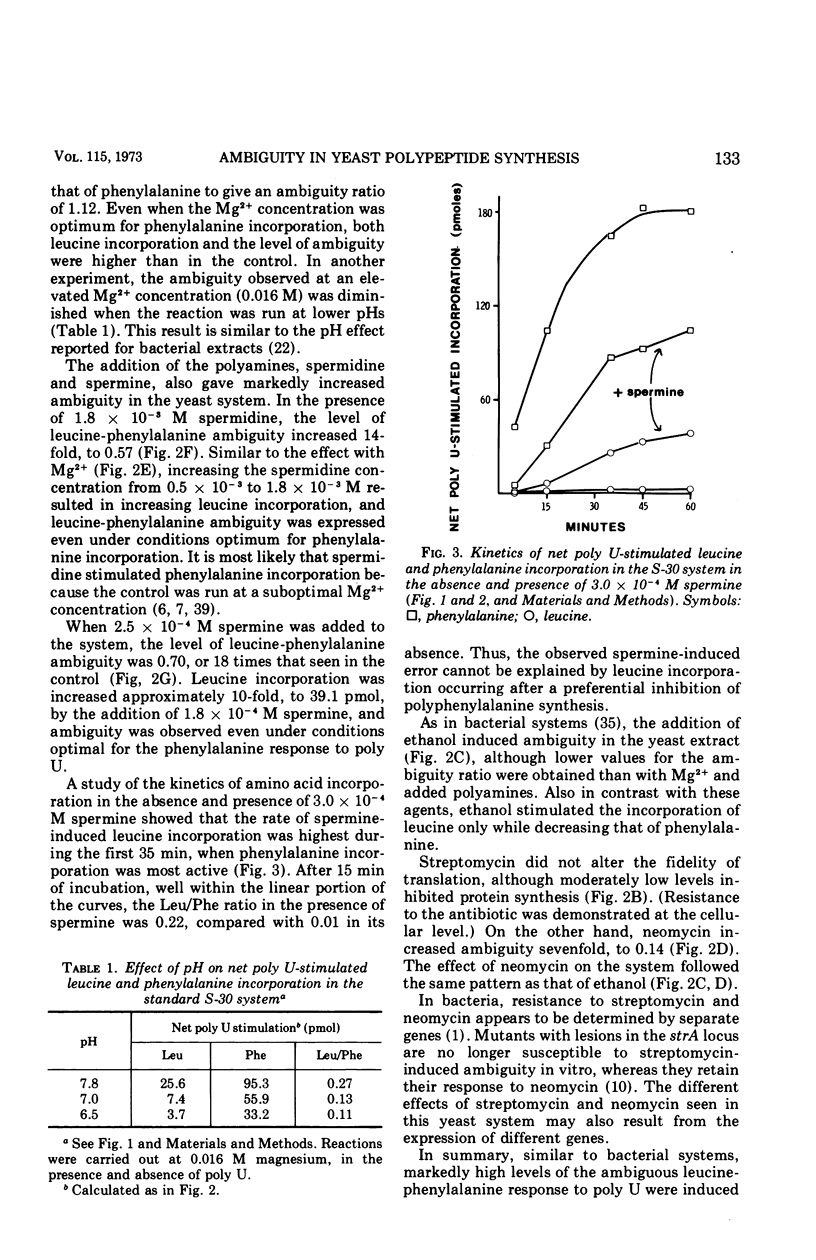
Abstract
Environmental factors known to induce ambiguity in bacterial extracts were tested in an in vitro cytoplasmic polypeptide-synthesizing system derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Increasing concentrations of magnesium, spermine, and spermidine resulted in extensive leucine-phenylalanine ambiguity in polyuridylic acid-directed polypeptide synthesis. Kinetic studies showed that spermine-mediated stimulation of leucine incorporation occurred when phenylalanine was being actively incorporated. In addition to leucine, the amino acids isoleucine and serine were incorporated in the presence of added magnesium and spermine. Ambiguity in the presence of a high Mg2+ concentration was decreased when the pH of the reaction mixture was lowered. Ethanol and neomycin enhanced ambiguity to a small, but significant, extent. Streptomycin and temperature had no effect on ambiguity. Leucine, isoleucine, and serine were not attached to phenylalanine transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA) when the aminoacylation reaction was performed at increasing Mg2+ and spermine concentrations. On the other hand, increasing levels of Mg2+ and spermine stimulated the incorporation of leucine from tRNA into polypeptide during the transfer reaction. The formal similarity between the findings in the yeast and Escherichia coli systems implies the existence of a tRNA-screening site on the yeast ribosome comparable to that suggested for bacteria. A proposal is made as to the manner in which this site may function to produce the ambiguous codon translation observed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Coresistance to neomycin and kanamycin by mutations in an Escherichia coli locus that affects ribosomes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):768–776. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.768-776.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRETTHAUER R. K., MARCUS L., CHALOUPKA J., HALVORSON H. O., BOCK R. M. AMINO ACID INCORPORATION INTO PROTEIN BY CELL-FREE EXTRACTS OF YEAST. Biochemistry. 1963 Sep-Oct;2:1079–1084. doi: 10.1021/bi00905a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss F. T., Vinopal R. T. Selection of ribosomal mutants by antibiotic suppression in yeast. Science. 1971 Dec 24;174(4016):1339–1341. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4016.1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas D. K., Gorini L. Restriction, de-restriction and mistranslation in missense suppression. Ribosomal discrimination of transfer RNA's. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):119–134. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bose K. K., Woodley C. L., Chatterjee N. K., Gupta N. K. Poly r-U directed ambiguous amino acid incorporation in the rabbit reticulocyte system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Sep 24;37(1):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90897-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. H. Codon--anticodon pairing: the wobble hypothesis. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):548–555. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES J., GILBERT W., GORINI L. STREPTOMYCIN, SUPPRESSION, AND THE CODE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 May;51:883–890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.5.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Gorini L., Davis B. D. Misreading of RNA codewords induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Mol Pharmacol. 1965 Jul;1(1):93–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Jones D. S., Khorana H. G. A further study of misreading of codons induced by streptomycin and neomycin using ribopolynucleotides containing two nucleotides in alternating sequence as templates. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):48–57. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derr R. F., Scanlon K. S. Fidelity of genetic code translation in a rat liver ribosomal system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 20;182(1):253–254. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90542-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirheimer G., Ebel J. P., Bonnet J., Gangloff J., Keith G., Krebs B., Kuntzel B., Roy A., Weissenbach J., Werner C. Structure primaire des tRN. Biochimie. 1972;54(2):127–144. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(72)80097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger J., Feuer B., Yamane T. Codon-anticodon binding in tRNAphe. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 26;231(21):126–128. doi: 10.1038/newbio231126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN S. M., WEINSTEIN I. B. LACK OF FIDELITY IN THE TRANSLATION OF SYNTHETIC POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:988–996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. M., Berezney R., Weinstein I. B. Fidelity in protein synthesis. The role of the ribosome. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 10;243(19):5044–5048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORINI L., KATAJA E. PHENOTYPIC REPAIR BY STREPTOMYCIN OF DEFECTIVE GENOTYPES IN E. COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Mar;51:487–493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.3.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNBERG-MANAGO M., DONDON J. INFLUENCE OF PH AND S-RNA CONCENTRATION ON CODING AMBIGUITIES. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Feb 17;18:517–522. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90784-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorini L. Ribosomal discrimination of tRNAs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 29;234(52):261–264. doi: 10.1038/newbio234261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorini L. The contrasting role of strA and ram gene products in ribosomal functioning. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:101–109. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh D., Gold L. Translation of the UGA triplet in vitro by tryptophan transfer RNA's. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 14;58(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90363-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G. Ribosome structure and function emergent. Science. 1970 Sep 18;169(3951):1171–1177. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3951.1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamfrom H., Grunberg-Manago M. Ambiguities of translation of poly U in the rabbit reticulocyte system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Apr 7;27(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M. W., MATTHAEI J. H. The dependence of cell-free protein synthesis in E. coli upon naturally occurring or synthetic polyribonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1588–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Mizushima S., Ozaki M., Traub P., Lowry C. V. Structure and function of ribosomes and their molecular components. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:49–61. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki M., Mizushima S., Nomura M. Identification and functional characterization of the protein controlled by the streptomycin-resistant locus in E. coli. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):333–339. doi: 10.1038/222333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. I. The effect of streptomycin and ribosomal dissociation on 14-C-aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid binding to ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 25;241(2):367–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SO A. G., DAVIE E. W. THE EFFECTS OF ORGANIC SOLVENTS ON PROTEIN BIOSYNTHESIS AND THEIR INFLUENCE ON THE AMINO ACID CODE. Biochemistry. 1964 Aug;3:1165–1169. doi: 10.1021/bi00896a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SO A. G., DAVIE E. W. The incorporation of amino acids into protein in a cell-free system from yeast. Biochemistry. 1963 Jan-Feb;2:132–136. doi: 10.1021/bi00901a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZER W., OCHOA S. COMPLEXING ABILITY AND CODING PROPERTIES OF SYNTHETIC POLYNUCLEOTIDES. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jun;8:823–834. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scragg A. H., Morimoto H., Villa V., Nekhorocheff J., Halvorson H. O. Cell-free protein synthesizing system from yeast mitochondria. Science. 1971 Mar 5;171(3974):908–910. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3974.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. I., Simpson M. V. The role of ribosomal conformation in protein biosynthesis: the streptomycin-ribosome interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1388–1395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavy L. Miscoding in a cell-free system from spleen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):347–353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y. Polyamines and protein synthesis. I. The effect of polyamines on cell free polyphenylalanine synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1969 Sep;66(3):345–349. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Suzuka I., Kaji A. Comparative studies on specific and nonspecific binding of transfer ribonucleic acid to ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1075–1081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towers N. R., Dixon H., Kellerman G. M., Linnane A. W. Biogenesis of mitochondria. 22. The sensitivity of rat liver mitochondria to antibiotics; a phylogenetic difference between a mammalian system and yeast. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Aug;151(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90510-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein I. B., Ochoa M., Jr, Friedman S. M. Fidelity in the translation of messenger ribonucleic acids in mammalian subcellular systems. Biochemistry. 1966 Oct;5(10):3332–3339. doi: 10.1021/bi00874a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R. A., Garvin R. T., Gorini L. Alteration of a 30S ribosomal protein accompanying the ram mutation in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2263–2267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


